In essence, industrial centrifuges are fundamental tools for separation. They are used across numerous sectors—from food processing and pharmaceuticals to waste management and manufacturing—to efficiently separate liquids from solids, or to separate two immiscible liquids, based on their density differences. This process is critical for purifying products, recovering valuable materials, and treating waste streams at a massive scale.
The core function of an industrial centrifuge is to replace gravity with a much more powerful centrifugal force. This force dramatically accelerates the natural separation process, making it possible to achieve in minutes what might otherwise take hours, days, or even be impossible through simple settling.

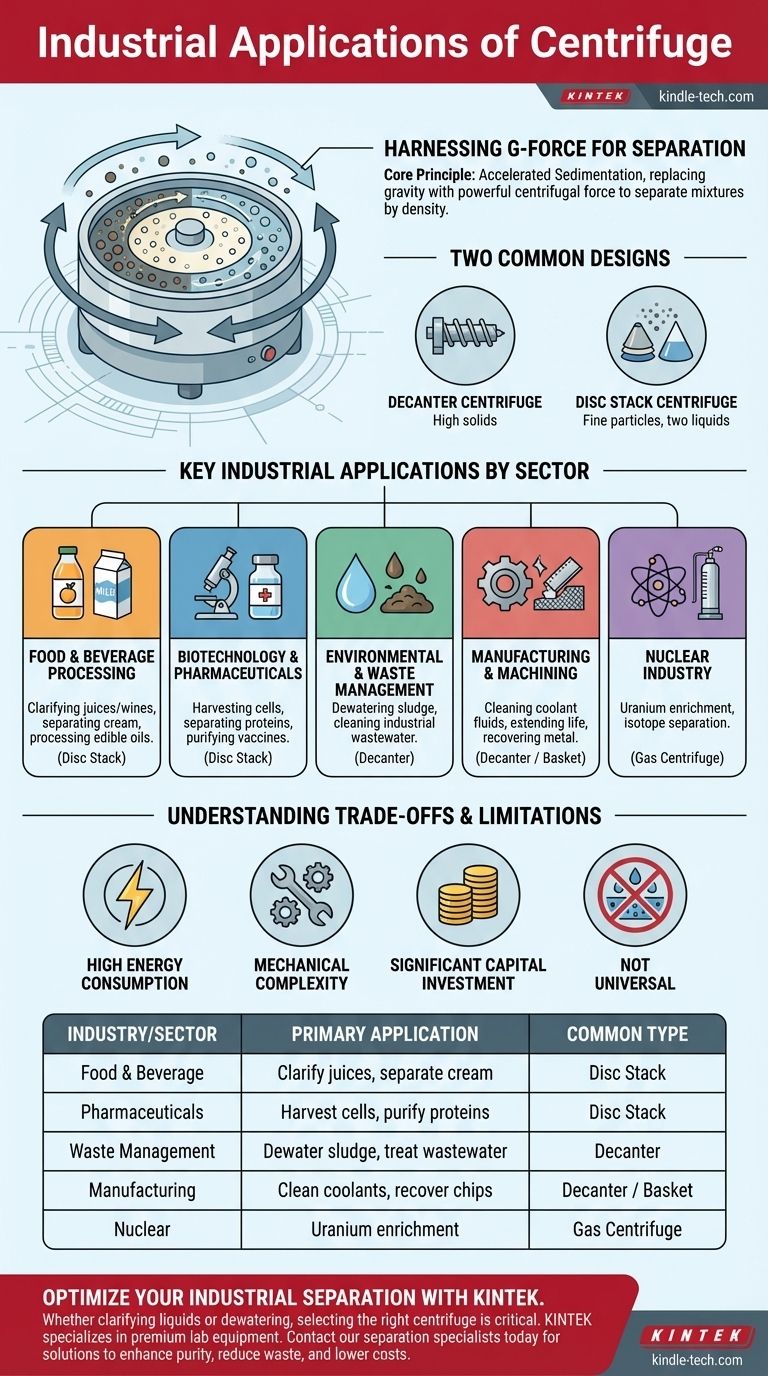
The Core Principle: How Industrial Centrifuges Work
An industrial centrifuge operates on the principle of accelerated sedimentation. By spinning a mixture at extremely high speeds, it generates a powerful centrifugal force, often thousands of times stronger than Earth's gravity.
Harnessing G-Force for Separation
This intense force compels the denser components of the mixture to move outward, away from the axis of rotation. The less dense components remain closer to the center.
This action effectively and rapidly separates materials that would otherwise mix or separate very slowly.
Decanter vs. Disc Stack Centrifuges
While many types exist, two common designs are decanter and disc stack centrifuges.
Decanter centrifuges use a helical screw to continuously discharge separated solids, making them ideal for handling high solid concentrations, like dewatering sludge. Disc stack centrifuges use a series of conical discs to create a large surface area, which is highly effective for separating fine particles or two liquid phases, such as separating cream from milk.
Key Industrial Applications by Sector
The versatility of centrifugation makes it a cornerstone technology in many industries. Its application is defined by the need for efficient, large-scale separation.
Food and Beverage Processing
This is one of the most common applications. Centrifuges are used to clarify juices and wines by removing pulp and yeast, separate cream from milk in dairies, and process edible oils.
Biotechnology and Pharmaceuticals
In bioprocessing, centrifuges are indispensable for harvesting cells from culture media, separating proteins, and purifying vaccines and other biologics where product purity is paramount.
Environmental and Waste Management
Municipal wastewater treatment plants use large decanter centrifuges to dewater sludge, reducing its volume and disposal costs. They are also used to clean industrial wastewater by separating out oils, greases, and suspended solids.
Manufacturing and Machining
In metalworking, centrifuges are used to separate fine metal chips and contaminants from coolant fluids. This extends the life of the coolant, reduces waste, and improves the quality of the machined parts.
Nuclear Industry
A highly specialized application is the gas centrifuge, used for uranium enrichment. These devices spin uranium hexafluoride gas at incredible speeds to separate the slightly heavier uranium-238 isotope from the lighter, fissile uranium-235.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, industrial centrifuges are not without their challenges. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for their effective implementation.
High Energy Consumption
Spinning a heavy bowl and its contents at thousands of RPMs requires a significant amount of electrical energy. This operational cost is a major consideration in any large-scale process.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
Centrifuges are precision-engineered machines subject to immense mechanical stress. They require rigorous maintenance schedules, and bearing or seal failures can lead to costly downtime and repairs.
Significant Capital Investment
Industrial-grade centrifuges are complex and expensive pieces of equipment. The initial purchase price represents a major capital expenditure for any facility.
It's Not a Universal Solution
Centrifugation is only effective when the components of a mixture have a sufficient density difference. It cannot separate dissolved substances or components with very similar densities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of a centrifuge technology depends entirely on the specific separation task.
- If your primary focus is liquid clarification: A disc stack centrifuge is often the best choice for removing very fine solid particles from a liquid to achieve high clarity.
- If your primary focus is dewatering a high volume of solids: A decanter or basket centrifuge is designed to handle high solid loads and produce the driest possible solid cake.
- If your primary focus is separating two immiscible liquids: A disc stack centrifuge is expertly designed for liquid-liquid separation, such as purifying oils or separating cream.
Ultimately, the centrifuge is a powerful and essential workhorse that enables purity and efficiency across the modern industrial landscape.
Summary Table:
| Industry/Sector | Primary Application | Common Centrifuge Type |
|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Clarify juices, separate cream from milk | Disc Stack |
| Pharmaceuticals | Harvest cells, purify vaccines & proteins | Disc Stack |
| Waste Management | Dewater sludge, treat wastewater | Decanter |
| Manufacturing | Clean coolant fluids, recover metal chips | Decanter / Basket |
| Nuclear | Uranium enrichment (isotope separation) | Gas Centrifuge |
Optimize your industrial separation process with KINTEK.
Whether you need to clarify liquids, dewater sludge, or purify sensitive biopharmaceuticals, selecting the right centrifuge is critical for your efficiency and bottom line. KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, serving diverse laboratory and industrial needs. Our experts can help you identify the ideal centrifuge technology—from decanter to disc stack—for your specific application.
Contact our separation specialists today to discuss your requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your product purity, reduce waste, and lower operational costs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
People Also Ask
- When was sputtering invented? From 1852 Discovery to 1920 Industrial Breakthrough
- What are the basics of an electric arc furnace? A Guide to Efficient Metal Recycling
- What is magnetron sputtering coating? A High-Performance Thin Film Deposition Process
- What is sintering of powdered metals and ceramics? The Key to Creating Dense, High-Performance Parts
- What is the RF sputtering technique? A Guide to Depositing Insulating Thin Films
- What is the minimum coating thickness? How Steel Thickness Determines Your Galvanizing Needs
- What chemicals are used in heat treatment? Master the Quenching Process for Optimal Metal Properties
- Why is pyrolysis of solid waste important? Transform Waste into Fuel and Valuable Resources



















