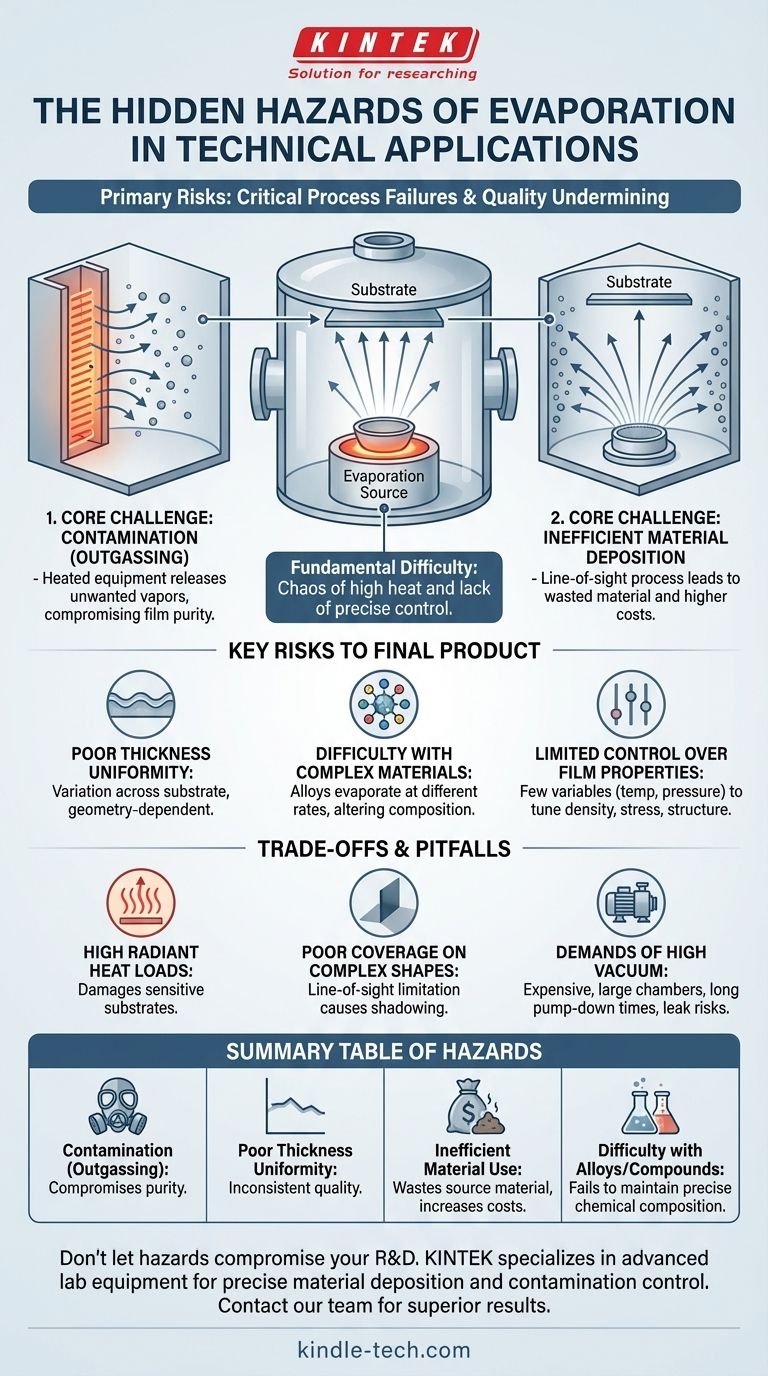
The primary hazards of evaporation in technical applications are not physical dangers, but critical process failures that undermine the quality of the final product. These risks include chemical contamination from the equipment itself, an inability to control the thickness and uniformity of the deposited material, and significant inefficiencies in the use of source materials.
Evaporation is fundamentally a difficult process to control. While simple in concept, its reliance on high heat creates a chaotic environment where contamination, poor surface coverage, and material inconsistencies are common hazards to achieving a high-quality outcome.

The Core Challenge: Lack of Precise Control
Evaporation is a thermal process where a material is heated in a vacuum until its atoms or molecules boil off, travel through the chamber, and condense on a cooler surface, known as a substrate. The "hazards" emerge from the inherent simplicity and brute-force nature of this method.
The Problem of Contamination
In a high-vacuum chamber, the intense heat required for evaporation doesn't just affect the source material. It also heats the surrounding equipment components.
These hot objects can release their own unwanted vapors, a process called outgassing. These stray molecules can react with your desired material mid-flight, contaminating the final film and compromising its purity and performance.
Inefficient Material Deposition
Once atoms evaporate from the source, they travel in a straight line in all directions. This is a "line-of-sight" process.
As a result, only a fraction of the evaporated material actually lands on your target substrate. A significant amount coats the internal walls of the chamber, representing wasted material and leading to higher operational costs and more frequent maintenance.
Key Risks to Your Final Product
These fundamental control issues create specific, tangible risks to the quality, uniformity, and composition of the material you are trying to create.
Poor Thickness Uniformity
The coating deposited by evaporation is often not uniform. The thickness can vary significantly across the surface of the substrate, especially over large areas.
This lack of uniformity is a direct result of the geometry between the source and the substrate, making it a major challenge for applications requiring precise and consistent film thickness.
Difficulty with Complex Materials
Evaporation is particularly challenging for depositing compounds or alloys made of multiple elements.
Different materials have different melting points and vapor pressures, meaning they will evaporate at different rates. This makes it extremely difficult to ensure the final deposited film has the same chemical composition (stoichiometry) as the source material.
Limited Control Over Film Properties
Compared to more advanced deposition techniques, evaporation offers very few variables for process control—essentially just temperature and pressure.
This limitation means you have little ability to fine-tune important film properties like density, internal stress, or crystalline structure, which are often critical for the performance of the final device.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While effective for certain applications, it's crucial to understand the practical limitations and consequences of choosing evaporation.
High Radiant Heat Loads
The intense heat generated by the evaporation source radiates throughout the chamber. This high thermal load can easily damage sensitive substrates, such as plastics or certain electronic components.
Poor Coverage on Complex Shapes
Because evaporation is a line-of-sight process, it performs poorly when coating complex, three-dimensional surfaces.
Areas that are not in the direct line of sight of the source will receive little to no coating, a phenomenon known as "shadowing." This requires complex and costly rotating fixtures to even partially mitigate.
The Demands of High Vacuum
Achieving the necessary high-vacuum environment requires expensive, large-volume chambers and powerful pumping systems.
This not only represents a significant capital investment but also introduces practical challenges like long pump-down times between runs and the constant risk of vacuum leaks that can ruin the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To avoid these hazards, you must align the capabilities of evaporation with the specific needs of your project.
- If your primary focus is a simple, single-element coating on a flat surface: Evaporation can be a cost-effective method, provided you can tolerate some variation in film uniformity.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D objects or achieving high uniformity: The line-of-sight hazard makes evaporation a poor choice, and you should investigate alternative methods like sputtering.
- If your primary focus is depositing precise alloys or advanced compounds: The difficulty in controlling material composition makes evaporation highly challenging, and more sophisticated techniques are almost certainly required.
By understanding these inherent process hazards, you can select the right tool for your application and mitigate risks to your final product's quality and performance.
Summary Table:
| Hazard | Impact on Process & Product |
|---|---|
| Contamination (Outgassing) | Compromises film purity and performance. |
| Poor Thickness Uniformity | Leads to inconsistent coating quality. |
| Inefficient Material Use | Wastes source material, increasing costs. |
| Difficulty with Alloys/Compounds | Fails to maintain precise chemical composition. |
Don't let evaporation hazards compromise your R&D or production. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for precise material deposition and contamination control. Our experts can help you select the right technology to ensure uniform coatings and efficient material use. Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- How does evaporation deposition work? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Coating
- What are the applications for evaporation? Harnessing Its Power for Industrial Innovation
- Why do we need a vacuum for thin-film deposition? To Ensure Purity, Adhesion, and Process Control
- What are the advantages of electron beam evaporation? Achieve High-Purity, High-Rate Thin Films
- What is the mechanism of evaporation? Unlock High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- How do you evaporate metal? Mastering Thermal vs. E-beam Evaporation for Thin Films
- What is the process of evaporation coating? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- Why is an alumina boat selected for catalyst precursors? Ensure Sample Purity at 1000 °C



















