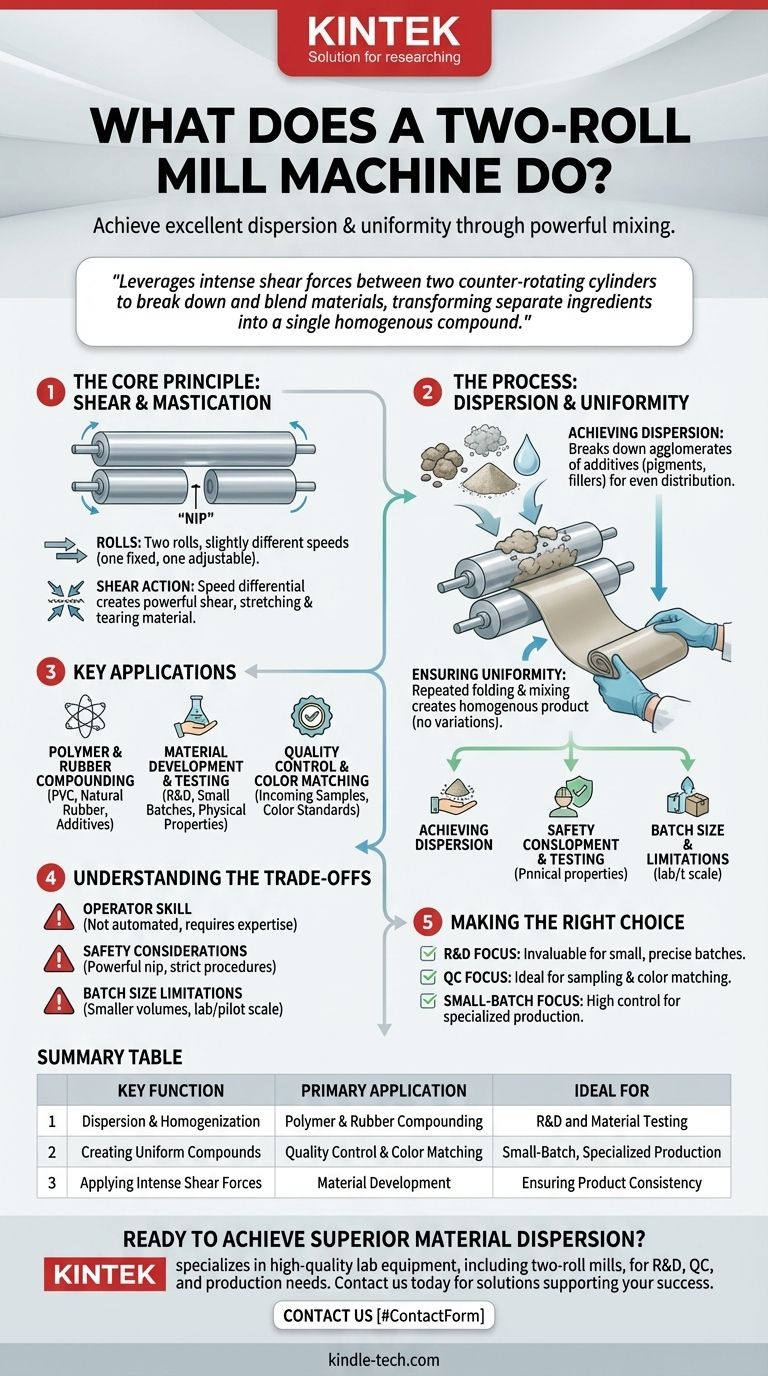
At its core, a two-roll mill machine is a powerful mixing device designed to perform two fundamental functions: achieving excellent dispersion of ingredients within a base material and ensuring a high degree of uniformity throughout the final compound. It accomplishes this by subjecting materials like rubber or plastic to intense mechanical forces between two large, rotating cylinders.
A two-roll mill leverages the intense shear forces created between two counter-rotating cylinders to break down and blend materials like polymers, elastomers, and additives. Its primary value lies in transforming separate raw ingredients into a single, consistent, and homogenous compound.

The Core Principle: Shear and Mastication
To understand what a two-roll mill does, you must first understand the physical forces it applies to a material. The entire process is centered on the gap, or "nip," between its two rolls.
How the Rolls Work
The machine consists of two parallel, horizontal rolls that rotate towards each other at slightly different speeds. One roll is typically fixed, while the other can be adjusted to control the size of the nip.
This speed differential is critical. It creates a powerful shearing action that pulls the material through the nip, stretching and tearing it on a microscopic level.
Achieving Dispersion
Many compounds require mixing a base polymer with additives like pigments, fillers, or chemical agents. These additives often start as clumps or agglomerates.
The shear force in the nip is strong enough to break down these agglomerates, distributing the individual particles evenly throughout the base material. This process is essential for achieving consistent properties.
Ensuring Uniformity
As the material passes through the nip, it forms a sheet on one of the rolls. The operator then cuts and folds this sheet, continuously feeding it back into the nip.
This repeated folding and mixing ensures that all ingredients are thoroughly blended, resulting in a completely homogenous final product with no variations in color, texture, or performance.
Key Applications Across Industries
The two-roll mill's ability to create highly uniform dispersions makes it a fundamental tool in several contexts, from lab-scale testing to specialized production.
Polymer and Rubber Compounding
This is the most common application. The mill is used to mix base elastomers or plastics (like PVC or natural rubber) with ingredients like carbon black, curing agents, and plasticizers to create a final "compound" ready for manufacturing.
Material Development and Testing
In research and development, a two-roll mill is invaluable. It allows material scientists to create and evaluate small, precise batches of new formulations to test their physical properties.
Quality Control and Color Matching
Factories use these mills for quality assurance. A small sample of an incoming raw material can be mixed to verify its quality before it's used in large-scale production.
It is also a critical tool for creating precise color samples for approval, ensuring that a plastic or rubber product matches a specific color standard.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the two-roll mill is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Operator Skill Dependency
A two-roll mill is not an automated, "push-button" machine. Achieving a perfect mix requires a skilled operator who knows how to manipulate the material on the rolls, when to cut it, and how to manage temperature.
Safety Considerations
The exposed, powerful nip between the rolls presents a significant safety hazard. Strict operational procedures, training, and safety guards are absolutely essential to prevent serious injury.
Batch Size Limitations
Compared to large internal mixers like a Banbury mixer, a two-roll mill is generally used for smaller volumes. It excels at lab-scale work, pilot projects, and specialized small-batch production rather than high-volume manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding if a two-roll mill fits your needs depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is research and development: The two-roll mill is an invaluable tool for creating and testing small, precise batches of new material formulations.
- If your primary focus is quality assurance: This machine is ideal for sampling incoming raw materials or creating color masters to ensure product consistency.
- If your primary focus is specialized, small-batch production: A two-roll mill provides the high level of control and dispersion needed for high-performance compounds where uniformity is critical.
Ultimately, the two-roll mill is a fundamental piece of equipment for anyone who needs to precisely control the physical properties of a polymer or rubber compound.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Primary Application | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Dispersion & Homogenization | Polymer & Rubber Compounding | R&D and Material Testing |
| Creating Uniform Compounds | Quality Control & Color Matching | Small-Batch, Specialized Production |
| Applying Intense Shear Forces | Material Development | Ensuring Product Consistency |
Ready to achieve superior material dispersion and uniformity in your lab?
A two-roll mill is essential for precise polymer and rubber compounding. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including two-roll mills, to meet your specific R&D, quality control, and production needs. Our expertise ensures you get the right tool to enhance your material development and maintain consistent product quality.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Open Type Two Roll Mixing Mill Machine for Rubber Crusher
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Jar Mill with Agate Grinding Jar and Balls
People Also Ask
- What is the use of two roll mill? Essential for Polymer Mixing, R&D, and Quality Control
- What is the disadvantage of a two-roll mill? Limited Thickness Reduction Due to Roll Flattening
- What is meant by two high rolling mill? A Guide to Core Material Processing
- What is a two roll mill for rubber compounding? A Foundational Tool for Polymer Processing
- What fillers for rubber compounds? Choose the Right Filler for Performance vs. Cost



















