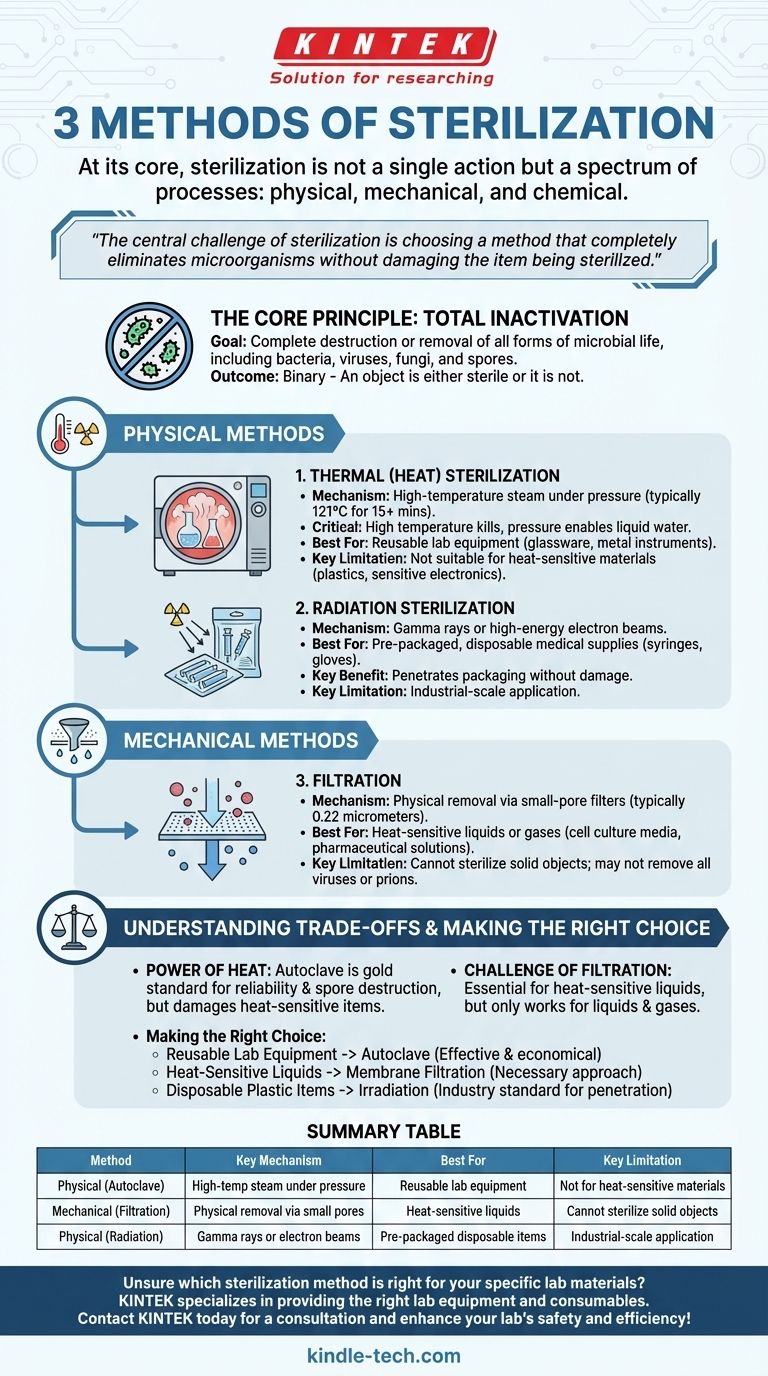
At its core, sterilization is not a single action but a spectrum of processes. While many methods exist, they are best understood as belonging to three primary categories: physical, mechanical, and chemical. The most common and effective method for general laboratory use is physical sterilization using an autoclave, which applies high-temperature steam under pressure to destroy all microbial life.
The central challenge of sterilization is choosing a method that completely eliminates microorganisms without damaging the item being sterilized. While heat is a powerful and reliable agent, methods like filtration and irradiation are critical for handling sensitive materials.

The Core Principle: Total Inactivation
Sterilization is an absolute process. Its goal is the complete destruction or removal of all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores.
An object is either sterile or it is not. This binary outcome is what distinguishes sterilization from disinfection, which only reduces the number of viable microorganisms.
Physical Sterilization Methods
Physical methods use energy like heat or radiation to kill microorganisms.
Thermal (Heat) Sterilization
The most reliable and widely used sterilization method is applying heat. This is most often accomplished with an autoclave.
An autoclave is a chamber that uses pressurized steam to achieve a high temperature—typically 121°C for at least 15 minutes.
It is critical to understand that it is the high temperature that kills microorganisms, not the pressure itself. The pressure simply allows water to remain liquid as steam at temperatures above its normal boiling point, enabling efficient heat transfer.
For this process to succeed, all air must first be evacuated from the chamber. This allows superheated steam to penetrate all surfaces of the items being sterilized, ensuring complete thermal stress and cell death.
Radiation Sterilization
Another physical method is irradiation, which uses gamma rays or high-energy electron beams.
This method is excellent for sterilizing pre-packaged, disposable medical supplies like syringes and gloves, as the radiation can penetrate the packaging without damaging the product.
Mechanical Sterilization Methods
Mechanical methods do not kill microbes but physically remove them from a substance.
Filtration
Filtration is the primary mechanical method, used to sterilize heat-sensitive liquids or gases.
The fluid is passed through a filter with a pore size smaller than the microorganisms, typically 0.22 micrometers. This effectively traps and removes bacteria.
While effective at removing bacteria, filtration may not remove all viruses or prions, which are much smaller.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single sterilization method is perfect for every application. The choice is always a balance between effectiveness and material compatibility.
The Power and Limits of Heat
The autoclave is the gold standard for its reliability and ability to destroy even the most heat-resistant spores.
However, the high temperatures will destroy or damage many plastics, sensitive electronics, and certain chemical solutions. It is only suitable for thermostable items.
The Challenge of Filtration
Filtration is essential for sterilizing liquids like cell culture media or pharmaceutical solutions that would be destroyed by heat.
Its primary limitation is that it only works for liquids and gases. It cannot be used to sterilize solid objects, like surgical instruments or glassware.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct method requires understanding the nature of the item you need to sterilize.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing reusable lab equipment (glassware, metal instruments): The autoclave is the most effective and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive liquids (e.g., media, protein solutions): Membrane filtration is the correct and necessary approach.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing disposable plastic items at an industrial scale: Irradiation is the industry standard for its ability to penetrate packaging.
Ultimately, effective sterilization hinges on matching the method to the material to achieve total microbial inactivation without compromising the item's integrity.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Mechanism | Best For | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical (Autoclave) | High-temperature steam under pressure | Reusable lab equipment (glassware, metal instruments) | Not suitable for heat-sensitive materials |
| Mechanical (Filtration) | Physical removal via small-pore filters | Heat-sensitive liquids (media, solutions) | Cannot sterilize solid objects |
| Physical (Radiation) | Gamma rays or electron beams | Pre-packaged disposable items (syringes, gloves) | Industrial-scale application |
Unsure which sterilization method is right for your specific lab materials? KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for your sterilization needs, from autoclaves for robust instruments to filtration systems for sensitive solutions. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution to ensure complete microbial inactivation without compromising your materials. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and enhance your lab's safety and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How does an autoclave ensure the reliability of experimental results? Achieving a Sterile Baseline for Lab Research
- How should solid materials in bags be prepared for decontamination? Master Steam Penetration for Safe Sterilization
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing
- What is the primary purpose of an autoclave in the preparation of media for the biological leaching of uranium?
- How is an autoclave utilized in antimicrobial experiments? Ensure Precise Nanoparticle Research Integrity



















