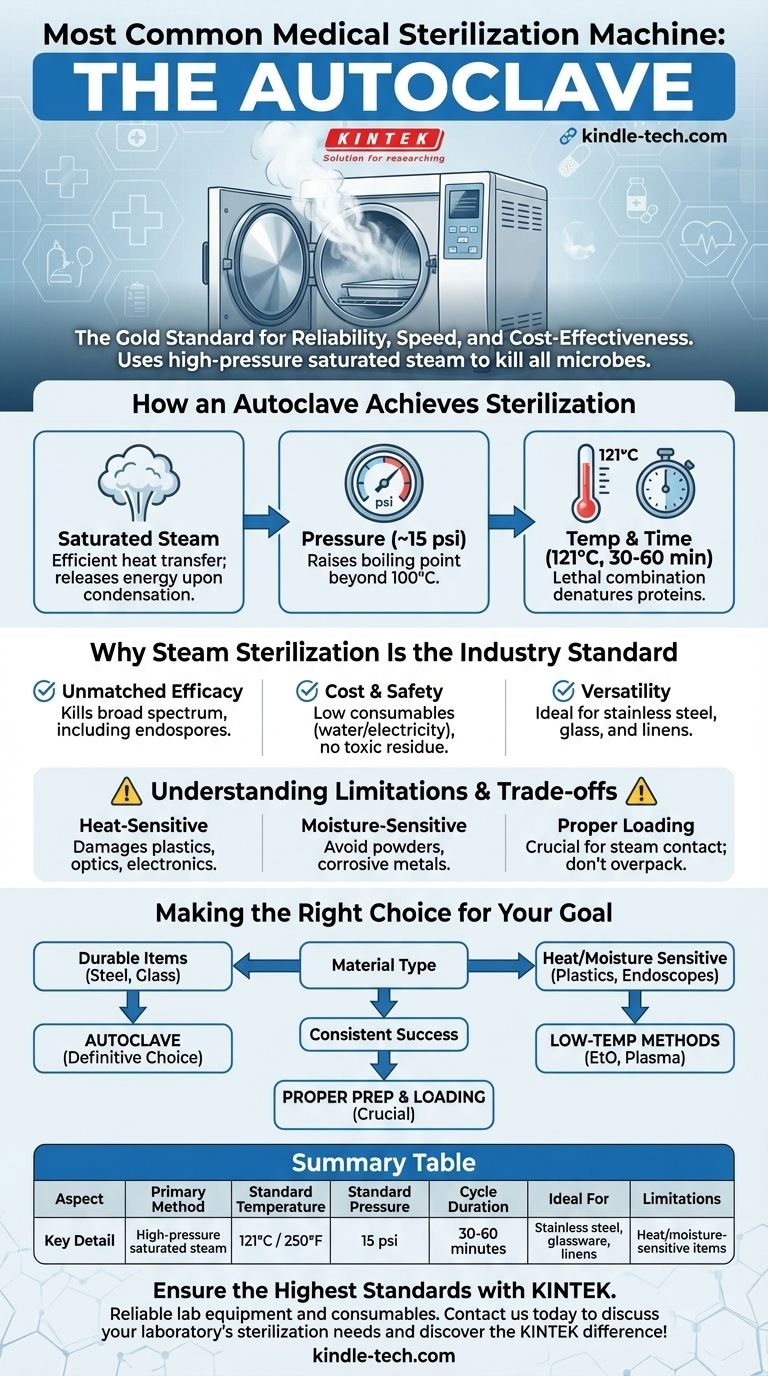
By far, the most common machine used to sterilize medical supplies is the autoclave. It is the gold standard in healthcare settings, from hospitals to dental offices, for its reliability, speed, and cost-effectiveness. This device uses high-pressure, saturated steam to eliminate all forms of microbial life, including resilient bacteria, viruses, and spores.
The autoclave's dominance is not due to complexity, but to its mastery of basic physics. By using pressurized steam to transfer heat, it provides a far more rapid and effective method of killing microorganisms than any form of dry heat, making it the workhorse of medical sterilization.

How an Autoclave Achieves Sterilization
The autoclave's effectiveness lies in its precise manipulation of steam, pressure, and temperature. It doesn't simply heat items; it forces lethal heat into every crack and crevice.
The Critical Role of Saturated Steam
The true agent of sterilization is saturated steam, not just hot air. Steam is a highly efficient carrier of thermal energy.
When this steam makes contact with a cooler item (like a surgical instrument), it immediately condenses back into water, releasing its stored energy and rapidly heating the instrument's surface.
The Function of Pressure
An autoclave operates at a pressure significantly above normal atmospheric pressure, typically around 15 psi.
The primary purpose of this pressure is to increase the boiling point of water. This allows the steam inside the chamber to reach temperatures far beyond 100°C (212°F), which is necessary for effective sterilization.
Temperature and Time: The Lethal Combination
With the aid of pressure, the steam reaches a standard sterilizing temperature of 121°C (250°F).
This intense heat is maintained for a specific duration, usually between 30 and 60 minutes, depending on the size and contents of the load. This combination of extreme heat and sustained exposure is what effectively denatures the proteins and enzymes essential for a microorganism's survival.
Why Steam Sterilization Is the Industry Standard
While other sterilization methods exist, the autoclave remains the default choice for several key reasons.
Unmatched Efficacy
Steam sterilization is incredibly effective. It reliably kills a broad spectrum of microorganisms, including the toughest bacterial endospores, which are highly resistant to other forms of disinfection.
Cost-Effectiveness and Safety
The primary consumables for an autoclave are water and electricity, making it an exceptionally low-cost method for daily operations.
Furthermore, the process leaves no toxic residue, unlike some chemical sterilization methods, making it safer for both patients and healthcare workers.
Versatility for Common Materials
Autoclaves are ideal for sterilizing the majority of items used in medical procedures. This includes stainless steel surgical instruments, reusable glassware, and heat-resistant linens and textiles.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Despite its dominance, steam sterilization is not a universal solution. Its primary limitations are tied directly to its method of action: heat and moisture.
Heat-Sensitive Materials Cannot Be Autoclaved
The intense heat will destroy or damage many common medical materials. This includes most plastics, fiber optics, and delicate electronic devices like endoscopes or power drills.
Moisture Can Damage Certain Items
Items that are sensitive to moisture cannot be processed in an autoclave. This includes powders, certain metals prone to corrosion, or items that cannot be dried effectively after the cycle.
Proper Loading is Non-Negotiable
The effectiveness of an autoclave cycle is entirely dependent on steam contacting every single surface. Overpacking the chamber or using improper wrapping can create air pockets that insulate items from the steam, leading to a failed sterilization cycle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sterilization method is critical for patient safety and equipment longevity. The material of the item is the single most important factor in this decision.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing durable, heat-resistant items: The autoclave is the definitive and most efficient choice for materials like stainless steel, glass, or autoclavable fabrics.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat or moisture-sensitive devices: You must use an alternative "low-temperature" method, such as Ethylene Oxide (EtO) gas or hydrogen peroxide plasma sterilization.
- If your primary focus is ensuring successful sterilization every time: Remember that proper cleaning, packaging, and loading of the autoclave are just as crucial as the machine's parameters.
Mastering the principles of steam sterilization is fundamental to ensuring the integrity of medical instruments and the safety of every patient.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Method | High-pressure saturated steam |
| Standard Temperature | 121°C (250°F) |
| Standard Pressure | 15 psi |
| Cycle Duration | 30-60 minutes |
| Ideal For | Stainless steel instruments, glassware, linens |
| Limitations | Heat/moisture-sensitive items (plastics, electronics) |
Ensure the highest standards of sterilization in your laboratory.
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables to meet the demanding needs of healthcare and research facilities. Whether you are setting up a new sterilization protocol or need to upgrade your existing autoclave, our experts are here to help you select the right equipment for safety, efficiency, and compliance.
Contact us today to discuss your laboratory's sterilization needs and discover the KINTEK difference!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How is an autoclave utilized in antimicrobial experiments? Ensure Precise Nanoparticle Research Integrity
- How does an autoclave ensure the reliability of experimental results? Achieving a Sterile Baseline for Lab Research
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise
- How should solid materials in bags be prepared for decontamination? Master Steam Penetration for Safe Sterilization
- Why is a 24-hour hydrothermal treatment in an autoclave necessary for BMO nanosheets? Unlock Superior Photocatalysis



















