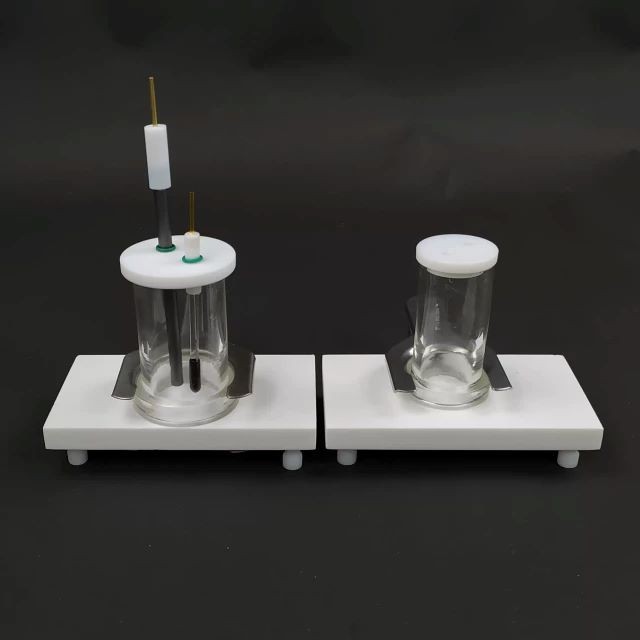

Electrochemical Consumables
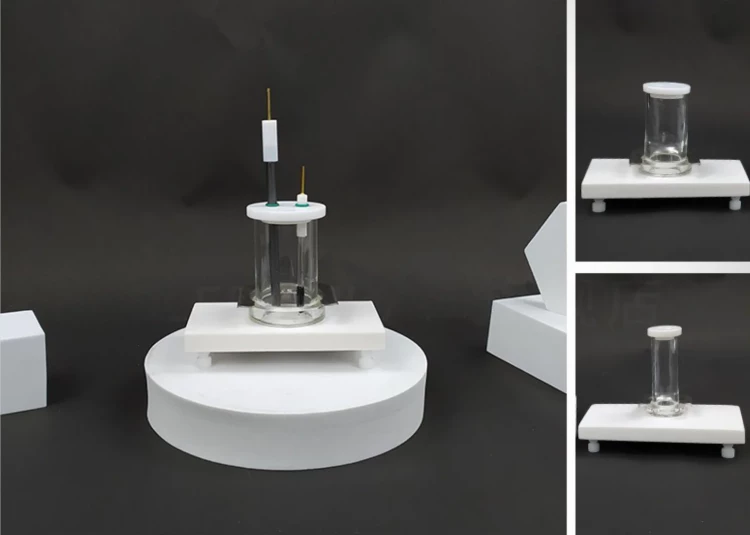
Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
Item Number : ELEC
Price varies based on specs and customizations
$199.90 / set
- Specifications
- 8/30/50/80ml
- Applicable temperature range
- 0 ~ 60℃
- Reaction area
- 0.5~ 2cm²
- Material
- boron glass + PTFE
Shipping:
Contact us to get shipping details Enjoy On-time Dispatch Guarantee.
Why Choose Us
Easy ordering process, quality products, and dedicated support for your business success.
Coating Evaluation Electrolytic Cells for Electrochemical Experiments, corrosion resistance, complete specifications, good sealing, high-quality material selection, safe and durable, can be customized.
Technical specifications
| Specifications | 8/30/50/80ml |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Reaction area | 0.5~ 2cm² |
| Material | boron glass + PTFE |
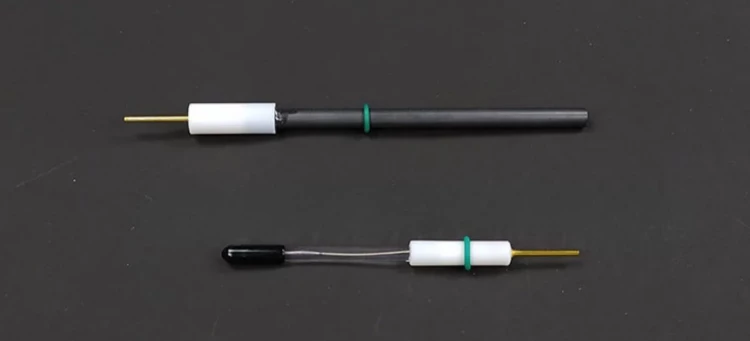
| Opening hole of electrolytic cell | Two electrode holes (including graphite rod electrode*1 silver chloride electrode*1) |
Detail & Parts
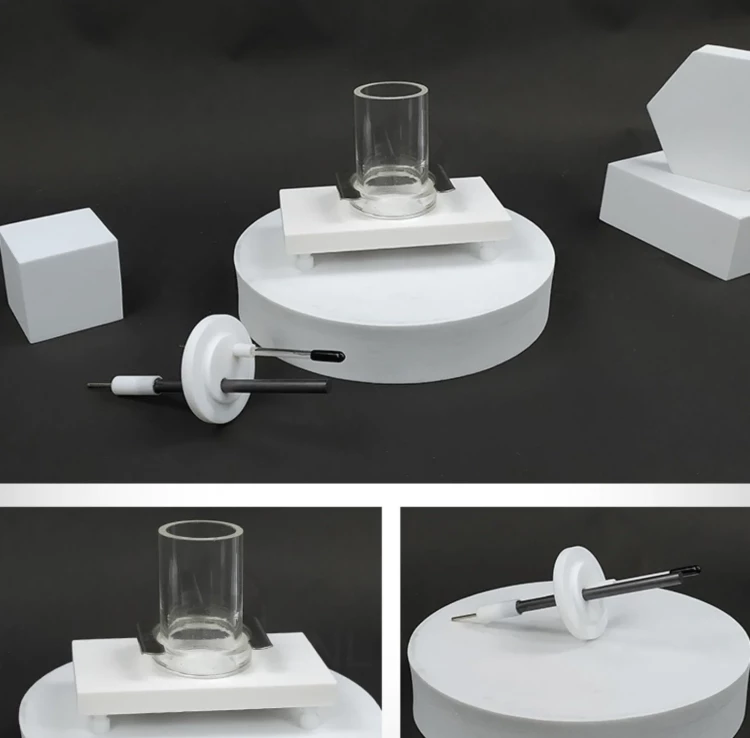
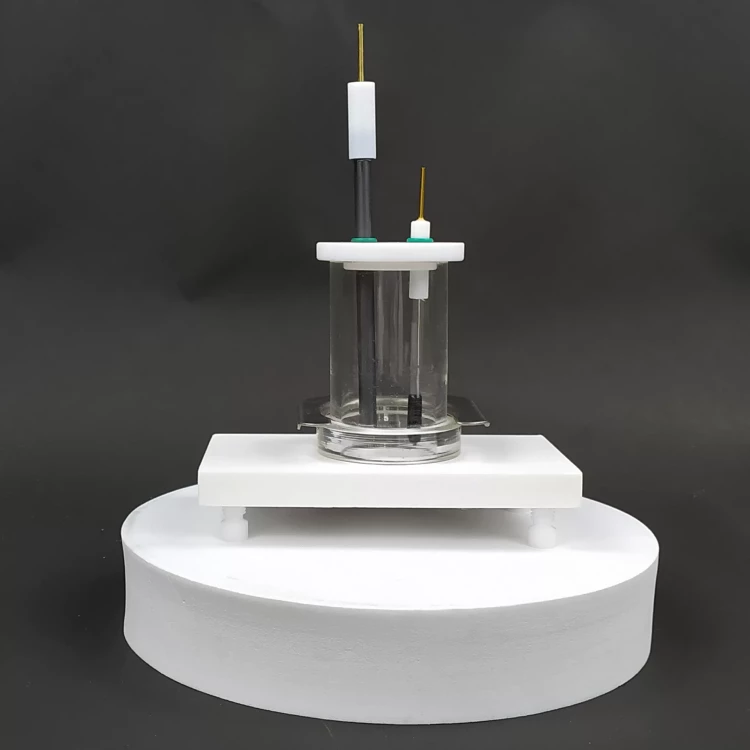
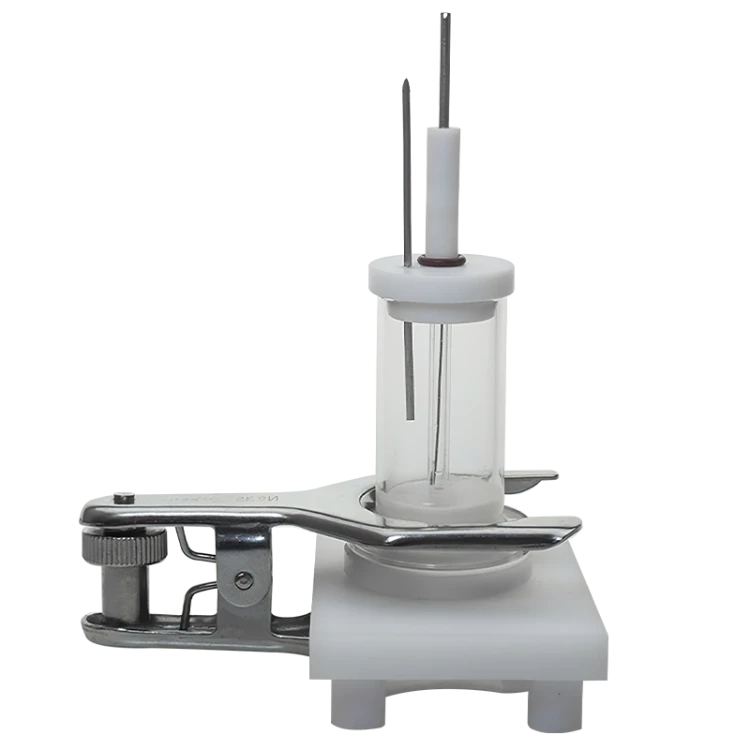




Designed for You
KinTek provide deep custom made service and equipment to worldwide customers, our specialized teamwork and rich experienced engineers are capable to undertake the custom tailoring hardware and software equipment requirements, and help our customer to build up the exclusive and personalized equipment and solution!
Would you please drop your ideas to us, our engineers are ready for you now!
Trusted by Industry Leaders

FAQ
What Are Electrolytic Cells Used For?
What Are The Materials Used In Electrochemical Cell?
What Is The Difference Between Galvanic Cell And Electrolytic Cell?
What Are The Examples Of Electrochemical Material?
What Is An Electrolytic Cell And How Does It Work?
What Are The Two Points Of Difference Between Electrochemical And Electrolytic Cells?
What Is The Example Of Electrolytic Cell?
Are Electrolytic Cells Spontaneous?
4.9 / 5
Excellent electrolytic cell for coating evaluation. Fast delivery and great quality.
4.7 / 5
The electrolytic cell is very well-made and works perfectly for my experiments. Very satisfied with my purchase.
4.8 / 5
The cell is of high quality and is very easy to use. I highly recommend it to anyone who needs to perform coating evaluations.
5.0 / 5
This electrolytic cell is a must-have for any lab that does coating evaluations. It is very well-made and produces consistent results.
4.6 / 5
The electrolytic cell arrived quickly and was well-packaged. It is exactly as described and works great. I am very happy with my purchase.
4.9 / 5
The electrolytic cell is very easy to use and clean. It is also very durable and has held up well to repeated use.
5.0 / 5
I am very impressed with the quality and performance of this electrolytic cell. It is a great value for the price.
4.8 / 5
This electrolytic cell is a great addition to my lab. It is very versatile and can be used for a variety of experiments.
4.7 / 5
The electrolytic cell is very well-made and is very easy to use. I am very happy with my purchase and would definitely recommend it to others.
4.9 / 5
I am very impressed with the quality and performance of this electrolytic cell. It is a great value for the price.
5.0 / 5
This electrolytic cell is a must-have for any lab that does coating evaluations. It is very well-made and produces consistent results.
4.8 / 5
The electrolytic cell arrived quickly and was well-packaged. It is exactly as described and works great. I am very happy with my purchase.
4.7 / 5
The electrolytic cell is very easy to use and clean. It is also very durable and has held up well to repeated use.
4.9 / 5
Excellent electrolytic cell for coating evaluation. Fast delivery and great quality.
4.8 / 5
The cell is of high quality and is very easy to use. I highly recommend it to anyone who needs to perform coating evaluations.
5.0 / 5
This electrolytic cell is a great addition to my lab. It is very versatile and can be used for a variety of experiments.
4.6 / 5
The electrolytic cell is very well-made and is very easy to use. I am very happy with my purchase and would definitely recommend it to others.
4.9 / 5
I am very impressed with the quality and performance of this electrolytic cell. It is a great value for the price.
5.0 / 5
This electrolytic cell is a must-have for any lab that does coating evaluations. It is very well-made and produces consistent results.
REQUEST A QUOTE
Our professional team will reply to you within one business day. Please feel free to contact us!
Related Products

Flat Corrosion Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Discover our flat corrosion electrolytic cell for electrochemical experiments. With exceptional corrosion resistance and complete specifications, our cell guarantees optimal performance. Our high-quality materials and good sealing ensure a safe and durable product, and customization options are available.

Optical Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Upgrade your electrolytic experiments with our Optical Water Bath. With controllable temperature and excellent corrosion resistance, it's customizable for your specific needs. Discover our complete specifications today.

Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
Looking for a reliable quartz electrochemical cell? Our product boasts excellent corrosion resistance and complete specifications. With high-quality materials and good sealing, it's both safe and durable. Customize to meet your needs.

H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
Double-layer H-type optical water bath electrolytic cells, with excellent corrosion resistance and a wide range of specifications available. Customization options are also available.

PTFE Electrolytic Cell Electrochemical Cell Corrosion-Resistant Sealed and Non-Sealed
Choose our PTFE Electrolytic Cell for reliable, corrosion-resistant performance. Customize specifications with optional sealing. Explore now.

Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
Streamline your laboratory consumables with Kintek's Electrolytic Cell with five-port design. Choose from sealed and non-sealed options with customizable electrodes. Order now.

Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
Looking for a high-quality gas diffusion electrolysis cell? Our liquid flow reaction cell boasts exceptional corrosion resistance and complete specifications, with customizable options available to suit your needs. Contact us today!

Super Sealed Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Super-sealed electrolytic cell offers enhanced sealing capabilities, making it ideal for experiments that require high airtightness.

Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
Discover our high-quality Multifunctional Electrolytic Cell Water Baths. Choose from single or double-layer options with superior corrosion resistance. Available in 30ml to 1000ml sizes.

RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
Elevate your electrochemical research with our Rotating Disk and Ring Electrodes. Corrosion resistant and customizable to your specific needs, with complete specifications.

Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
Upgrade your electrochemical experiments with our Platinum Disc Electrode. High-quality and reliable for accurate results.

Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Tungsten Crucible and Molybdenum Crucible for High Temperature Applications
Tungsten and molybdenum crucibles are commonly used in electron beam evaporation processes due to their excellent thermal and mechanical properties.

Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Gold Plating Tungsten Molybdenum Crucible for Evaporation
These crucibles act as containers for the gold material evaporated by the electron evaporation beam while precisely directing the electron beam for precise deposition.

Proton Exchange Membrane for Batteries Lab Applications
Thin proton exchange membrane with low resistivity; high proton conductivity; low hydrogen permeation current density; long life; suitable for electrolyte separators in hydrogen fuel cells and electrochemical sensors.

Lab Electrochemical Workstation Potentiostat for Laboratory Use
Electrochemical workstations, also known as laboratory electrochemical analyzers, are sophisticated instruments designed for precise monitoring and control in various scientific and industrial processes.
Related Articles

Advanced Techniques in Coating Evaluation Using Electrolytic Cells
Explore the comprehensive guide on coating evaluation using electrolytic cells, covering electroplating, sol-gel methods, and wet chemical techniques. Enhance your understanding of metal coating properties and applications.

The Art of Isolation: Why Super-Sealed Cells Define Modern Electrochemistry
Discover how super-sealed electrolytic cells eliminate environmental variables, ensuring precision in battery testing, corrosion research, and chemical synthesis.

Handheld Coating Thickness Gauges: Accurate Measurement for Electroplating and Industrial Coatings
Discover the best practices and technologies for measuring coating thickness using handheld gauges. Ideal for electroplating, automotive paint, and powder coatings.

Understanding Flat Corrosion Electrolytic Cells: Applications, Mechanisms, and Prevention Techniques
Explore the detailed workings of flat corrosion electrolytic cells, their role in industrial processes, and effective strategies to mitigate corrosion. Learn about electrolytic cells, their components, and applications in electroplating and metal purification.

Understanding Saturated Calomel Reference Electrodes: Composition, Uses, and Considerations
Explore the detailed guide on saturated calomel reference electrodes, including their composition, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Ideal for researchers and lab technicians.

The Architecture of Precision: Why the Invisible Details Define Electrochemical Success
Master the art of pre-use inspection for electrolytic cells. From physical integrity to electrode purity, learn why the invisible details dictate experimental safety.

The Transparency Paradox: Mastering the Fragile Art of Electrolytic Cells
Glass electrolytic cells are precision instruments, not simple containers. Learn the systematic approach to handling glass to ensure safety and data integrity.

The Vessel of Truth: Why the Container Matters More Than the Chemistry
The success of an electrolytic experiment often hangs on the material of the cell body. Discover the trade-offs between Borosilicate, Quartz, and PTFE.

The Glass Heart: Why Good Science Dies in Dirty Cells
The reliability of your electrolytic cell isn't just about chemistry; it's about discipline. Learn the systemic protocols for quartz and electrode maintenance.

Advanced Electrolytic Cell Techniques for Cutting-Edge Lab Research
Electrolytic cells are devices that utilize an electric current to induce a non-spontaneous chemical reaction.

The Fragile Vessel of Truth: A Maintenance Manifesto for Electrolytic Cells
Data integrity relies on equipment health. Discover the psychological and technical art of maintaining five-port electrolytic cells for reproducible science.

Electrochemical Electrodes in Chemical Analysis
Electrochemical electrodes are essential tools used in many chemical analysis techniques and experiments. These electrodes are devices that allow us to measure the electrical potential difference in a chemical reaction.