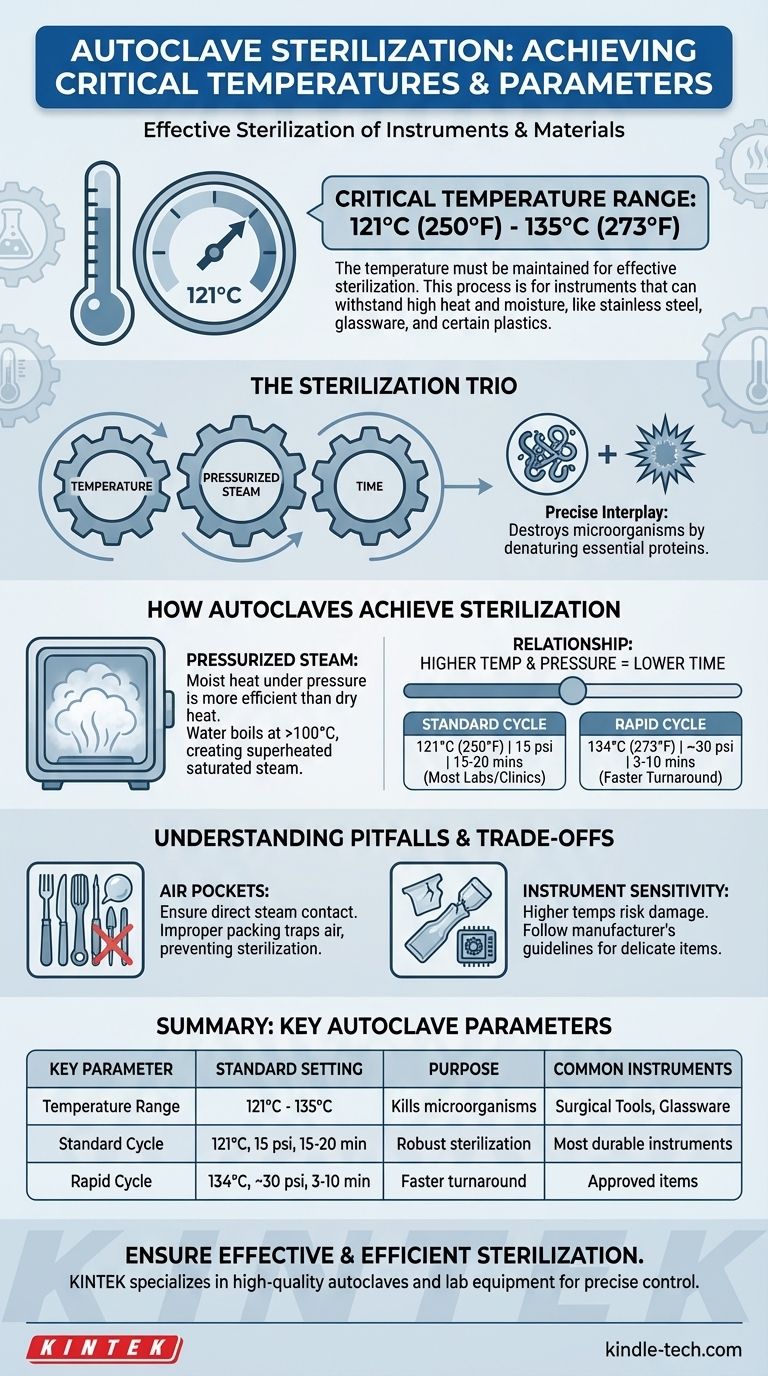
For an autoclave to effectively sterilize instruments, the temperature must be maintained between 121°C (250°F) and 135°C (273°F). This process is used for instruments and materials that can withstand high heat and moisture, such as stainless steel surgical tools, glassware, and certain types of plastics. The most common setting combines a temperature of 121°C with pressurized steam for at least 15 minutes to ensure all microorganisms are destroyed.
The critical takeaway is that sterilization in an autoclave is not just about heat. It is the result of a precise interplay between temperature, pressurized steam, and time, working together to denature the essential proteins of all microorganisms.

How Autoclaves Achieve Sterilization
An autoclave doesn't function like a simple oven. Its effectiveness comes from using moist heat under pressure, a far more efficient method of sterilization than dry heat alone.
The Role of Pressurized Steam
At normal atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). An autoclave is a sealed chamber that increases the pressure, which allows water to exist as saturated steam at much higher temperatures.
This superheated steam can penetrate materials and transfer heat more effectively than dry air, rapidly killing microbes.
The Critical Relationship: Temperature, Pressure, and Time
The three core variables of autoclaving are linked. Increasing the temperature and pressure allows you to decrease the required sterilization time.
A standard cycle for many labs and clinics is 121°C (250°F) at 15 psi (pounds per square inch) of pressure for 15-20 minutes.
However, a faster cycle might run at 134°C (273°F) at nearly double the pressure (~30 psi) for as little as 3-10 minutes. This demonstrates a clear inverse relationship: as temperature goes up, required time comes down.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Trade-offs
Simply reaching the target temperature does not guarantee sterilization. The process is sensitive, and several factors can lead to failure.
The Danger of Air Pockets
Effective sterilization requires direct steam contact with every surface. If instruments are packed too densely or wrapped improperly, air can become trapped.
These air pockets prevent steam from reaching the instrument surfaces, leaving them unsterilized even though the autoclave's sensors report that the cycle reached the correct temperature and pressure.
Instrument and Material Sensitivity
While higher temperatures allow for faster cycles, they also increase the risk of damage to instruments. Delicate equipment, plastics, or complex devices with lumens may be degraded or damaged by the higher heat and pressure of a rapid "flash" cycle.
Always follow the instrument manufacturer's guidelines for sterilization. Not all "autoclavable" items can withstand every type of cycle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The cycle you choose depends entirely on the items being sterilized and your operational needs.
- If your primary focus is robust sterilization of durable goods: Use the standard cycle of 121°C at 15 psi for at least 15 minutes, as this is a universally accepted and highly effective method for most surgical instruments and glassware.
- If your primary focus is rapid turnaround of simple, unwrapped instruments: A higher temperature cycle (e.g., 132°C-135°C) for a shorter time may be appropriate, but use it with caution and only for items approved for this process.
- If you are sterilizing complex or delicate items: Always default to the instrument manufacturer's specific instructions, which may require lower temperatures, longer cycles, or even different sterilization methods altogether.
Understanding these core principles empowers you to ensure every cycle is not just complete, but truly effective.
Summary Table:
| Key Autoclave Sterilization Parameter | Standard Setting | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 121°C - 135°C | Kills microorganisms by denaturing proteins |
| Standard Cycle | 121°C at 15 psi for 15-20 min | Most common setting for durable instruments |
| Rapid Cycle | 134°C at ~30 psi for 3-10 min | Faster sterilization for approved items |
| Common Instruments | Surgical tools, glassware, certain plastics | Items that withstand heat and moisture |
Ensure your lab's sterilization is both effective and efficient. KINTEK specializes in high-quality autoclaves and lab equipment designed for precise temperature control and reliable performance. Whether you need to sterilize surgical instruments, glassware, or specialized lab consumables, our solutions help you maintain critical sterilization standards. Contact us today to find the perfect autoclave for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is autoclave in laboratory? Achieve Total Sterility for Your Lab
- What are the specifications of a laboratory autoclave? A Guide to Key Features for Safe Sterilization
- What is the size of the autoclave? Choose the Right Capacity for Your Lab
- Why is it important to autoclave the prepared reagents before using? Ensure Sterility and Reliable Results
- What is the life expectancy of an autoclave machine? Maximize Your Investment with Proper Care



















