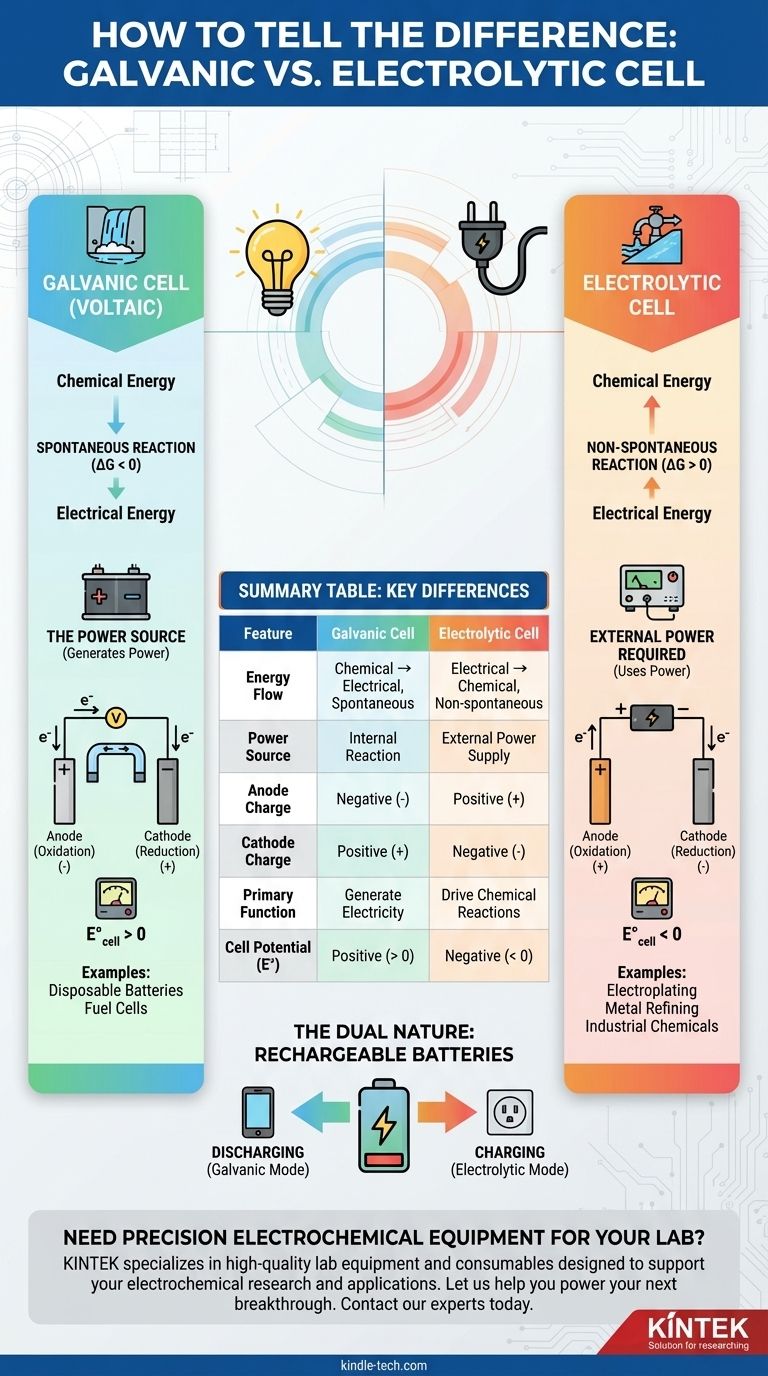
The fundamental difference between a galvanic and an electrolytic cell lies in the flow of energy. A galvanic cell, also known as a voltaic cell, uses a spontaneous chemical reaction to generate electrical energy. In contrast, an electrolytic cell uses external electrical energy to force a non-spontaneous chemical reaction to occur.
Think of it this way: A galvanic cell is like a waterfall generating power as it flows downhill naturally. An electrolytic cell is like a pump using external power to push water back uphill against gravity.

The Core Principle: Spontaneity and Energy Conversion
The behavior of any electrochemical cell is dictated by whether its internal reaction proceeds on its own or requires external intervention.
Galvanic Cells: Releasing Chemical Energy
A galvanic cell is defined by a spontaneous redox reaction. This means the reaction wants to happen on its own, releasing energy in the process.
This process converts stored chemical energy directly into electrical energy. The cell itself is the power source.
Thermodynamically, this corresponds to a negative Gibbs free energy (ΔG < 0) and a positive cell potential (E°_cell > 0).
Electrolytic Cells: Inputting Electrical Energy
An electrolytic cell involves a non-spontaneous reaction. Without an external push, this reaction would not proceed.
It requires an external power source, like a battery or DC supply, to drive the reaction forward. This process converts electrical energy into chemical energy.
This corresponds to a positive Gibbs free energy (ΔG > 0) and a negative cell potential (E°_cell < 0). The external voltage must be greater than this negative potential to force the reaction.
How to Identify Each Cell: Key Indicators
Beyond the direction of energy flow, you can distinguish between the two cells by observing electrode polarity and the overall circuit.
The Source of Power
This is the most straightforward indicator. If the electrochemical cell is the battery powering a device, it is a galvanic cell.
If the cell is connected to an external battery or power supply, it is an electrolytic cell. The external source provides the energy to drive the process.
Electrode Polarity (A Common Point of Confusion)
The definitions of anode and cathode are constant for both cell types:
- Anode: The electrode where oxidation occurs.
- Cathode: The electrode where reduction occurs.
However, their positive/negative charge (polarity) flips:
In a galvanic cell, the spontaneous reaction at the anode releases electrons, making it the negative (-) terminal. The cathode, which consumes electrons, is the positive (+) terminal.
In an electrolytic cell, the external power source dictates the polarity. It pulls electrons away from the anode, making it the positive (+) terminal, and pushes electrons to the cathode, making it the negative (-) terminal.
Common Applications and Pitfalls
The purpose of the cell is its most practical differentiator. One creates power, while the other uses power to create a substance or change.
The Purpose of a Galvanic Cell
The sole function of a galvanic cell is to act as a source of electrical power.
Common examples include disposable batteries (AA, AAA), fuel cells, and the primary function of a car battery when it starts the engine.
The Purpose of an Electrolytic Cell
The goal of an electrolytic cell is to drive a useful chemical transformation that wouldn't happen otherwise.
Typical applications include electroplating a thin layer of metal onto a surface, refining metals like copper and aluminum, and producing industrial chemicals like chlorine gas.
The Dual Nature of Rechargeable Batteries
A rechargeable battery is the perfect example of both cell types in one device.
- When discharging (powering your phone): It acts as a galvanic cell, with a spontaneous reaction generating electricity.
- When charging (plugged into the wall): It acts as an electrolytic cell, with external energy forcing the non-spontaneous reverse reaction to store energy.
Making the Right Distinction for Your Goal
To quickly determine which cell you are dealing with, focus on the flow of energy and the overall goal of the system.
- If your primary focus is generating power: You are dealing with a galvanic cell, where a spontaneous reaction releases energy.
- If your primary focus is creating a substance or reversing a reaction: You are using an electrolytic cell, which requires an external power source to drive a non-spontaneous process.
- If you are analyzing electrode signs: Remember that in a galvanic cell the anode is negative, while in an electrolytic cell it is positive, because the energy source is either internal or external.
Ultimately, understanding whether energy is a product or a requirement is the key to distinguishing between these two fundamental electrochemical cells.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Galvanic Cell | Electrolytic Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Flow | Chemical → Electrical (Spontaneous) | Electrical → Chemical (Non-spontaneous) |
| Power Source | Internal Reaction | External Power Supply |
| Anode Charge | Negative (-) | Positive (+) |
| Cathode Charge | Positive (+) | Negative (-) |
| Primary Function | Generate Electricity | Drive Chemical Reactions (e.g., electroplating) |
| Cell Potential (E°) | Positive (> 0) | Negative (< 0) |
Need Precision Electrochemical Equipment for Your Lab?
Understanding the nuances of galvanic and electrolytic cells is crucial for advanced laboratory work. Whether you're developing new battery technologies, performing electroplating, or conducting material analysis, having the right equipment is essential.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables designed to support your electrochemical research and applications. We provide reliable solutions that ensure accurate results and enhance your lab's efficiency.
Let us help you power your next breakthrough. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how our products can drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
- Hydrophilic Carbon Paper TGPH060 for Battery Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the proper storage procedures for the multifunctional electrolytic cell? Protect Your Investment and Ensure Data Accuracy
- How can leaks be prevented when using a five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Ensure a Reliable and Safe Electrochemical Setup
- How can contamination be avoided during experiments with the five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Master the 3-Pillar Protocol
- What general precaution should be taken when handling the electrolytic cell? Ensure Safe and Accurate Lab Results
- What are the standard components of the five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Master the Precision Instrument for Electrochemical Analysis



