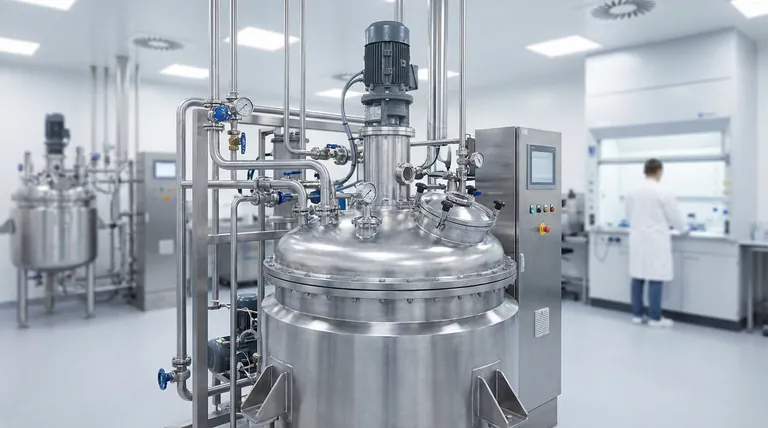
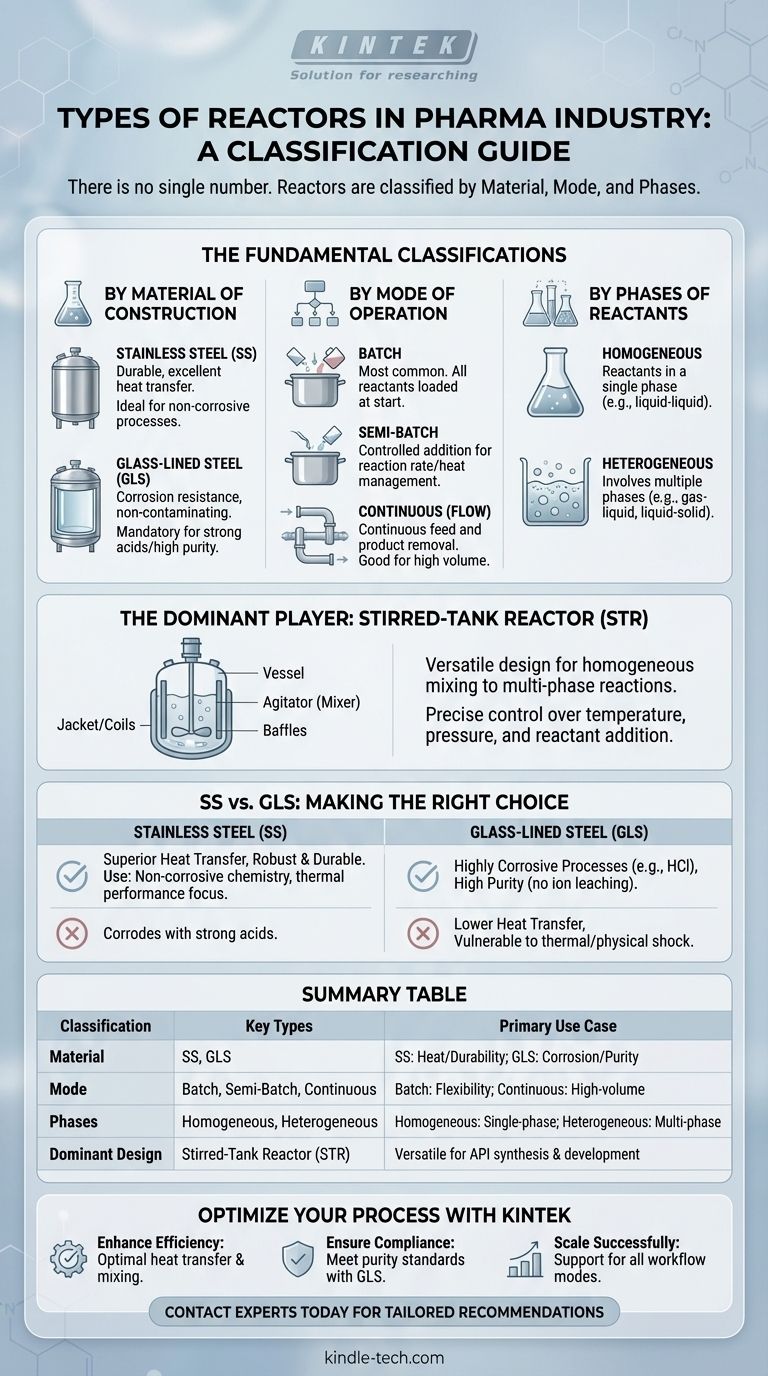
There is no single number of reactor types in the pharmaceutical industry. Instead, reactors are classified based on a few key characteristics, including their material of construction, mode of operation, and the phases of the chemicals being reacted. Understanding these classifications is essential for selecting the right equipment for a specific chemical process.
The "type" of a reactor is not a fixed label but a description of its design and function. The most critical decision is not about choosing from a long list, but about matching the reactor's material, operational mode, and mixing capabilities to the precise demands of your chemical synthesis and production scale.

The Fundamental Ways to Classify Reactors
To understand the landscape of pharmaceutical reactors, it's best to think in terms of these fundamental classification systems. Most reactors you encounter will be a combination of these attributes.
By Material of Construction
This is often the first and most critical decision point, driven by chemical compatibility and purity requirements.
- Stainless Steel (SS) Reactors: Typically made from grades like 316L stainless steel, these are the industry workhorses. They offer excellent durability and heat transfer.
- Glass-Lined Steel (GLS) Reactors: These feature a steel shell with an interior surface of specialized glass. The steel provides structural strength, while the glass provides near-universal corrosion resistance and a non-contaminating surface.
By Mode of Operation
This describes how raw materials are added and products are removed, which dictates the production workflow.
- Batch Reactors: This is the most common mode in pharma. All reactants are loaded into the vessel at the beginning, the reaction proceeds over time, and the final product is discharged at the end. Think of it like baking a cake in a single bowl.
- Semi-Batch Reactors: In this mode, the vessel is initially charged with some reactants, and others are added continuously or in portions over the course of the reaction. This is useful for controlling reaction rates or managing heat generation.
- Continuous Reactors (Flow Chemistry): Reactants are continuously fed into the reactor, and the product is continuously removed. This is less common for multi-product pharma plants but is gaining traction for high-volume, dedicated processes. Plug Flow Reactors (PFRs) are a primary example.
By Phases of Reactants
This classification is based on the physical state of the chemicals involved.
- Homogeneous Reactors: All reactants are in a single phase (e.g., liquid-liquid). The primary challenge here is ensuring adequate mixing.
- Heterogeneous Reactors: The reaction involves multiple phases (e.g., gas-liquid, liquid-solid, or gas-liquid-solid). These are more complex as they require ensuring efficient mass transfer between the different phases, not just mixing.
The Dominant Player: The Stirred-Tank Reactor (STR)
The vast majority of reactors used in both pharmaceutical development and manufacturing are Stirred-Tank Reactors (STRs), also known as Continuously Stirred-Tank Reactors (CSTRs) in a continuous setup.
Why is the STR so common?
The STR is exceptionally versatile. Its design effectively handles a wide range of reaction types, from simple homogeneous mixing to complex multi-phase reactions. It allows for precise control over temperature, pressure, and reactant addition, making it ideal for the complex, multi-step syntheses common in API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient) manufacturing.
Key Components of an STR
- Vessel: The main body, either stainless steel or glass-lined.
- Jacket/Coils: An external shell or internal coils through which heating or cooling fluids are circulated to control the reaction temperature.
- Agitator: The "mixer" inside the vessel, consisting of a shaft and one or more impellers. Its design is critical for mixing efficiency and mass transfer.
- Baffles: Vertical plates on the vessel wall that prevent the formation of a vortex (swirl) and improve top-to-bottom mixing.
Understanding the Trade-offs: SS vs. Glass-Lined
Choosing between Stainless Steel and Glass-Lined Steel is a pivotal decision with significant consequences for your process.
When to Choose Stainless Steel (SS)
SS is the default choice when your process chemistry allows for it. It is preferred for its superior heat transfer capabilities, which allow for faster heating and cooling cycles. It is also more robust and resistant to mechanical shock and thermal shock compared to glass.
When to Choose Glass-Lined Steel (GLS)
GLS is mandatory for highly corrosive processes, especially those involving strong acids like hydrochloric acid (HCl), which would quickly degrade stainless steel. It also provides a high-purity, inert surface that prevents metallic ion leaching, which is critical for cGMP compliance and sensitive products. The trade-off is lower heat transfer efficiency and a vulnerability to physical damage or rapid temperature changes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your choice of reactor is a strategic engineering decision tailored to your specific goals.
- If your primary focus is process versatility and multi-product manufacturing: A batch or semi-batch Stirred-Tank Reactor is the most flexible and widely used solution.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive agents or ensuring maximum product purity: A Glass-Lined Steel (GLS) reactor is the necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is thermal performance with non-corrosive chemistry: A Stainless Steel (SS) reactor offers superior durability and heat transfer.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, dedicated production of a single molecule: A continuous or flow reactor system (like a PFR) may offer significant efficiency advantages.
Ultimately, selecting the right reactor begins with a deep understanding of your chemical process and production objectives.
Summary Table:
| Classification | Key Types | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Material of Construction | Stainless Steel (SS), Glass-Lined Steel (GLS) | SS for heat transfer/durability; GLS for corrosive processes/purity |
| Mode of Operation | Batch, Semi-Batch, Continuous (Flow) | Batch for flexibility; Continuous for high-volume production |
| Phases of Reactants | Homogeneous, Heterogeneous | Homogeneous for single-phase; Heterogeneous for multi-phase reactions |
| Dominant Design | Stirred-Tank Reactor (STR) | Versatile choice for most API synthesis and development |
Optimize Your Pharmaceutical Process with the Right Reactor
Choosing the correct reactor is critical for your API synthesis, scalability, and cGMP compliance. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including versatile stirred-tank reactors (STRs) in stainless steel and glass-lined configurations.
We help you:
- Enhance Efficiency: Select reactors with optimal heat transfer, mixing, and corrosion resistance.
- Ensure Compliance: Meet strict purity standards with GLS reactors for sensitive processes.
- Scale Successfully: From R&D to production, our solutions support batch, semi-batch, and continuous workflows.
Let’s discuss your specific needs — Contact our experts today for a tailored recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What role does an autoclave play in simulating PWR conditions? Advanced Material Validation for Nuclear Safety
- How does a high-pressure reactor demonstrate its value in accelerated aging? Predict Catalyst Durability Fast
- What roles do autoclaves play in MFI zeolite synthesis? Master Hydrothermal Crystalline Growth
- Why are high-pressure autoclaves essential for preparing bio-based polyamide curing agents from dimeric acid?
- What is the purpose of using high-purity argon gas in a high-pressure reactor? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Data



















