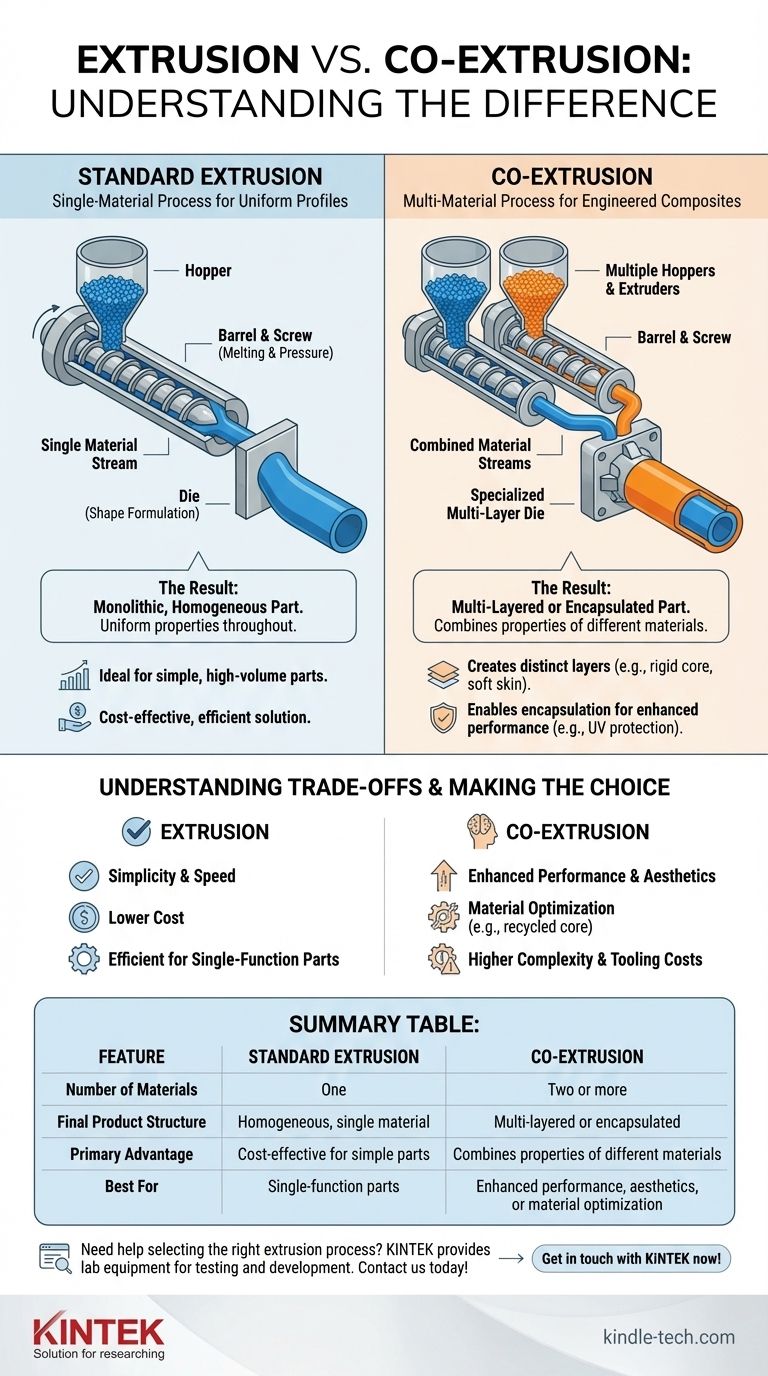
The fundamental difference between extrusion and co-extrusion is the number of materials processed at once. Standard extrusion involves melting and shaping a single plastic material through a die to create a uniform profile. In contrast, co-extrusion uses multiple extruders to combine two or more different materials into a single, multi-layered or encapsulated part before they exit the die.
While both are manufacturing processes that shape plastic, the distinction is critical. Standard extrusion creates a simple, homogenous part, whereas co-extrusion engineers a composite part that strategically combines the properties of different materials into one integrated profile.
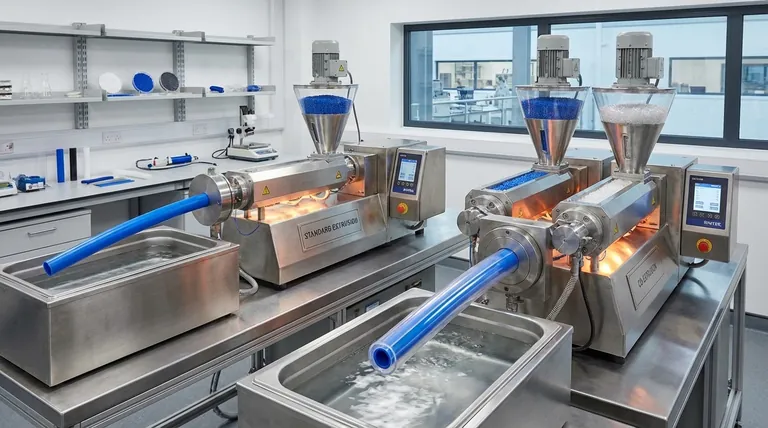

The Mechanics of Standard Extrusion
The Single-Material Process
In a standard extrusion line, solid plastic pellets of a single type are fed from a hopper into a barrel. Inside the barrel, a rotating screw melts the plastic through heat and pressure.
This molten plastic is then forced through a shaped tool, known as a die, which gives the final product its cross-sectional shape, like a pipe or a window frame.
The Resulting Product
The final part is monolithic, meaning it is composed of the same material throughout. Its physical, chemical, and aesthetic properties are uniform from the core to the surface.
This process is ideal for creating simple, high-volume parts where the requirements can be met by a single polymer.
How Co-Extrusion Expands the Possibilities
Combining Multiple Material Streams
Co-extrusion employs two or more extruders, each feeding a different material (or the same material with a different color or additive) into a single, specialized die.
The die is engineered to precisely combine these molten streams into a single, unified shape just before they exit.
Creating Multi-Layered Structures
This process allows for the creation of parts with distinct layers. For example, you can form a product with a rigid, structural core and a soft, flexible outer skin.
Another common use is encapsulation, where one material completely surrounds another. This is often done to add a protective outer layer, such as a UV-resistant cap over a less durable core material.
The Engineering Advantage
The primary benefit of co-extrusion is the ability to combine the best properties of different plastics. You can merge the strength of one material with the weather resistance of another, or the low cost of a recycled core with the pristine appearance of a virgin surface layer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Complexity and Cost
Co-extrusion is an inherently more complex process. It requires multiple extruders, a more sophisticated (and expensive) die design, and tighter process controls to manage the different material flows.
This increased complexity translates to higher initial tooling costs and potentially more challenging production runs.
Material Compatibility
A critical consideration in co-extrusion is the compatibility of the materials being combined. The polymers must have similar melt temperatures and flow characteristics to process smoothly together.
Most importantly, they must be able to form a strong adhesive bond. If the materials are not compatible, the final part can suffer from delamination, where the layers peel apart under stress.
When Standard Extrusion Is Better
For applications that do not require multi-material properties, standard extrusion is the more efficient and cost-effective solution. If a single polymer can meet all design requirements, the added complexity of co-extrusion is unnecessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the decision between extrusion and co-extrusion is driven by the specific requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for a single-function part: Standard extrusion is the superior choice due to its simplicity, speed, and lower operational overhead.
- If your primary focus is enhanced performance or specific aesthetics: Co-extrusion is necessary when you need to combine properties like weather resistance, color variation, barrier protection, or texture in a single profile.
- If your primary focus is material optimization: Co-extrusion allows you to use an inexpensive core material (like recycled plastic) and cap it with a thin layer of a high-performance polymer, optimizing the overall part cost without sacrificing surface quality.
Understanding this distinction moves you from simply choosing a process to strategically engineering a final product.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Extrusion | Co-Extrusion |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Materials | One | Two or more |
| Final Product Structure | Homogeneous, single material | Multi-layered or encapsulated |
| Primary Advantage | Cost-effective for simple parts | Combines properties of different materials |
| Best For | Single-function parts with uniform requirements | Enhanced performance, aesthetics, or material optimization |
Need help selecting the right extrusion process for your plastic profile?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables necessary for testing and developing high-quality extruded and co-extruded products. Whether you're analyzing material compatibility, melt flow, or final product performance, our solutions help you optimize your process and achieve superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in polymer processing and materials science.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What to do with injection molding? Mass-Produce High-Quality Plastic Parts Efficiently
- What is the process of calendering in plastic processing? A Guide to High-Volume Film & Sheet Production
- What is the internal structure of a mixer? A Guide to Core Components and Operation
- What is the raw material for blown film extrusion? Selecting the Right Polyethylene for Your Film
- What is the main purpose of vulcanization? Transform Rubber into a Durable, Elastic Material
- What is the principle of calendering? Enhance Fabric Surface with Heat and Pressure
- How to make compound rubber? Master the Sequence to Prevent Scorch and Ensure Quality
- What is the screw extrusion process? A Guide to Continuous Plastic Profiling



















