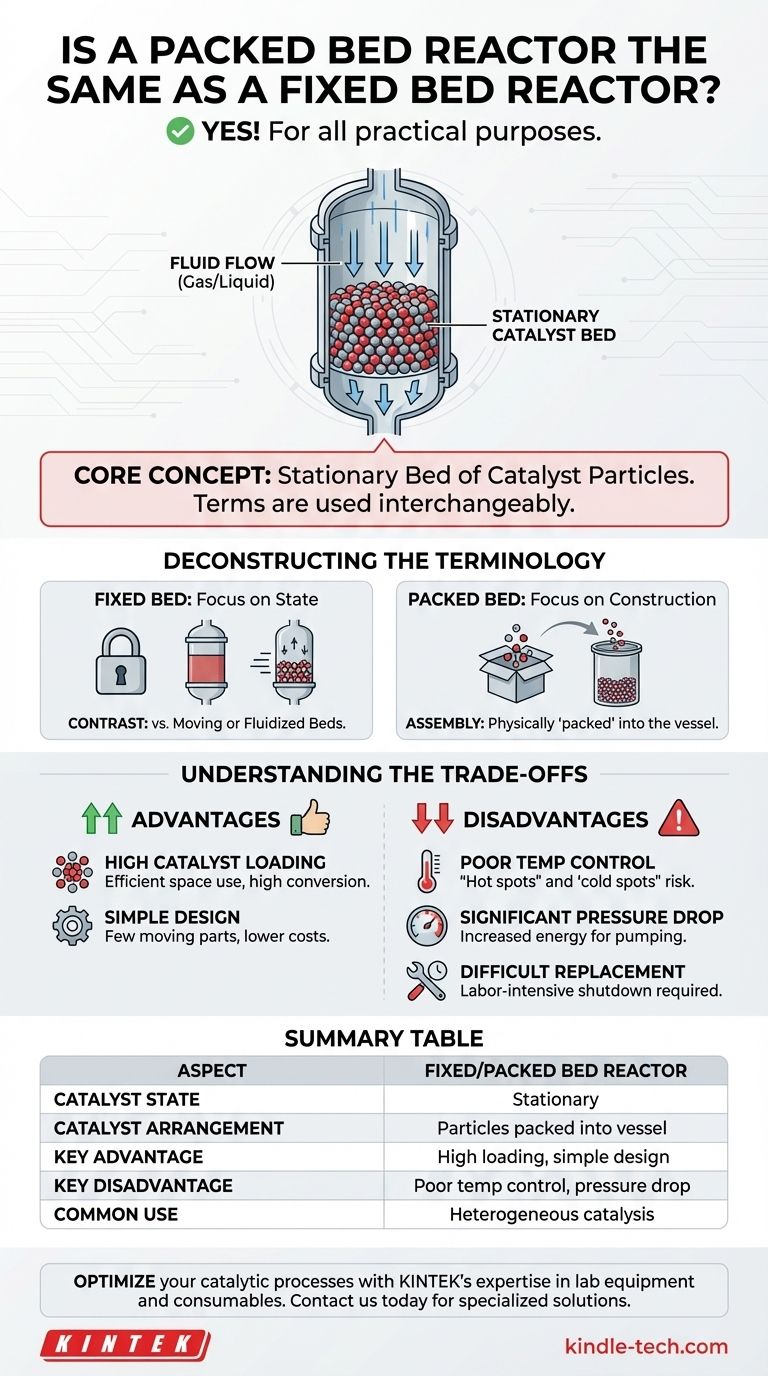
For all practical purposes, yes. A packed bed reactor and a fixed bed reactor are the same type of chemical reactor. The terms are used interchangeably in chemical engineering literature, industry, and academia to describe a reactor vessel filled with solid catalyst particles through which fluids flow.
The core concept uniting both terms is a stationary bed of catalyst particles. While "fixed" emphasizes the catalyst's state (it doesn't move) and "packed" describes its construction (it's packed into a vessel), they ultimately refer to the same fundamental design.

What Defines These Reactors?
To understand why the terms are synonymous, it's essential to grasp the core principles of the reactor's design and function.
The Stationary Catalyst Bed
The defining characteristic is that the solid catalyst particles are held in place and do not move. A fluid phase, either a gas or a liquid, flows through the empty spaces (the void volume) between these stationary particles.
Heterogeneous Catalysis
These reactors are the workhorses of heterogeneous catalysis. This is a process where the phase of the catalyst (solid) is different from the phase of the reactants (gas or liquid). The reaction occurs on the surface of the catalyst particles.
Common Industrial Examples
This reactor design is fundamental to the chemical industry. Well-known processes like the Haber-Bosch synthesis of ammonia, the Claus process for sulfur recovery, and catalytic converters in automobiles all rely on fixed/packed bed reactors.
Deconstructing the Terminology: "Packed" vs. "Fixed"
The minor difference between the terms is a matter of emphasis, not a difference in hardware or operation.
"Fixed Bed": A Focus on State
The term "fixed" highlights the physical state of the catalyst bed. It is used to create a clear contrast with other reactor types where the catalyst is in motion, such as a fluidized bed reactor (where particles are suspended in the fluid) or a moving bed reactor (where particles slowly move through the vessel).
"Packed Bed": A Focus on Construction
The term "packed" emphasizes how the reactor is assembled. The vessel is physically "packed" with catalyst particles (e.g., pellets, spheres, or rings) before operation. This term describes the physical arrangement of the catalyst within the vessel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Regardless of what you call it, this reactor design has distinct advantages and disadvantages that are critical to understand for any application.
Advantage: High Catalyst Loading
Because the particles are packed tightly, these reactors offer a very high concentration of catalyst per unit volume. This leads to high conversion rates and efficient use of reactor space.
Advantage: Simple Design
Compared to more complex systems like fluidized beds, the design is mechanically simple. There are few or no moving parts, which generally leads to lower capital and maintenance costs.
Disadvantage: Poor Temperature Control
This is the most significant drawback. In highly exothermic reactions, heat can build up within the bed, creating "hot spots" that can damage the catalyst or cause unwanted side reactions. In endothermic reactions, "cold spots" can form, slowing the reaction rate.
Disadvantage: Significant Pressure Drop
Forcing a fluid through a dense bed of particles creates resistance, resulting in a pressure drop from the inlet to the outlet. This increases the energy required for pumping or compression, raising operational costs.
Disadvantage: Difficult Catalyst Replacement
When the catalyst is deactivated or "spent," it must be replaced. This often requires a complete shutdown of the process to physically unload and reload the entire bed, which can be a labor-intensive and time-consuming operation.
How to Use These Terms Correctly
While the terms are interchangeable, you can communicate with greater precision by being mindful of the context.
- If your focus is general engineering and academic discussion: Use the terms interchangeably. "Fixed bed reactor" is perhaps slightly more formal and common in textbooks.
- If your focus is contrasting reactor types: Use "fixed bed" to clearly distinguish it from "fluidized bed," "slurry," or "moving bed" reactors.
- If your focus is the physical loading process: Using "packed bed" can be slightly more descriptive when discussing the act of filling the reactor vessel.
Ultimately, the key is understanding the principle of a stationary catalyst bed, which is the foundation of this vital industrial technology.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Fixed/Packed Bed Reactor |
|---|---|
| Catalyst State | Stationary (does not move) |
| Catalyst Arrangement | Particles packed into vessel |
| Key Advantage | High catalyst loading, simple design |
| Key Disadvantage | Poor temperature control, pressure drop |
| Common Use | Heterogeneous catalysis (e.g., ammonia synthesis) |
Optimize your catalytic processes with KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables. Whether you're researching fixed/packed bed reactors or scaling up industrial applications, our specialized solutions ensure precision, efficiency, and reliability. Let us help you select the right reactor components or catalysts for your laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the contribution of a hydrothermal reactor to graded pore construction? Precision Templates for TAS
- Why are sealed laboratory reaction vessels necessary in the hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites? Ensure Purity and Yield
- What is the purpose of using high-purity argon gas in a high-pressure reactor? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Data
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature hydrothermal reactor? Enhance Iodine@Activated Carbon Cathode Synthesis
- What is the function of a constant temperature hydrothermal reactor? Master Coal Fly Ash Activation



















