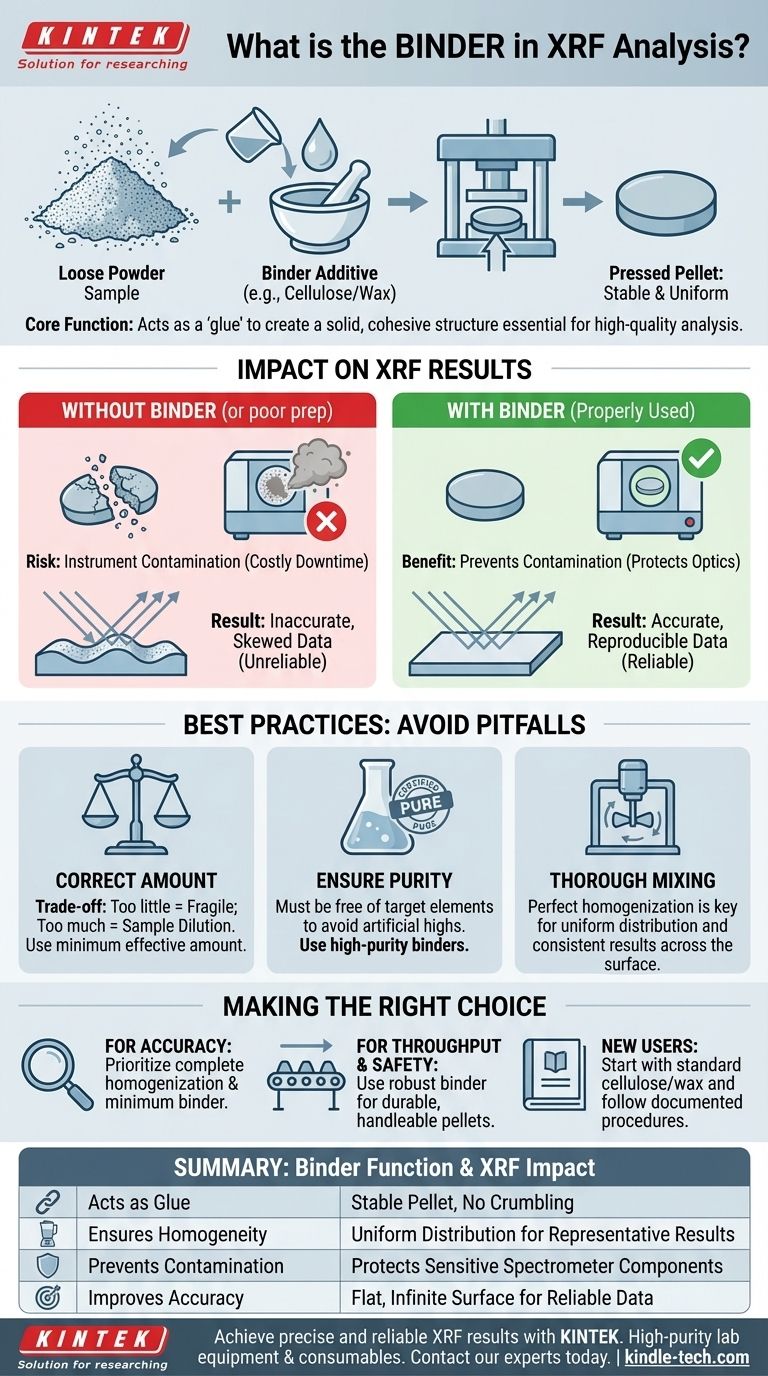
In X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis, a binder is an additive mixed with a powdered sample before it is compressed. Its fundamental purpose is to act as a glue, holding the fine sample particles together to form a solid, stable disc known as a pressed pellet. This process is essential for creating a suitable sample for analysis.
The role of a binder goes beyond simply holding a sample together. It is a critical component for creating a uniform, durable pellet that prevents instrument contamination and ensures the analytical results are both accurate and reproducible.

The Core Function of a Binder in Sample Preparation
To understand XRF, you must first understand the sample. The quality of the pressed pellet directly dictates the quality of your data. The binder is the key ingredient that makes a high-quality pellet possible.
Acting as a 'Glue' for Powders
A finely ground sample is just a loose collection of particles. A binder, typically a cellulose/wax mixture, coats these particles during mixing. When high pressure is applied in a pellet press, the binder helps lock these particles into a solid, cohesive structure.
Ensuring Homogeneity
The X-ray beam only analyzes a small surface area of the pellet. If the sample is not perfectly uniform, the results will not be representative. The binder aids the mixing process, ensuring the sample material is evenly distributed throughout the pellet.
Creating a Durable, Stable Pellet
During pressing, an effective binder recrystallizes under pressure, forming a strong bond between sample grains. This creates a mechanically stable pellet that will not crumble during handling or inside the spectrometer.
How a Binder Directly Impacts Your XRF Results
Using a binder is not optional; it is a fundamental step for quality control. A poorly prepared pellet can invalidate your entire analysis.
Preventing Instrument Contamination
The single greatest risk of analyzing loose powders or fragile pellets is instrument contamination. If a pellet breaks apart, fine powder can get into the sensitive optics and detectors of the XRF spectrometer, leading to costly downtime and repairs.
Improving Analytical Accuracy
XRF measurements assume the sample has a perfectly flat, uniform, and infinitely thick surface relative to the X-ray beam. A well-made pellet meets these conditions. A crumbling or non-uniform pellet will scatter X-rays unpredictably and skew the elemental composition results.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
While essential, the binder itself is a variable that must be controlled. Simply adding it is not enough; how you use it matters significantly.
Using the Correct Amount
There is a trade-off with the quantity of binder. Too little, and the pellet will be fragile and fall apart. Too much, and you will dilute your sample, which can weaken the fluorescence signal from the elements you are trying to measure.
Ensuring Binder Purity
The binder must be free of any elements you are analyzing. A contaminated binder will introduce those elements into your sample, creating artificially high readings and invalidating your data. Always use a high-purity, certified binder.
The Importance of Thorough Mixing
The binder and sample must be perfectly homogenized before pressing. Inadequate mixing leads to an uneven distribution of both binder and sample, resulting in a physically weak pellet and inconsistent analytical results across its surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Your analytical goals should guide your sample preparation technique.
- If your primary focus is maximum analytical accuracy: Prioritize complete homogenization of the sample and binder, and use the minimum effective amount of binder to reduce any sample dilution effects.
- If your primary focus is sample throughput and safety: A robust binder that creates highly durable pellets is key to preventing instrument contamination and allowing for confident, rapid handling of samples.
- If you are new to pellet preparation: Start with a standard, high-purity cellulose/wax binder and follow a documented mixing and pressing procedure to establish a reliable and repeatable baseline.
Properly utilizing a binder transforms a loose powder into a high-quality analytical sample, forming the foundation for reliable XRF data.
Summary Table:
| Binder Function | Impact on XRF Analysis |
|---|---|
| Acts as a Glue | Creates a solid, stable pellet that won't crumble |
| Ensures Homogeneity | Provides uniform distribution for accurate, representative results |
| Prevents Contamination | Protects sensitive spectrometer components from powder |
| Improves Accuracy | Creates a flat, infinite-thickness surface for reliable data |
Achieve precise and reliable XRF results with KINTEK.
Proper sample preparation is the foundation of accurate analysis. KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including the binders and pellet presses you need to create perfect samples every time. Our products are designed to help your laboratory prevent costly instrument contamination and ensure data reproducibility.
Ready to optimize your XRF sample preparation? Contact our experts today to find the right solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- XRF Boric Acid Lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for Laboratory Use
- XRF & KBR plastic ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- How do you prepare a sample for XRF analysis? Master the Key Methods for Accurate Results
- What are pellet dies made of? Choose the Right Material for Accurate XRF Analysis
- How do you make XRF pellets? A 4-Step Guide to Flawless Sample Preparation
- What are the samples for XRF analysis? A Guide to Preparing Solids, Powders, and Liquids
- What are the five key considerations when designing a sample preparation recipe for pressed pellets in XRF analysis?



















