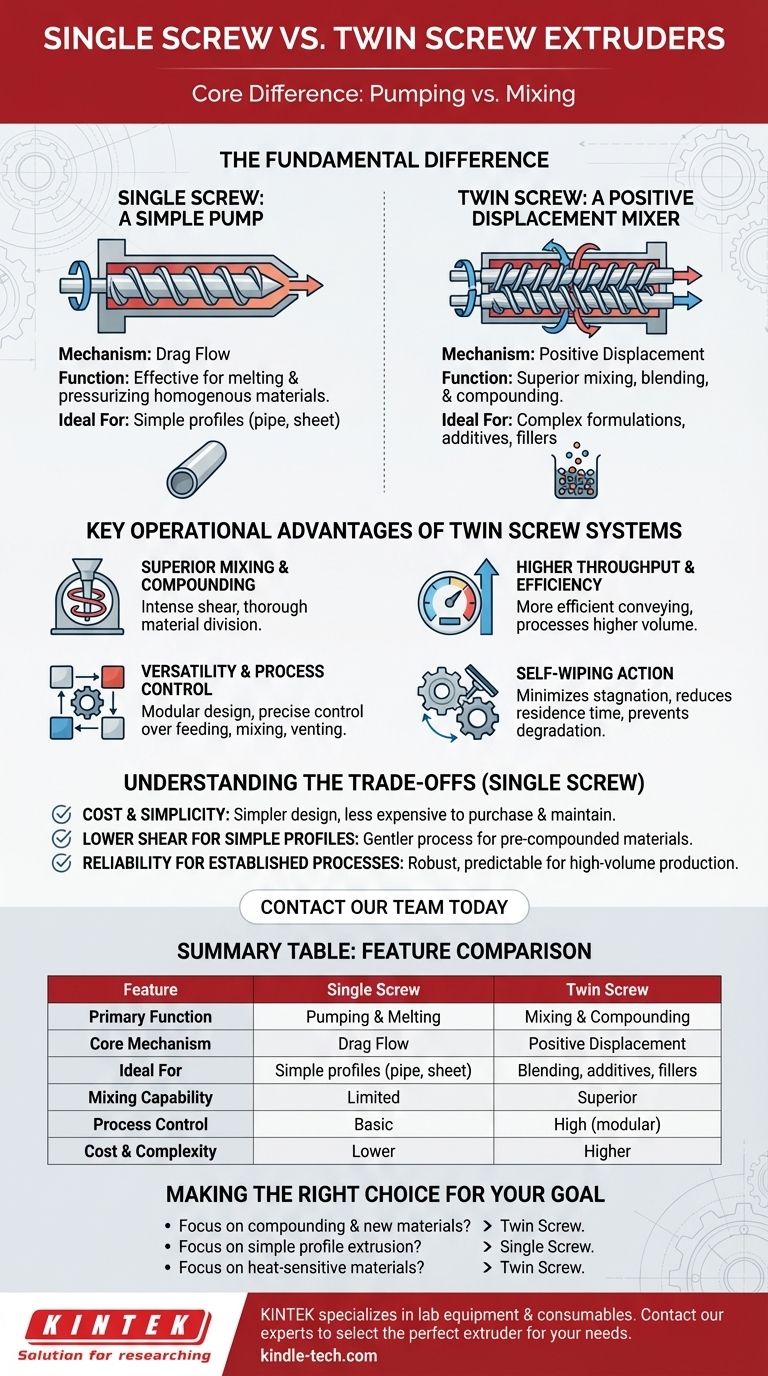
At its core, the difference between a single screw and a twin screw extruder lies in the number of screws used to process material. A single screw extruder uses one screw rotating within a barrel, while a twin screw extruder uses two intermeshing screws. This seemingly simple design change creates a profound difference in how they function, with the single screw acting primarily as a pump and the twin screw functioning as a highly effective mixer.
The central takeaway is this: single screw extruders are ideal for conveying and melting a single, uniform material. Twin screw extruders are sophisticated compounding machines designed for mixing, blending, and reacting multiple ingredients with a high degree of control.
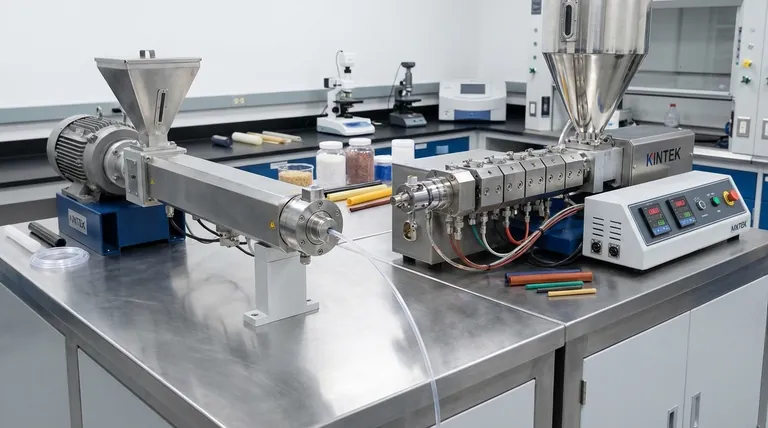

The Fundamental Difference: Pumping vs. Mixing
The mechanism by which material moves through the extruder defines its core capability. The number of screws directly dictates this mechanism.
The Single Screw Extruder: A Simple Pump
A single screw extruder operates on a principle called drag flow. The material is dragged forward by the friction between the polymer, the rotating screw, and the stationary barrel.
This process is effective for melting and pressurizing a homogenous, pre-compounded polymer for applications like pipe, sheet, or profile extrusion. However, its mixing capability is inherently limited.
The Twin Screw Extruder: A Positive Displacement Mixer
A twin screw extruder uses two intermeshing screws that rotate together inside the barrel. This configuration acts like a positive displacement pump, actively conveying the material forward in a controlled manner.
This mechanism is far less dependent on friction and provides superior process control, making it a fundamentally different and more versatile machine.
Key Operational Advantages of Twin Screw Systems
The positive displacement and intermeshing nature of twin screws unlock several critical processing advantages, particularly for complex materials.
Superior Mixing and Compounding
This is the primary advantage. The intricate interaction between the two screws creates intense shear and divides the material, forcing it to be mixed thoroughly and repeatedly.
This makes twin screw extruders essential for compounding—the process of blending polymers with additives, fillers, colorants, or other polymers to create a specialized material.
Higher Throughput and Efficiency
The positive conveying action of twin screws is more efficient than the drag flow of a single screw. This allows them to process a higher volume of material in the same amount of time, leading to increased productivity.
Versatility and Process Control
Twin screw designs are often modular. Different screw elements can be arranged along the shaft to create specific zones for feeding, mixing, venting (removing volatiles), and pressurizing. This gives operators unparalleled control over the entire process.
Self-Wiping Action
The close proximity of the intermeshing screws means they constantly wipe each other clean. This self-wiping feature minimizes material stagnation, reduces residence time, and prevents material degradation, which is critical for heat-sensitive polymers.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Single Screw Still Has a Place
Despite the clear advantages of twin screw systems, single screw extruders remain a vital part of the industry for several important reasons.
Cost and Simplicity
Single screw extruders have a much simpler design. They are significantly less expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain due to fewer complex parts like gearboxes and segmented screws.
Lower Shear for Simple Profiles
For applications that simply require melting and forming a pre-compounded material, the high-intensity mixing of a twin screw is unnecessary and can even be detrimental. A single screw provides a gentler process ideal for creating simple profiles like pipe or sheet.
Reliability for Established Processes
When running a single, high-volume product 24/7, the robust and straightforward nature of a single screw extruder offers exceptional reliability and predictability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct choice depends entirely on your material and your final product objective.
- If your primary focus is compounding, blending, or developing new material formulations: The superior mixing, control, and versatility of a twin screw extruder are non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is extruding a simple profile (pipe, sheet, film) from a single, pre-compounded material: A single screw extruder provides the most cost-effective and reliable solution.
- If your primary focus is processing heat-sensitive materials or materials requiring devolatilization: The controlled residence time and venting capabilities of a twin screw system are a significant advantage.
Choosing the right extruder is a strategic decision about the processing capabilities you require for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Single Screw Extruder | Twin Screw Extruder |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Pumping & Melting | Mixing & Compounding |
| Core Mechanism | Drag Flow | Positive Displacement |
| Ideal For | Simple profiles (pipe, sheet) | Blending polymers, additives, fillers |
| Mixing Capability | Limited | Superior |
| Process Control | Basic | High (modular design) |
| Cost & Complexity | Lower | Higher |
Still unsure which extruder is right for your lab's materials processing needs?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect extruder—whether a simple single screw for reliable melting or a sophisticated twin screw for advanced compounding—to enhance your R&D and production efficiency.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover the KINTEK advantage!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Cutting Tools for Carbon Paper Cloth Diaphragm Copper Aluminum Foil and More
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Precision Wire Saw Laboratory Cutting Machine with 800mm x 800mm Workbench for Diamond Single Wire Circular Small Cutting
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of diamond cutting tool material? Achieve Superior Precision and Productivity
- What industrial uses are there for diamonds? Unlock High-Performance Applications
- What are the specific uses of a precision disc cutter in the assembly of solid-state batteries? Ensure Burr-Free Accuracy
- How should carbon paper be handled during cutting? Prevent Fractures with a Delicate, Precise Approach
- What is a substitute for tungsten carbide? Explore Advanced Materials for Superior Performance



















