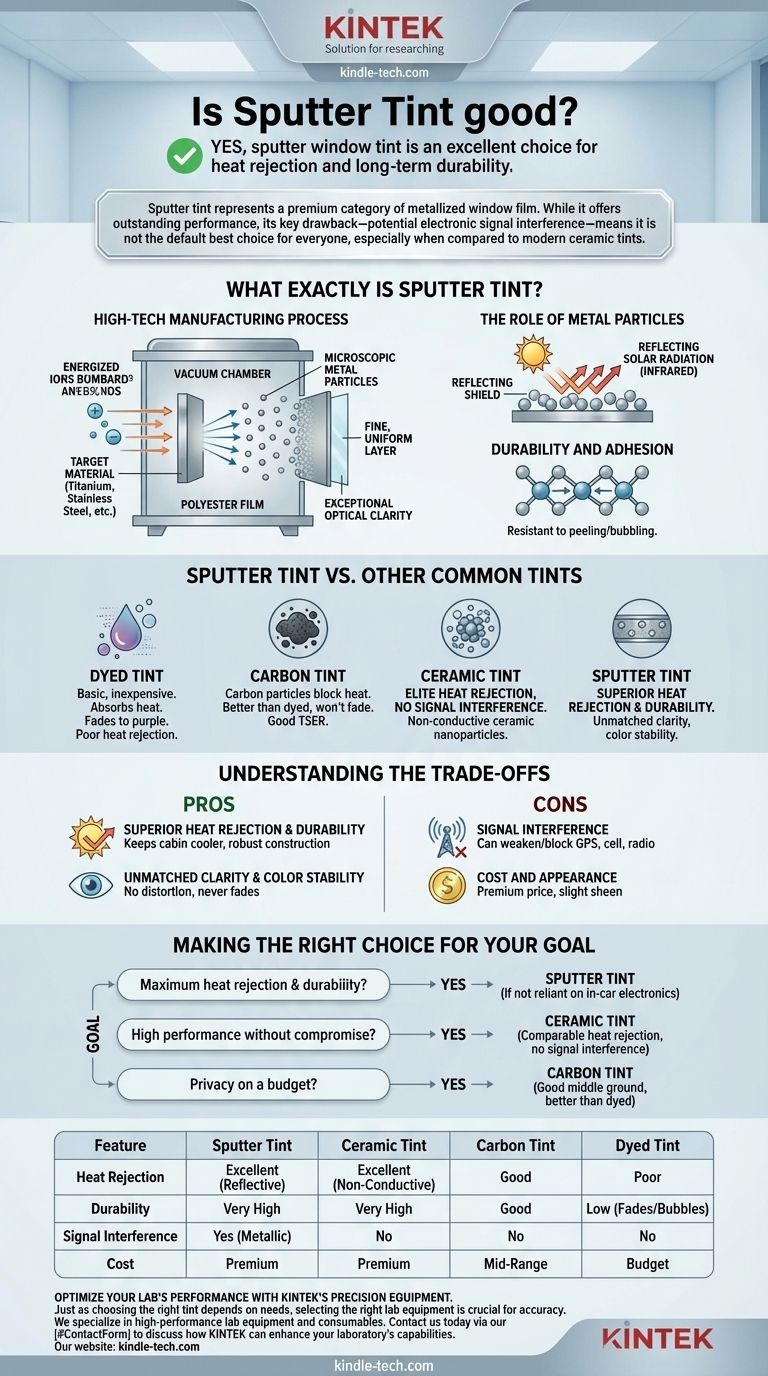
Yes, sputter window tint is an excellent choice for those prioritizing heat rejection and long-term durability. It uses a sophisticated, high-vacuum manufacturing process to embed microscopic metal particles onto the film. This results in a highly stable and effective barrier against solar energy, outperforming basic dyed or carbon films significantly.
Sputter tint represents a premium category of metallized window film. While it offers outstanding performance, its key drawback—potential electronic signal interference—means it is not the default best choice for everyone, especially when compared to modern ceramic tints.

What Exactly Is Sputter Tint?
Sputter tint is defined by its manufacturing process. This advanced technique provides a level of precision and material selection that cheaper methods cannot match, directly impacting the film's performance and longevity.
A High-Tech Manufacturing Process
The term "sputtering" refers to a process called sputter deposition. In a vacuum chamber, a target material (like titanium, stainless steel, or even precious metals) is bombarded with energized ions.
This bombardment ejects microscopic particles from the target, which then deposit onto the polyester film in an extremely fine, uniform layer. This precision is why sputter-deposited films are known for their exceptional optical clarity.
The Role of Metal Particles
The embedded metal particles are the core of the technology. These particles are highly effective at reflecting solar radiation, particularly infrared light, which is the primary source of heat.
Unlike dyed films that simply absorb heat and can fade over time, a sputter tint's metallic layer provides a durable, reflective shield that will not degrade or change color.
Durability and Adhesion
The sputtering process creates a very strong molecular bond between the metal particles and the film. This superior adhesion, as noted in industrial applications, means the tint is exceptionally resistant to peeling, bubbling, or delaminating over its lifespan.
Sputter Tint vs. Other Common Tints
Understanding where sputter tint fits requires comparing it to the other major technologies on the market.
vs. Dyed Tint
This is the most basic and inexpensive type of tint. Dyed films use a layer of dye to absorb solar energy. They offer privacy but provide minimal heat rejection and are prone to fading to a purple color and bubbling over time. Sputter tint is vastly superior in every performance metric.
vs. Carbon Tint
Carbon tint infuses the film with carbon particles, which are more effective at blocking heat than dye and won't fade. However, high-quality sputter tints generally offer a higher level of total solar energy rejection (TSER) than standard carbon films.
vs. Ceramic Tint
This is the most critical comparison for modern buyers. Ceramic tints use non-conductive, non-metallic ceramic nanoparticles to block heat. They offer a similar level of elite heat rejection to sputter tints but with one crucial advantage: they do not block electronic signals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single tint technology is perfect. Choosing the right one involves weighing the benefits against the inherent disadvantages.
Pro: Superior Heat Rejection & Durability
Sputter tint's primary advantage is its ability to reflect a significant amount of solar energy. This keeps a vehicle's cabin noticeably cooler. Its robust construction ensures this performance will last for the life of the vehicle.
Pro: Unmatched Clarity & Color Stability
The precise manufacturing process ensures the film has no visual distortion. Furthermore, because the color comes from stable metals, the film will never fade or change hue.
Con: Signal Interference
This is the most significant drawback of any metallized tint, including sputter films. The metal layer that blocks heat can also interfere with radio waves. This can weaken or block signals for GPS, cell phones, satellite radio, and keyless entry systems.
Con: Cost and Appearance
Sputter tint is a premium product, and its price reflects the complex manufacturing process. While more subtle than older, mirror-like metallic tints, it can still have a slight sheen or reflectivity that some people may not prefer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be based on a clear understanding of your priorities and tolerance for the trade-offs.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat rejection and durability: Sputter tint is a fantastic choice, provided you are not heavily reliant on in-car electronics that could be affected by signal interference.
- If your primary focus is high performance without compromise: A high-quality ceramic tint is the superior modern choice, offering comparable heat rejection without any risk of signal interference.
- If your primary focus is privacy on a budget: A quality carbon film is a good middle ground, offering better performance and longevity than dyed film without the cost or signal issues of metallized tints.
Understanding the core technology of each tint type empowers you to choose the film that truly aligns with your needs and priorities.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Sputter Tint | Ceramic Tint | Carbon Tint | Dyed Tint |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Rejection | Excellent (Reflective) | Excellent (Non-Conductive) | Good | Poor |
| Durability | Very High | Very High | Good | Low (Fades/Bubbles) |
| Signal Interference | Yes (Metallic) | No | No | No |
| Cost | Premium | Premium | Mid-Range | Budget |
Optimize Your Lab's Performance with KINTEK's Precision Equipment
Just as choosing the right window tint depends on your specific needs, selecting the right lab equipment is crucial for your research accuracy and efficiency. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables designed for durability and precision. Whether you need advanced heating systems, vacuum chambers, or material deposition tools, our solutions are engineered to deliver reliable results without interference.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and support your scientific goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Aluminum-Plastic Flexible Packaging Film for Lithium Battery Packaging
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
People Also Ask
- What materials are used in thin film optical coating? Key Materials for Precise Light Control
- What does a layered film mean? Unpacking the Depths of Cinematic Storytelling
- What is the difference between single layer film and multi layer film? A Guide to Material Selection
- What is a sustainable solution to reduce plastic waste? A Guide to the Waste Hierarchy
- What are the properties of Aluminium (Al) relevant to its use in coatings? High Reflectivity & Conductivity Explored





