At its core, sieve screening is a straightforward yet critical mechanical method for separating a granular material into different size fractions. It operates on a simple principle: by passing material through a woven wire mesh or a perforated plate (a sieve) with uniform apertures, particles smaller than the openings fall through, while larger particles are retained on the screen's surface. This process is fundamental to both industrial production and quality control analysis.
Sieve screening isn't just about simple separation; it's a foundational tool for characterizing materials. The primary goal is often to determine a material's particle size distribution (PSD), a metric that directly impacts product quality, process efficiency, and final performance.
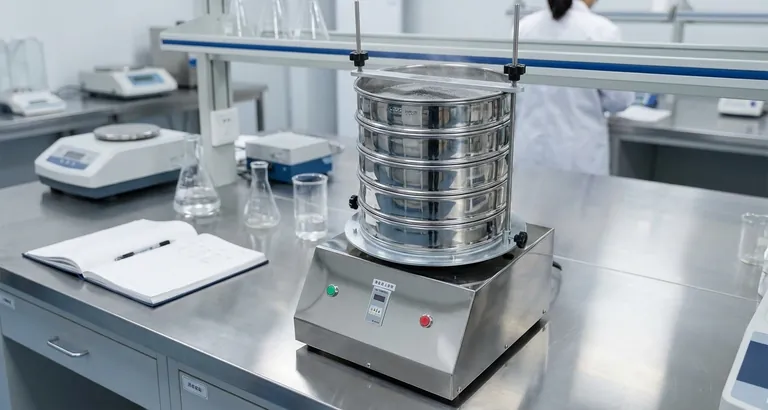

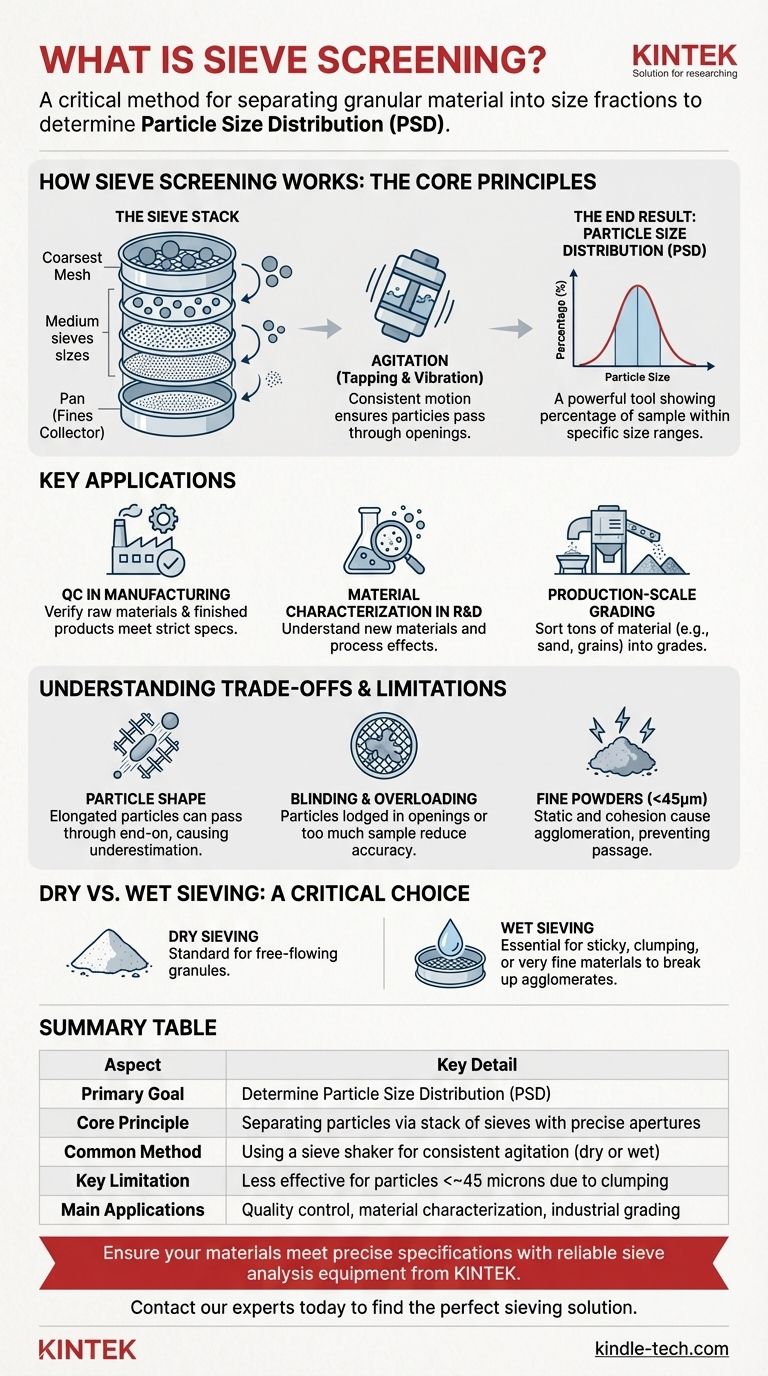
How Sieve Screening Works: The Core Principles
Sieve screening, often performed as a sieve analysis, is a systematic process designed to yield repeatable and reliable data about a material's physical properties.
The Sieve Stack: A Cascade of Precision
The most common laboratory method involves a stack of test sieves. These are precisely manufactured circular frames holding a screen of a specific, certified aperture size.
Sieves are stacked in order of descending aperture size, with the coarsest sieve (largest openings) at the top and the finest sieve (smallest openings) at the bottom. A solid pan is placed at the very bottom to collect the smallest particles.
The Role of Agitation: Ensuring Accurate Separation
A carefully weighed sample of the material is placed in the top sieve. The entire stack is then placed in a sieve shaker, a machine that imparts consistent motion—typically a combination of tapping and vibration.
This agitation serves a crucial purpose: it ensures each particle is presented to the screen openings multiple times and in various orientations, maximizing the chance of it passing through if it is small enough.
The End Result: A Particle Size Distribution
After a set time, the agitation is stopped. The material retained on each individual sieve is then carefully collected and weighed.
By calculating the weight percentage of material on each sieve, you can construct a particle size distribution (PSD) curve. This graph is a powerful visual tool that shows what percentage of the sample falls within specific size ranges.
Key Applications: Where Sieve Screening is Essential
The data derived from sieve screening is vital across a vast range of industries, from pharmaceuticals to heavy construction.
Quality Control in Manufacturing
This is the most common application. Manufacturers use sieve analysis to verify that both incoming raw materials and outgoing finished products meet strict particle size specifications. For example, the texture of flour, the dissolving rate of a chemical powder, or the strength of concrete all depend on a controlled PSD.
Material Characterization in R&D
In research and development, sieve screening is used to characterize new materials or understand how processing changes affect particle size. This foundational data is essential for developing new products and improving existing ones.
Production-Scale Grading
Beyond lab analysis, the principle is used in large-scale industrial screeners. These machines continuously sort tons of material per hour, separating products like sand, gravel, agricultural grains, and recycled plastics into different grades for sale.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sieve screening is a mechanical process with inherent limitations that every user must understand to interpret results correctly.
The Challenge of Particle Shape
Sieve analysis provides a measure of particle size based on a two-dimensional aperture. However, most particles are not perfect spheres. Elongated or flaky particles can pass through a screen opening end-on or diagonally, leading to an underestimation of their true size.
Sieve Blinding and Overloading
Blinding occurs when particles become lodged in the sieve openings, effectively reducing the available area for separation and skewing results. Overloading a sieve with too much sample material can also prevent particles from reaching the screen surface, leading to inaccurate measurements.
Limitations with Very Fine Powders
Sieve screening becomes less effective and reliable for particles smaller than approximately 45 microns. At this scale, forces like static electricity and surface cohesion can cause particles to agglomerate (clump together), preventing them from passing through the fine mesh.
Dry vs. Wet Sieving: A Critical Choice
For materials that are sticky, tend to agglomerate, or are extremely fine, wet sieving is often necessary. In this method, a liquid (usually water with a wetting agent) is used to wash the sample through the sieve stack, breaking up clumps and carrying fine particles through the apertures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right approach to sieve screening depends entirely on your material and your objective.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control of dry, free-flowing granules: A standard set of certified test sieves and a mechanical shaker is the industry-standard, cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is analyzing fine powders or materials that clump: You must use wet sieving techniques to ensure particle deagglomeration and achieve accurate results.
- If your primary focus is high-precision analysis of sub-micron particles: Sieve screening is not the appropriate tool; you should investigate alternative methods like laser diffraction or image analysis.
By understanding these principles and limitations, you can leverage sieve screening as a powerful and reliable tool to guarantee material consistency and product quality.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Determine Particle Size Distribution (PSD) |
| Core Principle | Separating particles via a stack of sieves with precise apertures |
| Common Method | Using a sieve shaker for consistent agitation (dry or wet sieving) |
| Key Limitation | Less effective for particles smaller than ~45 microns due to clumping |
| Main Applications | Quality control, material characterization, and industrial grading |
Ensure your materials meet precise specifications with reliable sieve analysis equipment from KINTEK.
Whether your lab focuses on quality control for pharmaceuticals, construction materials, or chemical powders, accurate particle size data is non-negotiable. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including certified test sieves and sieve shakers, designed to deliver the repeatable and reliable results you need.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your specific material and application. Let us help you guarantee product consistency and improve your process efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process



















