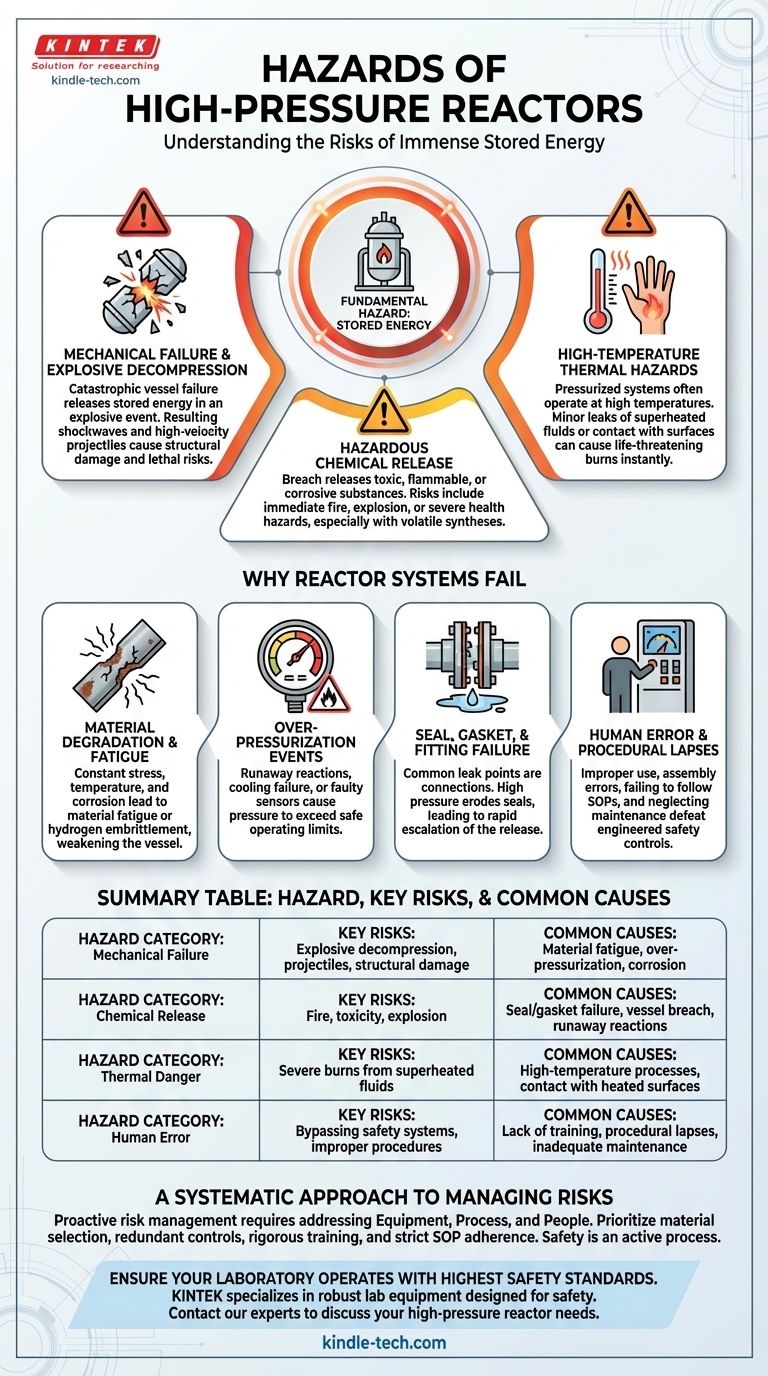
The fundamental hazard of a high-pressure reactor is the immense stored energy it contains. A sudden, uncontrolled release of this energy—whether from mechanical failure or an operational error—can result in a catastrophic event with explosive force, releasing high-temperature fluids and potentially hazardous chemical substances.
The primary danger is not just the pressure itself, but the combination of high pressure, high temperature, and often volatile chemical contents. Consequently, safety is not a single feature but a comprehensive system encompassing material science, automated controls, and strict operational protocols.

The Fundamental Hazards of Stored Energy
At its core, a pressurized vessel is a container of potential energy. The primary hazards stem from how this energy is released and what is released with it.
Mechanical Failure and Explosive Decompression
The most severe hazard is a catastrophic vessel failure. This is not a simple leak; it is an explosive decompression where the reactor ruptures, instantly releasing its contents.
The resulting shockwave can be powerful enough to cause structural damage to buildings and turn fragments of the reactor into high-velocity projectiles, posing a lethal risk to anyone in the vicinity.
Hazardous Chemical Release
High-pressure reactors are used to create conditions necessary for specific chemical syntheses, such as hydrogenation or alkoxylation.
A breach in the reactor vessel or its fittings releases these chemicals. Depending on the process, this can lead to the rapid dispersal of flammable, toxic, or corrosive materials, creating an immediate fire, explosion, or health hazard.
High-Temperature Thermal Hazards
Pressure and temperature are often linked. Many high-pressure reactions are also conducted at elevated temperatures.
Even a minor leak of a superheated fluid or gas can cause severe, life-threatening burns instantly. Contact with the heated external surfaces of the reactor itself also presents a significant thermal hazard.
Why Reactor Systems Fail
Understanding the hazards requires knowing the potential points of failure. These failures are rarely spontaneous and can typically be traced back to material, control, or procedural issues.
Material Degradation and Fatigue
The materials used to construct a reactor are under constant stress from pressure cycles, high temperatures, and chemical corrosion.
Over time, this can lead to material fatigue, stress cracking, or hydrogen embrittlement (a particular concern in hydrogenation reactions). This degradation weakens the vessel, making it susceptible to failure below its original design pressure.
Over-Pressurization Events
A reactor's pressure can exceed its safe operating limits for several reasons. The most common is a runaway reaction, where a chemical process accelerates uncontrollably, generating heat and gas that overwhelm the system.
Failure of a cooling system or a faulty pressure-control sensor can also lead directly to a dangerous over-pressurization event.
Seal, Gasket, and Fitting Failure
The most common points for leaks are not the vessel walls but the seals, gaskets, and fittings used for connections, instruments, and access ports.
While often starting as a small leak, the high pressure can quickly erode the sealing material, leading to a rapid escalation of the release. This is why leak-detection systems are a critical safety feature.
Human Error and Procedural Lapses
Engineered safety controls can be defeated by improper use. Errors in assembly, failing to follow correct startup or shutdown procedures, or neglecting scheduled maintenance are major contributing factors to incidents.
Procedural adherence is as critical to safety as the physical design of the reactor itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Designing and operating a high-pressure system involves balancing performance, cost, and safety. Recognizing these trade-offs is key to a robust safety culture.
Cost vs. Material Specification
The choice of materials is the first line of defense. Standard stainless steel may be adequate for some conditions, but more aggressive chemicals or higher temperatures and pressures require specialized and costly alloys like Hastelloy or Inconel.
Opting for a less-expensive material that is not suited for the process chemistry is a dangerous compromise that can lead to accelerated corrosion and premature failure.
Simplicity vs. Redundant Controls
Modern reactors feature sophisticated safety systems, including automatic pressure controls, emergency vents, and shutdown interlocks.
While these systems enhance safety, they add complexity and maintenance requirements. A simple system is easier to operate but may lack the redundant safety layers needed to handle an unexpected event. The key is ensuring operators are trained to manage the level of complexity involved.
A Systematic Approach to Managing Reactor Hazards
Proactive risk management is essential. Safety is achieved through a multi-layered approach that addresses the equipment, the process, and the people.
- If your primary focus is hands-on operation: Prioritize strict adherence to standard operating procedures (SOPs) and learn to recognize early warning signs like unusual noises or minor leaks.
- If your primary focus is engineering and design: Your priority must be material selection appropriate for the specific chemistry and temperature, combined with redundant pressure-control and emergency-relief systems.
- If your primary focus is laboratory management or safety oversight: Implement a comprehensive risk assessment for every process and ensure rigorous, documented training and maintenance protocols are established and followed.
Ultimately, safety in high-pressure environments is an active process, not a passive state guaranteed by equipment alone.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Key Risks | Common Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Failure | Explosive decompression, projectiles, structural damage | Material fatigue, over-pressurization, corrosion |
| Chemical Release | Fire, toxicity, explosion | Seal/gasket failure, vessel breach, runaway reactions |
| Thermal Danger | Severe burns from superheated fluids | High-temperature processes, contact with heated surfaces |
| Human Error | Bypassing safety systems, improper procedures | Lack of training, procedural lapses, inadequate maintenance |
Ensure your laboratory operates with the highest safety standards. The risks associated with high-pressure reactors are significant, but they can be effectively managed with the right equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in providing robust, reliable lab equipment and consumables designed with safety as a priority. Our reactors and associated safety systems are engineered to handle the demanding conditions of high-pressure syntheses like hydrogenation. Don't compromise on safety—contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and how we can help you build a safer, more efficient workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What role do laboratory stirred reactors and acid baths play in lignin-based vitrimers recycling? Achieve 100% Recovery
- What conditions does a high-pressure hydrothermal reactor provide for PE microplastic degradation? Master AOPs Today
- What is the function of a PTFE-lined high-pressure reactor? Enhance Your Perovskite Oxide Synthesis
- What is the core function of a high-pressure reactor in CO2 fixation? Drive 100% Conversion in Cyclic Carbonate Synthesis
- What is the primary role of high-pressure reactors in the in-situ preparation of confined metal catalysts? Expert Guide
- Why is the inclusion of an agitator in a plastic pyrolysis reactor critical? Boost Heat Transfer and Yield
- What are some important factors to monitor in a bioreactor? Essential Parameters for Optimal Bioprocess Control
- Why is a high-pressure laboratory reactor core for oilfield corrosion? Simulate Deep-Sea & Reservoir Conditions



















