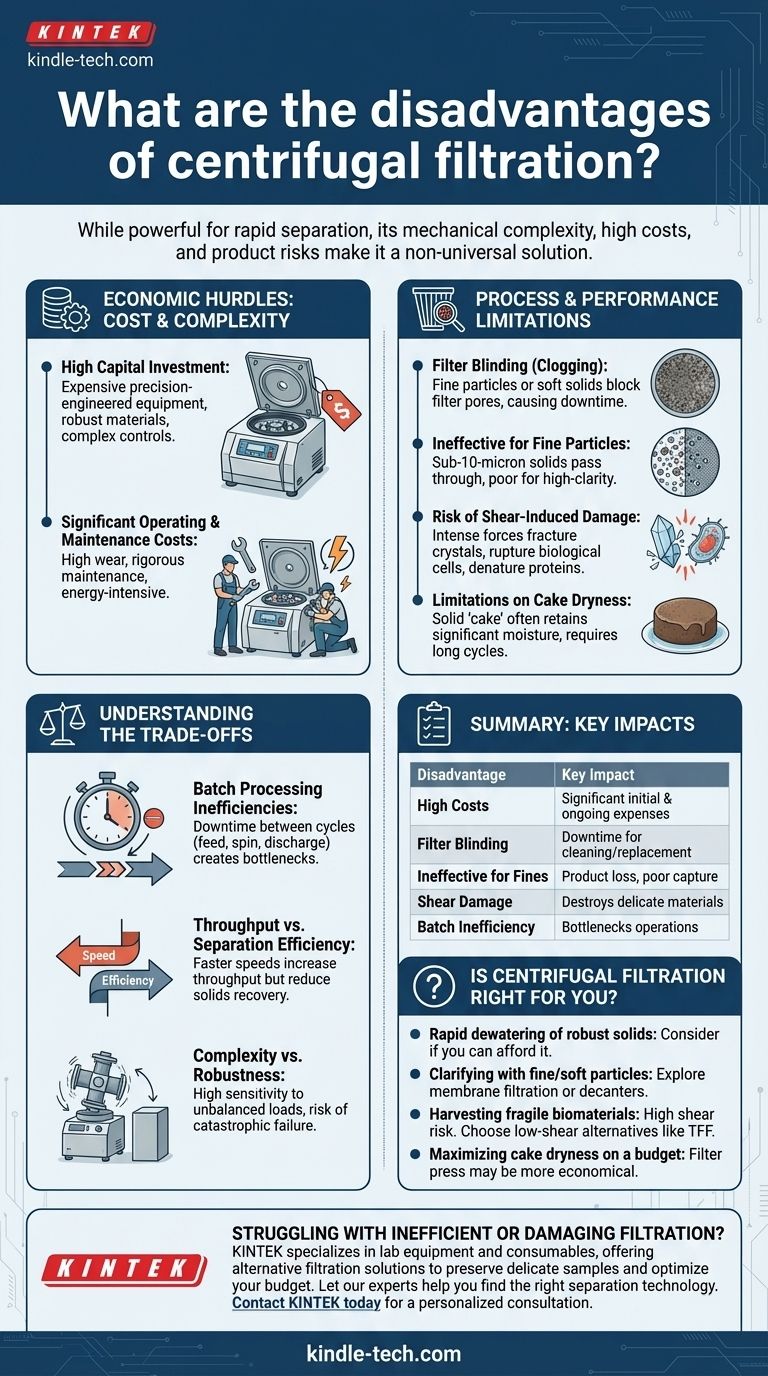
While a powerful tool for rapid solid-liquid separation, centrifugal filtration is not a universal solution. Its principal disadvantages stem from its mechanical complexity and reliance on high rotational speeds, leading to high capital costs, significant maintenance demands, potential for product damage from shear forces, and inefficiency when dealing with very fine or deformable particles.
The core trade-off of centrifugal filtration is speed versus cost and finesse. While it excels at quickly dewatering granular solids, this performance comes at the price of high investment, operational complexity, and a significant risk of damaging delicate materials or failing to capture fine particles.

The Economic Hurdles: Cost and Complexity
Centrifuges are sophisticated machines, and their cost extends far beyond the initial purchase price. Understanding the total cost of ownership is critical when evaluating this technology.
High Initial Capital Investment
A centrifuge is a piece of precision-engineered, high-speed rotating equipment. The manufacturing tolerances, robust materials required to handle immense forces, and complex control systems make them one of the more expensive types of separation equipment.
Significant Operating and Maintenance Costs
The high speeds generate substantial wear on mechanical components like bearings, seals, and drive systems. This necessitates a rigorous preventative maintenance schedule performed by skilled technicians. Furthermore, these machines are energy-intensive, contributing to high operational costs over their lifetime.
Process and Performance Limitations
Beyond the economics, centrifugal filtration has fundamental process limitations that make it unsuitable for certain applications. These limitations are tied directly to its operating principle.
The Challenge of Filter Blinding
The filter medium (a screen or cloth) is susceptible to blinding, or clogging. This occurs when fine particles plug the filter pores or when soft, gelatinous solids deform under pressure and smear across the surface, blocking liquid flow. Blinding brings the process to a halt and requires downtime for cleaning or media replacement.
Ineffectiveness with Very Fine Particles
Centrifugal filtration relies on a physical barrier. If the solid particles are smaller than the openings in the filter medium, they will pass through with the liquid (filtrate). This makes it a poor choice for applications requiring high-clarity liquid or for capturing solids in the sub-10-micron range.
Risk of Shear-Induced Product Damage
The intense acceleration and high G-forces can be destructive. This shear force can fracture delicate crystals, rupture biological cells, or denature sensitive protein precipitates. In biotechnology and pharmaceutical applications, this can lead to a direct loss of product value and integrity.
Limitations on Cake Dryness
While centrifugal filtration effectively removes bulk liquid, the resulting solid "cake" can retain significant moisture. Achieving a very low residual moisture content often requires longer cycle times or extremely high G-forces, which may not be practical or economical compared to a technology like a filter press.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing centrifugal filtration involves accepting a specific set of compromises. The primary trade-off is often between processing speed and overall quality or efficiency.
Batch Processing Inefficiencies
Many industrial centrifuges operate in batches. The cycle involves accelerating, feeding, spinning, decelerating, and discharging the solid cake. This non-productive downtime between batches can create a bottleneck in a continuous upstream or downstream process.
Throughput vs. Separation Efficiency
There is often an inverse relationship between throughput and efficiency. Running the process faster by reducing the "spin" time may increase the amount of material processed per hour, but it can also result in a wetter solid cake and higher loss of fine solids into the filtrate.
Complexity vs. Robustness
The mechanical complexity that enables high-speed performance also makes the system more sensitive. An unbalanced load, for example, can cause catastrophic failure. This contrasts with simpler, more robust technologies that can handle greater process variability with fewer risks.
Is Centrifugal Filtration Right for Your Application?
To make the right choice, you must align the technology's characteristics with your primary separation goal.
- If your primary focus is rapid dewatering of robust, crystalline solids: Centrifugal filtration is a strong candidate, provided you can accommodate the high capital and maintenance costs.
- If your primary focus is clarifying a liquid with very fine or soft particles: You should explore alternative methods like membrane filtration or a decanter centrifuge, as filter blinding and poor capture will be major issues.
- If your primary focus is harvesting fragile biological materials (e.g., cells, protein precipitates): The high shear forces present a significant risk. Low-shear alternatives like tangential flow filtration (TFF) are often a safer choice for preserving product integrity.
- If your primary focus is maximizing cake dryness on a budget: A filter press may achieve lower residual moisture at a fraction of the capital cost, albeit with higher labor involvement.
Ultimately, understanding these disadvantages ensures you select a separation technology based on a clear-eyed assessment of its true capabilities and costs.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Capital & Operating Costs | Significant initial investment and ongoing maintenance/energy expenses. |
| Filter Blinding & Clogging | Process downtime required for cleaning/replacing clogged filter media. |
| Ineffective for Fine Particles | Poor capture of sub-10-micron solids, leading to product loss. |
| Shear-Induced Product Damage | Risk of destroying delicate crystals, cells, or proteins. |
| Batch Processing Inefficiency | Non-productive downtime between cycles can bottleneck operations. |
Struggling with Inefficient or Damaging Filtration?
Centrifugal filtration's high costs and risks might not align with your lab's needs for gentle handling or cost-effective operation. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering alternative filtration solutions tailored to preserve delicate samples and optimize your budget.
Let our experts help you find the right separation technology for your specific application. We provide equipment that ensures product integrity and process efficiency.
Contact KINTEL today for a personalized consultation and discover how we can enhance your laboratory's filtration processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tubes
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the role of corundum tubes in oxygen permeation testing? Ensure Integrity for Bi-doped Membranes
- What are alloys in simple words? Unlock the Power of Engineered Materials
- Why are quartz reaction tubes preferred for fixed-bed reactors? Ensure Data Integrity in Methane Reforming
- What is the primary function of an Alumina (Al2O3) tube in LLZTO sintering? Optimize Your Thermal Processing
- What technical considerations are involved in selecting quartz reaction tubes for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Efficiency



















