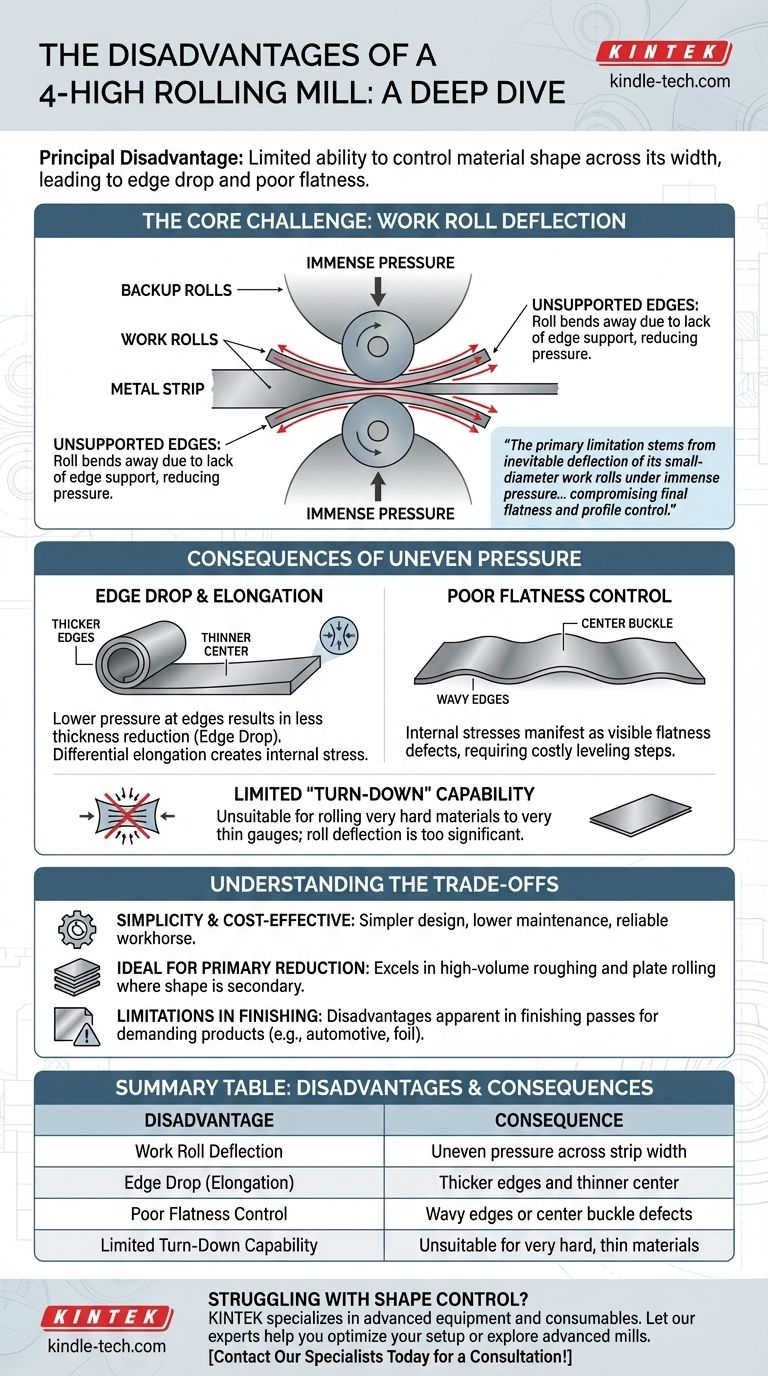
The principal disadvantage of a 4-high rolling mill is its limited ability to control the material's shape across its width. This often results in undesirable effects like edge elongation, also known as "edge drop," where the edges of the strip are thicker than the center. This occurs because the design, while robust, lacks direct support for the work rolls at the very edges of the material being processed.
The 4-high mill's primary limitation stems from the inevitable deflection of its small-diameter work rolls under immense pressure. While large backup rolls provide central support, the unsupported roll ends can bend, leading to a thinner center and thicker edges on the rolled material, which compromises final flatness and profile control.
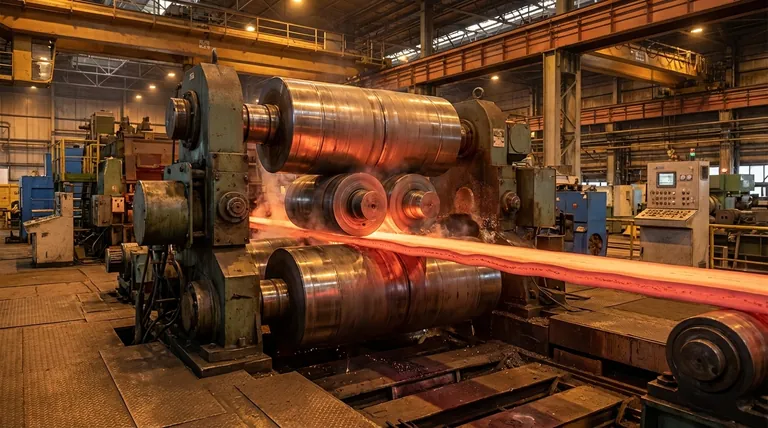

The Core Challenge: Work Roll Deflection
The central issue in any rolling operation is managing the immense forces required to reduce the thickness of metal. In a 4-high mill, this force creates a fundamental mechanical challenge.
The Mechanics of Bending
The two small-diameter work rolls are in direct contact with the metal strip. To deform the metal, they are subjected to millions of pounds of force.
Under this load, the work rolls behave like a beam supported at two points and bend slightly, with the greatest deflection occurring at the center.
The Role of Backup Rolls
To counteract this bending, two much larger backup rolls are placed in contact with the work rolls. Their massive diameter and rigidity provide crucial support.
This support, however, is not perfectly uniform across the entire length of the work roll. It effectively stiffens the center but does not eliminate deflection entirely.
The Unsupported Edges
The critical disadvantage arises at the edges of the metal strip. The backup rolls support the main body of the work rolls, but there is no supporting surface directly at the edges.
This lack of edge support allows the work rolls to bend away from the material at the extreme ends, reducing the rolling pressure at the edges compared to the center.
Consequences of Uneven Pressure
This uneven pressure profile across the strip's width leads directly to common quality defects that define the limits of a 4-high mill's performance.
Edge Drop and Elongation
Because the pressure is lower at the edges, the material there is not reduced in thickness as much as the material in the center. This results in a strip that is thicker at the edges—a defect known as edge drop.
This also means the material in the center is elongated more than the material at the edges. This differential elongation creates internal stress within the strip.
Poor Flatness Control
Internal stresses must be relieved. They manifest as visible flatness defects, such as wavy edges or a center buckle.
These shape defects are often unacceptable for high-precision applications and require additional leveling or processing steps to correct, increasing production time and cost.
Limited "Turn-Down" Capability
This design limitation makes 4-high mills less suitable for rolling very hard materials to very thin gauges. The roll deflection becomes too significant relative to the target thickness, making it nearly impossible to achieve a flat, uniform product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite these disadvantages, the 4-high mill remains a cornerstone of the metals industry for clear and practical reasons. Acknowledging its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
The 4-high configuration is mechanically simpler and less expensive to build and maintain than more advanced mill designs (such as 6-high or 20-high Cluster mills).
Its robustness makes it a reliable workhorse for a wide range of common rolling applications.
Ideal for Primary Reduction
4-high mills excel in "roughing" and "plate" rolling operations. In these early stages, the primary goal is significant thickness reduction, and precise final shape control is a secondary concern.
Limitations in Finishing
The mill's disadvantages become most apparent in "finishing" passes, where the final gauge, profile, and flatness are critical. For demanding products like automotive body sheets or thin foils, more complex mill designs are often necessary to overcome the inherent limitations of the 4-high setup.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right mill technology requires matching the equipment's capabilities to the final product requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-volume roughing or plate rolling: A 4-high mill is often the most cost-effective and robust solution due to its simple design and high throughput.
- If your primary focus is producing thin-gauge, high-strength strip with exceptional flatness: The shape control limitations of a 4-high mill may be unacceptable, and you should consider advanced configurations like 6-high or Cluster mills.
- If you are troubleshooting an existing 4-high mill: Focus on systems that counteract roll deflection, such as work roll bending jacks and specialized roll grinding profiles (crowns), to extend the mill's performance window.
Understanding a 4-high mill's inherent design limitations is the first step toward optimizing its performance or selecting a more suitable technology for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Work Roll Deflection | Uneven pressure across strip width |
| Edge Drop (Elongation) | Thicker edges and thinner center |
| Poor Flatness Control | Wavy edges or center buckle defects |
| Limited Turn-Down Capability | Unsuitable for very hard, thin materials |
Struggling with shape control or product quality in your rolling operations? The limitations of a 4-high mill can be a major bottleneck. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for materials testing and processing. Our experts can help you analyze your needs and recommend the right technology—whether it's optimizing your current setup or exploring more advanced mill configurations. Let's improve your product quality and efficiency together. Contact our specialists today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Jar Mill with Agate Grinding Jar and Balls
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
People Also Ask
- What is the preventive maintenance of ball mill? Ensure Maximum Uptime and Reliability
- What is the purpose of ball milling? A Versatile Tool for Material Synthesis and Modification
- What are the disadvantages of a ball mill? High Energy Use, Noise, and Contamination Risks
- What affects ball mill efficiency? Optimize Grinding Speed, Media, and Material for Peak Performance
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a sag mill? A Guide to Primary vs. Secondary Grinding



















