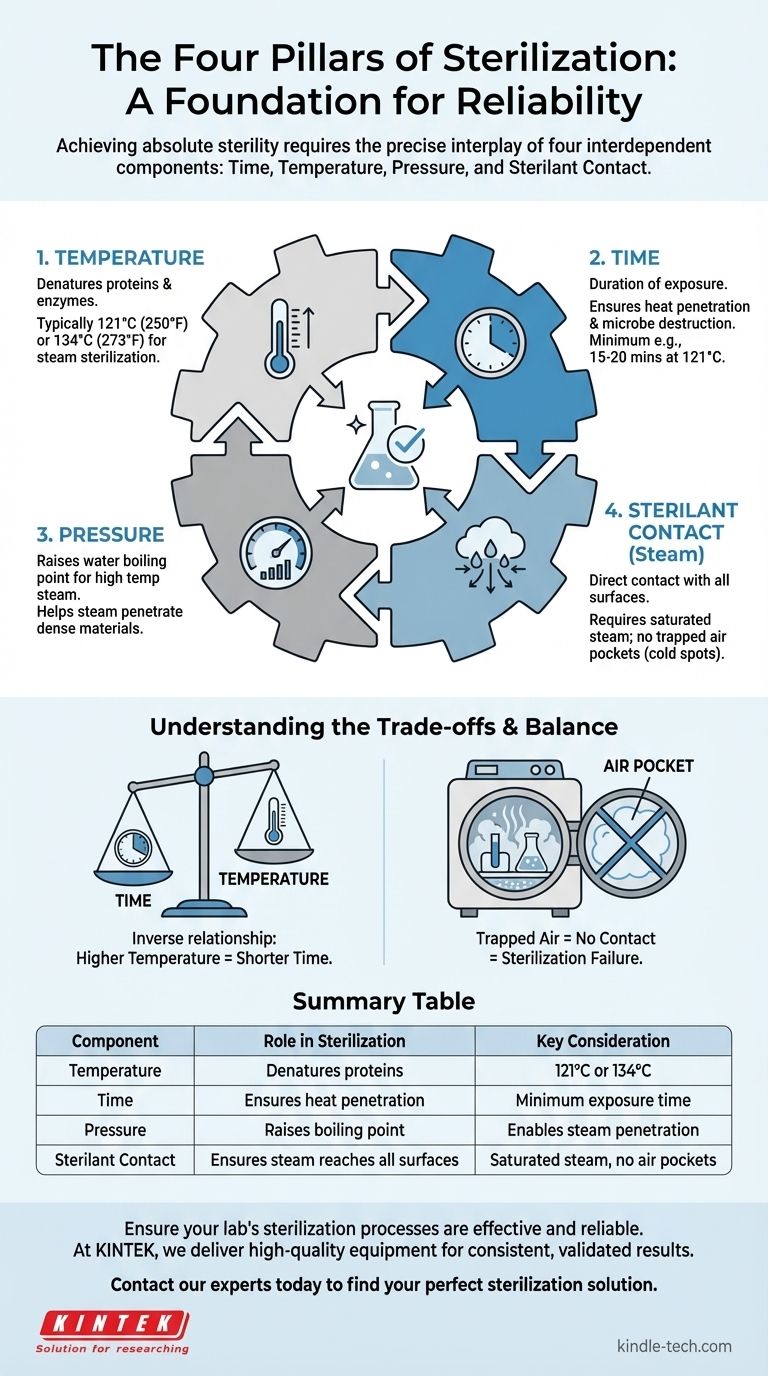
At its core, sterilization is achieved by controlling four critical and interdependent parameters. These components are time, temperature, pressure, and sterilant contact (such as steam). For any sterilization process to be effective and repeatable, each of these variables must be precisely managed and validated.
The success of sterilization doesn't come from a single factor, but from the precise interplay of its four core components. Understanding how time, temperature, pressure, and sterilant contact work together is the key to ensuring absolute sterility.
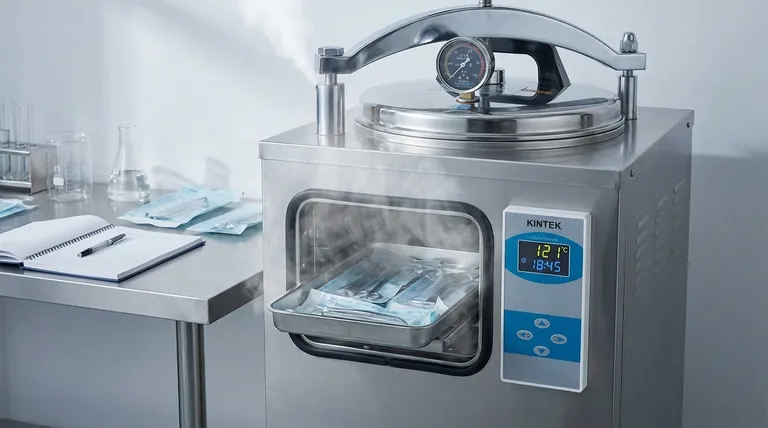

The Four Pillars of Sterilization
To achieve sterilization—the complete elimination of all microbial life—a process must be built on a foundation of four essential components. Each one plays a distinct and non-negotiable role.
1. Temperature
The level of heat applied is the primary agent for destroying microorganisms.
Temperature works by denaturing essential proteins and enzymes within microbial cells, causing irreversible damage and cell death.
The specific temperature required depends on the method, but for steam sterilization (autoclaving), this is typically 121°C (250°F) or 134°C (273°F).
2. Time
This is the duration for which the item is exposed to the critical temperature.
A minimum exposure time is required to ensure that the heat has penetrated the entire load and has been applied long enough to kill even the most resistant bacterial spores.
For example, a standard autoclave cycle at 121°C often requires a minimum exposure time of 15-20 minutes after the target temperature is reached.
3. Pressure
In steam sterilization, pressure is the mechanism used to achieve the necessary high temperatures.
Under normal atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C. By increasing the pressure inside a sealed chamber like an autoclave, we can raise the boiling point of water, allowing for the creation of steam at 121°C or higher.
Pressure itself contributes to the process by helping steam penetrate dense materials and reach all surfaces of the items being sterilized.
4. Sterilant Contact (Steam Quality)
The sterilizing agent must make direct contact with every surface. In an autoclave, this agent is saturated steam.
If air is trapped within the chamber or the load, it creates "cold spots" that the steam cannot reach, leading to sterilization failure. This is why the initial phase of an autoclave cycle focuses on purging air.
The quality of the steam is also critical. It must be "saturated"—containing the maximum amount of water vapor—to efficiently transfer heat to the load.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The four components of sterilization are locked in a dependent relationship. Altering one requires adjusting another, and failure to do so is the most common cause of process failure.
The Time and Temperature Balance
There is an inverse relationship between time and temperature. A higher temperature can achieve sterilization in a shorter time.
This is why some cycles run at 134°C for just 3-5 minutes, which is faster but may not be suitable for heat-sensitive materials.
The Risk of Trapped Air
Improper loading of an autoclave can trap air pockets, preventing steam contact regardless of how high the temperature or pressure is.
This is the single most common user error. It demonstrates that perfect time, temperature, and pressure are useless without complete sterilant contact.
The Problem with "Wet" Steam
If the steam contains too much liquid water ("wet steam"), it transfers heat less efficiently than saturated steam and can leave loads overly damp, risking recontamination after the cycle.
This is a equipment-level issue that highlights the importance of not just having steam, but having the right quality of steam.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Applying these principles correctly ensures your sterilization process is both effective and efficient.
- If your primary focus is routine sterilization of lab media or waste: Prioritize ensuring proper steam contact by not overloading the autoclave and leaving space between items.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing delicate instruments: Pay close attention to the time-temperature relationship to select a cycle that is effective without damaging the items.
- If you are validating a process for medical or pharmaceutical use: You must rigorously document and control all four components to prove the process is repeatable and reliable.
Ultimately, viewing sterilization through the lens of these four components transforms it from a simple machine cycle into a controllable scientific process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Sterilization | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Denatures proteins to kill microbes. | Typically 121°C or 134°C for steam sterilization. |
| Time | Ensures heat penetrates and kills all organisms. | Minimum exposure time (e.g., 15-20 mins at 121°C). |
| Pressure | Raises water's boiling point for high-temperature steam. | Enables steam penetration into dense materials. |
| Sterilant Contact | Ensures steam reaches all surfaces for complete sterilization. | Requires saturated steam and no trapped air pockets. |
Ensure your lab's sterilization processes are effective and reliable.
At KINTEK, we understand that precise control over time, temperature, pressure, and sterilant contact is non-negotiable for achieving absolute sterility. Our range of high-quality autoclaves and lab sterilization equipment is designed to deliver consistent, validated results for laboratories in research, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare.
Let us help you build a foundation of reliable sterilization.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sterilization solution for your specific needs and ensure your processes meet the highest standards of safety and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the function of laboratory autoclaves in SCWR research? Predict Material Compatibility and Corrosion Kinetics
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing



















