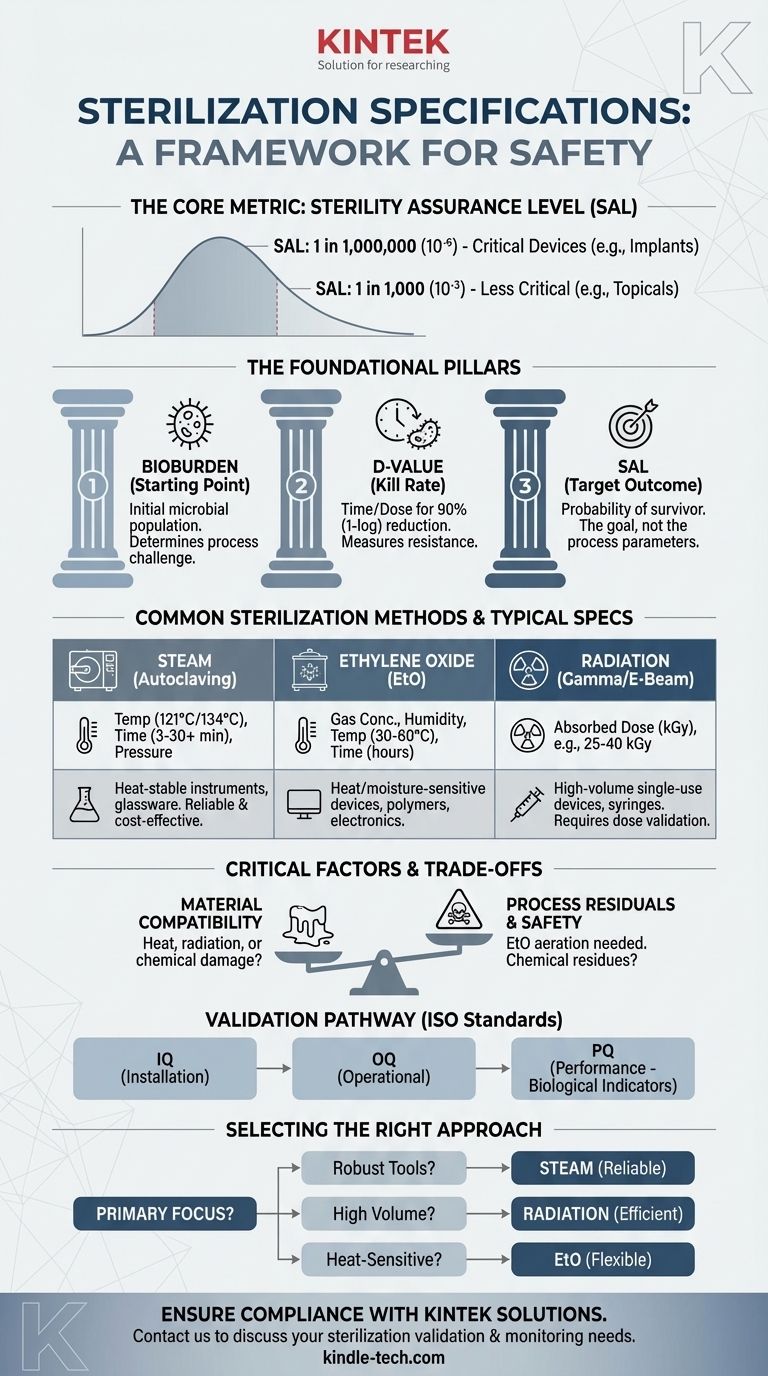
The specifications for sterilization are not a single set of numbers but a framework designed to achieve a specific outcome: a statistical probability that an item is free of viable microorganisms. The most critical specification is the Sterility Assurance Level (SAL), typically a probability of 1 in 1,000,000 (10⁻⁶) for invasive medical devices. The exact process parameters—such as time, temperature, or radiation dose—are then calculated based on this required SAL, the chosen sterilization method, and the initial microbial contamination (bioburden) of the product.
The central takeaway is that sterilization is not defined by a universal specification sheet. It is a validated process where you prove your chosen method consistently achieves a target Sterility Assurance Level (SAL) for your specific product, considering its materials and starting bioburden.

The Foundational Pillars of Sterilization
To understand sterilization specifications, you must first understand the principles that govern them. These are not just guidelines; they are the scientific basis for ensuring product safety and meeting regulatory requirements from bodies like the FDA.
Sterility Assurance Level (SAL): The Core Metric
The SAL is the most important specification. It is a quantitative measure representing the probability of a single viable microorganism surviving on an item after it has been subjected to the sterilization process.
A SAL of 10⁻⁶ is the standard for critical medical devices that contact sterile body tissue or the vascular system. It means there is a one-in-a-million chance of a non-sterile item. For less critical items, like topical products, a SAL of 10⁻³ (one-in-a-thousand) may be acceptable.
Bioburden: Your Starting Point
Bioburden refers to the population of viable microorganisms on a product before sterilization. You cannot define the endpoint of your process without knowing its starting point.
Regulatory bodies require routine monitoring of bioburden. A higher or more resistant bioburden requires a more aggressive sterilization cycle to achieve the target SAL.
D-value: Measuring Microbial Resistance
The D-value is the time or dose required under a defined set of conditions to achieve a 1-log (or 90%) reduction in a specific microbial population.
Think of it as the "kill rate." If a microbial population has a D-value of 1 minute, its population will be reduced by 90% every minute. This value is essential for calculating the total exposure time or dose needed to reach the required SAL.
Translating Theory into Practice: Common Methods
The specific parameters for a sterilization cycle are entirely dependent on the method chosen. The choice of method is, in turn, dictated by the product's material composition and design.
Steam Sterilization (Autoclaving)
- Key Parameters: Saturated Steam, Temperature, Pressure, and Time.
- Typical Spec: A common cycle for medical instruments is 121°C (250°F) at 15 psi for at least 30 minutes or 134°C (273°F) for 3-4 minutes.
- Use Case: Ideal for heat- and moisture-stable items like surgical steel instruments and glassware.
Ethylene Oxide (EtO) Gas
- Key Parameters: Gas Concentration, Humidity, Temperature, and Time.
- Typical Spec: Cycles often run for several hours at 30-60°C.
- Use Case: The standard for heat-sensitive or moisture-sensitive devices, such as complex plastic-based electronics or polymer tubing.
Radiation (Gamma & E-Beam)
- Key Parameters: Absorbed Dose, measured in kiloGrays (kGy).
- Typical Spec: The required dose (often in the 25-40 kGy range) is calculated based on bioburden data and a validation dose experiment per the ISO 11137 standard.
- Use Case: High-volume sterilization of single-use medical devices like syringes, sutures, and catheters.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
Selecting a method is a process of balancing efficacy with product integrity. There is no single "best" method, only the most appropriate one for a given application.
Material Compatibility
This is often the deciding factor. Steam will melt many polymers and destroy electronics. Radiation can make certain plastics brittle or discolored. EtO is highly compatible with most materials but comes with its own challenges.
Process Residuals and Safety
Chemical methods leave behind residues. For EtO, this is a major concern, as it is a known carcinogen. A specification for EtO sterilization must include strict limits on residuals and define an aeration period (often many hours or days) to allow the toxic gas to dissipate to safe levels.
Validation and Regulatory Burden
You cannot simply run a cycle and claim sterility. You must prove it through a rigorous validation process, typically involving three phases:
- Installation Qualification (IQ): Verifies the equipment is installed correctly.
- Operational Qualification (OQ): Verifies the equipment operates within specified parameters.
- Performance Qualification (PQ): Proves the process consistently produces sterile products (using biological indicators) for your specific device.
This entire process must be documented and defended according to international standards like ISO 11135 (for EtO) or ISO 11137 (for Radiation).
How to Select the Right Sterilization Approach
Your choice must be a deliberate, documented decision based on your product's unique requirements and intended use.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing robust, heat-resistant tools: Steam autoclaving is the most reliable, cost-effective, and well-understood method.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing single-use polymer devices in high volume: Radiation offers exceptional penetration and process efficiency, but requires comprehensive material compatibility testing.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive or electronic devices: Ethylene Oxide (EtO) or Vaporized Hydrogen Peroxide (VHP) are necessary but require careful management of process residuals and a more complex validation pathway.
- If your primary focus is regulatory compliance and patient safety: You must document your choice, validate your process according to the relevant ISO standard, and implement a routine monitoring program for bioburden and cycle parameters.
Ultimately, meeting sterilization specifications is a systematic process of risk management, validation, and control designed to ensure absolute patient safety.
Summary Table:
| Sterilization Method | Key Parameters | Typical Spec / Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Steam (Autoclaving) | Temperature, Time, Pressure | 121°C for 30 min; Heat-stable instruments |
| Ethylene Oxide (EtO) | Gas Concentration, Humidity, Time | Several hours at 30-60°C; Heat-sensitive devices |
| Radiation (Gamma/E-beam) | Absorbed Dose (kGy) | 25-40 kGy; Single-use polymer devices |
Ensure your sterilization process meets critical safety standards. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for validation and routine monitoring. Whether you're developing medical devices or managing a laboratory, our solutions help you achieve the required Sterility Assurance Level (SAL) with confidence. Contact us today to discuss your specific sterilization needs and how we can support your compliance and patient safety goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- Can autoclave sterilize liquid? Master Safe and Effective Liquid Sterilization
- What temperature must be reached for sterilization in 10-12 minutes? Achieve Rapid, Reliable Sterility with Flash Autoclaving
- Why is it important to autoclave the prepared reagents before using? Ensure Sterility and Reliable Results
- Do you need to autoclave glassware? A Guide to Sterilization vs. Cleaning
- What are the sizes of autoclaves? A Guide to Choosing the Right Capacity for Your Lab



















