
Optical Materials
Float Soda-Lime Optical Glass for Laboratory Use
Item Number : KTOM-FSO
Price varies based on specs and customizations
- Product thickness
- 0.03——5.0mm
- Transmittance
- 90%
- Main ingredient
- Na2O + K2O : 14 %
Shipping:
Contact us to get shipping details Enjoy On-time Dispatch Guarantee.
Why Choose Us
Easy ordering process, quality products, and dedicated support for your business success.
Float Soda Lime Sheet
Soda Lime Glass, also known as Float Glass contains both Sodium and Calcium, and is formed by drawing the glass over molten tin baths. As a new type of high-tech and high value-added glass, it has the advantages of high light transmittance, smooth surface, high hardness, good chemical stability, and wide application. It is widely used in the electronics industry, especially the information industry.
Detail & Parts
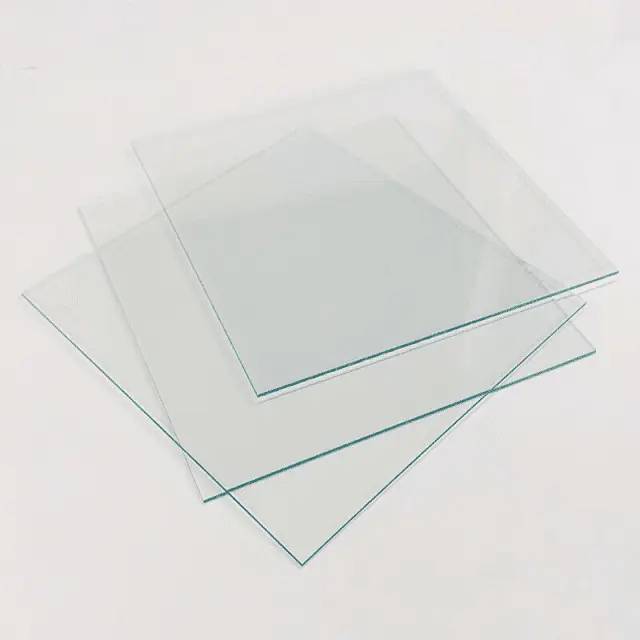
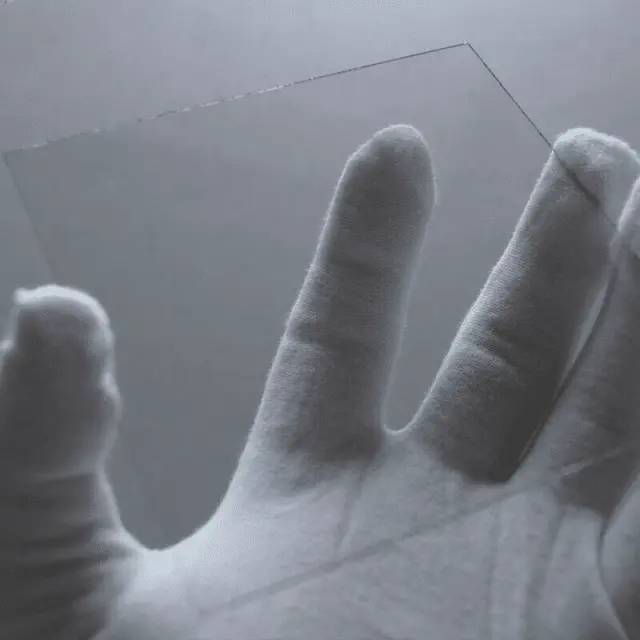



Applications of Float Thin Glass Sheet
- Mirrors
- microscopic slides
- touch screens
- photomasks
- glass masters
- data storage disks
- printed circuit substrates
- photographic plates
- wafers and optical windows
Properties of float soda lime glass
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.937 W/mK |
| Density (at 20 °C/68 °F) | 2.44 g/cm3 |
| Hardness (Moh's Scale) | 6 - 7 |
| Bulk Modulus | 4.3 x 1010 Pa |
| Optical Properties | Refractive Index (l=435): 1.523 (l=645)=1.513 |
| Electrical Properties Dielectric Constant | @ 20°C E= 7.75 |
| Specific Resistivity | 1000 Hz 25°C - log R ohms/cm: 9.7 |
Provide customized services
Through the implementation of innovative and state-of-the-art melting processes, we have acquired extensive expertise in the development and manufacture of quality glass products, offering a wide range of optical glass products for a variety of commercial, industrial and scientific applications. The company provides various specifications of optical glass such as raw glass, cut parts and finished components, and cooperates closely with customers to customize products according to customer needs. With an unwavering commitment to quality, we ensure our customers receive the perfect solution tailored to their requirements.
For further quotations, please contact us.
Trusted by Industry Leaders

FAQ
What Is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)?
What Are The Main Types Of Glass Substrates?
What Is Magnetron Sputtering?
What Are The Methods Used To Deposit Thin Films?
What Is Soda-lime Glass Used For?
Why Magnetron Sputtering?
What Is Thin Film Deposition Equipment?
What Are The Advantages Of Using Sapphire Substrates?
What Are The Materials Used In Thin Film Deposition?
Thin film deposition commonly utilizes metals, oxides, and compounds as materials, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages. Metals are preferred for their durability and ease of deposition but are relatively expensive. Oxides are highly durable, can withstand high temperatures, and can be deposited at low temperatures, but can be brittle and challenging to work with. Compounds offer strength and durability, can be deposited at low temperatures and tailored to exhibit specific properties.
The selection of material for a thin film coating is dependent on the application requirements. Metals are ideal for thermal and electrical conduction, while oxides are effective in offering protection. Compounds can be tailored to suit specific needs. Ultimately, the best material for a particular project will depend on the specific needs of the application.
What Is Thin-film Deposition Technology?
Why Is Boroaluminosilicate Glass Suitable For Laboratory Glassware And Cooking Utensils?
What Are The Methods To Achieve Optimal Thin Film Deposition?
To achieve thin films with desirable properties, high-quality sputtering targets and evaporation materials are essential. The quality of these materials can be influenced by various factors, such as purity, grain size, and surface condition.
The purity of sputtering targets or evaporation materials plays a crucial role, as impurities can cause defects in the resulting thin film. Grain size also affects the quality of the thin film, with larger grains leading to poor film properties. Additionally, the surface condition is crucial, since rough surfaces can result in defects in the film.
To attain the highest quality sputtering targets and evaporation materials, it is crucial to select materials that possess high purity, small grain size, and smooth surfaces.
Uses Of Thin Film Deposition
Zinc Oxide-Based Thin Films
ZnO thin films find applications in several industries such as thermal, optical, magnetic, and electrical, but their primary use is in coatings and semiconductor devices.
Thin-Film Resistors
Thin-film resistors are crucial for modern technology and are used in radio receivers, circuit boards, computers, radiofrequency devices, monitors, wireless routers, Bluetooth modules, and cell phone receivers.
Magnetic Thin Films
Magnetic thin films are used in electronics, data storage, radio-frequency identification, microwave devices, displays, circuit boards, and optoelectronics as key components.
Optical Thin Films
Optical coatings and optoelectronics are standard applications of optical thin films. Molecular beam epitaxy can produce optoelectronic thin-film devices (semiconductors), where epitaxial films are deposited one atom at a time onto the substrate.
Polymer Thin Films
Polymer thin films are used in memory chips, solar cells, and electronic devices. Chemical deposition techniques (CVD) offer precise control of polymer film coatings, including conformance and coating thickness.
Thin-Film Batteries
Thin-film batteries power electronic devices such as implantable medical devices, and the lithium-ion battery has advanced significantly thanks to the use of thin films.
Thin-Film Coatings
Thin-film coatings enhance the chemical and mechanical characteristics of target materials in various industries and technological fields. Anti-reflective coatings, anti-ultraviolet or anti-infrared coatings, anti-scratch coatings, and lens polarization are some common examples.
Thin-Film Solar Cells
Thin-film solar cells are essential to the solar energy industry, enabling the production of relatively cheap and clean electricity. Photovoltaic systems and thermal energy are the two main applicable technologies.
What Are The Advantages Of Using Thin Film Deposition Equipment?
What Are The Applications Of Optical Quartz Glass Sheets?
Factors And Parameters That Influence Deposition Of Thin Films
Deposition Rate:
The rate at which the film is produced, typically measured in thickness divided by time, is crucial for selecting a technology suitable for the application. Moderate deposition rates are sufficient for thin films, while quick deposition rates are necessary for thick films. It is important to strike a balance between speed and precise film thickness control.
Uniformity:
The consistency of the film across the substrate is known as uniformity, which usually refers to film thickness but can also relate to other properties such as the index of refraction. It is important to have a good understanding of the application to avoid under- or over-specifying uniformity.
Fill Capability:
Fill capability or step coverage refers to how well the deposition process covers the substrate's topography. The deposition method used (e.g., CVD, PVD, IBD, or ALD) has a significant impact on step coverage and fill.
Film Characteristics:
The characteristics of the film depend on the application's requirements, which can be categorized as photonic, optical, electronic, mechanical, or chemical. Most films must meet requirements in more than one category.
Process Temperature:
Film characteristics are significantly affected by process temperature, which may be limited by the application.
Damage:
Each deposition technology has the potential to damage the material being deposited upon, with smaller features being more susceptible to process damage. Pollution, UV radiation, and ion bombardment are among the potential sources of damage. It is crucial to understand the limitations of the materials and tools.
What Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting Thin Film Deposition Equipment?
What Makes K9 Glass Special?
What Safety Considerations Are Associated With Operating Thin Film Deposition Equipment?
What Is A CaF2 Window Used For?
What Are The Properties Of Magnesium Fluoride Crystal Substrates?
What Is Silicon Used For In The Near-infrared Range?
What Are Glass Vibration Beads Used For In Laboratories?
4.8 / 5
Float soda-lime glass provides high light transmittance, smooth surface, and excellent chemical stability, making it a reliable choice for laboratory applications.
4.9 / 5
The high cutting precision of soda-lime glass ensures accurate results and minimizes errors in laboratory experiments.
4.7 / 5
Soda-lime glass's resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for handling various chemicals and solvents commonly used in laboratory settings.
4.6 / 5
Float soda-lime glass's small thickness difference ensures consistent quality and performance, making it suitable for precise measurements and observations.
4.8 / 5
The diverse product range of float soda-lime glass caters to various laboratory needs, providing versatility and convenience for researchers.
4.9 / 5
Soda-lime glass's applications in mirrors, microscopic slides, and touch screens demonstrate its versatility and suitability for various laboratory and industrial purposes.
4.7 / 5
The thermal conductivity, density, hardness, and optical properties of float soda-lime glass make it an effective material for laboratory equipment and components.
4.6 / 5
The dielectric constant and specific resistivity of soda-lime glass ensure its electrical stability and performance in laboratory setups.
REQUEST A QUOTE
Our professional team will reply to you within one business day. Please feel free to contact us!
Related Products

Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
High-transparency XRD sample holders with zero impurity peaks. Available in square and round designs, and customizable to fit Bruker, Shimadzu, PANalytical, and Rigaku diffractometers.

400-700nm Wavelength Anti Reflective AR Coating Glass
AR coatings are applied on optical surfaces to reduce reflection. They can be a single layer or multiple layers that are designed to minimize reflected light through destructive interference.

CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
Diamond optical windows: exceptional broad band infrared transparency, excellent thermal conductivity & low scattering in infrared, for high-power IR laser & microwave windows applications.
Related Articles

Glassware vs. Plasticware - Which is the Better Choice for Your Needs?
Both glassware and plasticware have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two will depend on the specific needs of your laboratory.

How To Clean Laboratory Glassware - Part 1
Cleaning laboratory glassware isn't as simple as washing the dishes. Here's how to wash your glassware so that you won't ruin your chemical solution or laboratory experiment.

Optical Quartz Plate: A Comprehensive Guide to Applications, Specifications, and Usage
Discover the versatility of optical quartz plates, exploring their uses in various industries, key specifications, and factors that differentiate them from glass. Gain insights into their applications in ultraviolet transmission, precision optics, and more.

Controlling Color and Applications of Evaporated Silicon Oxide Films
Exploring color variation, control methods, and practical applications of silicon oxide thin films.

Thin Film System Design: Principles, Considerations, and Practical Applications
An in-depth exploration of thin film system design principles, technological considerations, and practical applications in various fields.

Understanding Fused Silica: Properties, Applications, and Advantages
An in-depth look at fused silica, its unique properties, and its diverse applications in various industries.

Electron Beam Evaporation: Advanced Thin Film Creation
Explores the technology and applications of electron beam evaporation in thin film production.

The Rise of Glass Substrates in Advanced Semiconductor Packaging
Explores the shift towards glass substrates in advanced semiconductor packaging, their advantages, and challenges.

Common Optical Materials and Their Properties
An overview of various optical materials, their properties, and applications across different spectral ranges.

Thin Film Deposition Processes in Semiconductor Manufacturing
An overview of thin film deposition techniques, focusing on Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) processes in semiconductor manufacturing.

Comprehensive Overview of Fused Silica: Properties, Production, Applications, and Market Prospects
An in-depth exploration of fused silica, its properties, production process, diverse applications, and promising market outlook.

The Fidelity of Light: Preserving the Quartz Interface in Spectroelectrochemistry
The quartz window is the critical interface between your sample and your data. Learn why protecting it from oils, scratches, and solarization is vital for optical accuracy.