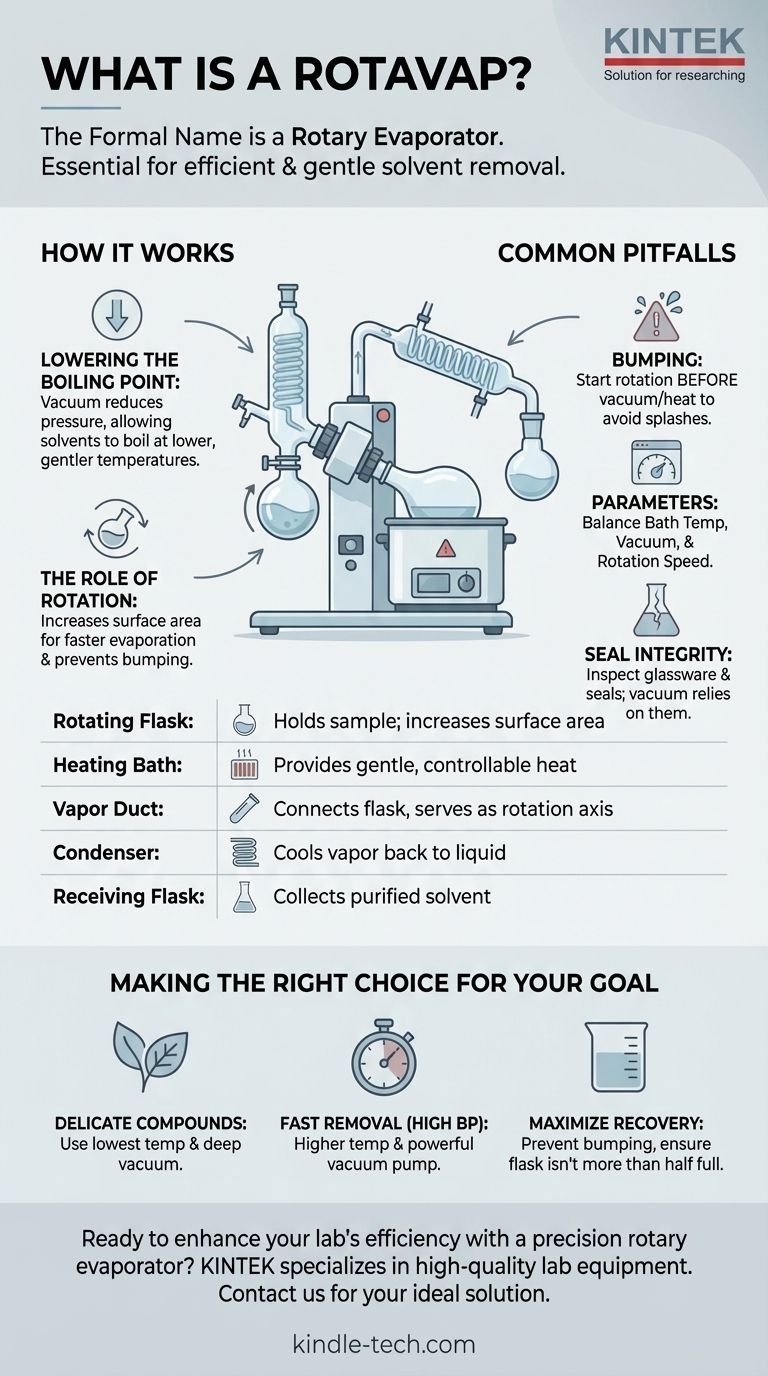
The formal name for the equipment commonly known as a 'rotovap' is a rotary evaporator. This device is a standard and essential piece of equipment in chemistry laboratories worldwide. It is specifically designed for the efficient and gentle removal of solvents from samples through evaporation.
A rotary evaporator is not simply a heater; it is a precision system that removes solvents by reducing pressure to lower their boiling point, while rotation simultaneously increases the sample's surface area for rapid and controlled evaporation.
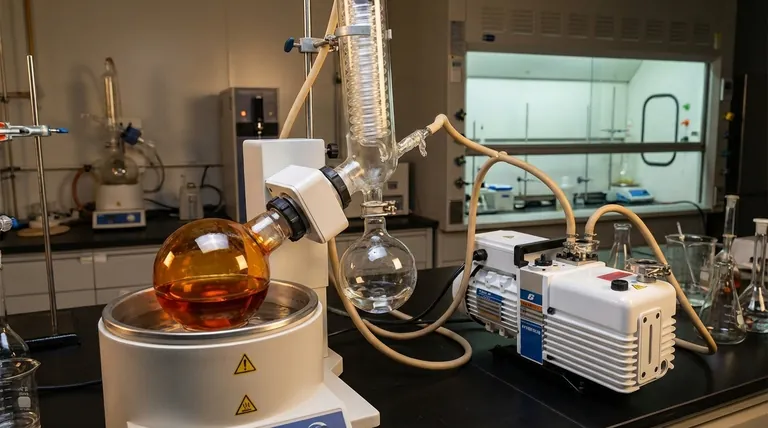

How a Rotary Evaporator Actually Works
To understand the value of a rotary evaporator, you must first understand the principles that make it far more effective than simply boiling a solvent away. It combines several physical principles into one elegant process.
The Core Principle: Lowering the Boiling Point
The fundamental concept is the relationship between pressure and a liquid's boiling point. Most people think of water boiling at 100°C (212°F), but that is only true at standard sea-level atmospheric pressure.
By connecting the rotovap to a vacuum system, the pressure inside the glassware is significantly reduced. This drop in pressure allows solvents to boil at much lower, gentler temperatures, often even at room temperature.
This is crucial for protecting heat-sensitive compounds that would be destroyed or degraded by the high temperatures required for boiling at normal atmospheric pressure.
The Role of Rotation
The rotation of the sample flask is what gives the instrument its name, and it serves two critical purposes.
First, it constantly spreads the sample into a thin film on the inner surface of the flask. This dramatically increases the surface area available for evaporation, making the process much faster and more efficient.
Second, the constant agitation prevents bumping—the sudden, violent boiling that can splash your sample out of the flask and lead to significant loss. Rotation ensures smooth, even evaporation.
The Key Components and Their Functions
A complete rotary evaporator system consists of several integrated parts:
- Rotating Flask: A round-bottom flask containing your sample (the solute dissolved in a solvent). It is angled and lowered into the heating bath.
- Heating Bath: A container of water or oil that provides gentle, uniform, and controllable heat to the rotating flask.
- Vapor Duct: The glass pathway that connects the rotating flask to the condenser and serves as the axis for rotation.
- Condenser: A coil of glass with a coolant (usually cold tap water or a chiller fluid) circulating through it. As the solvent vapor rises, it hits the cold surface of the condenser and turns back into a liquid.
- Receiving Flask: A flask at the bottom of the condenser that collects the purified, re-condensed solvent.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While powerful, a rotary evaporator is not a "set and forget" device. Proper operation requires attention to detail to ensure safety and effectiveness.
The Danger of "Bumping"
Even with rotation, a sample can bump if the vacuum is applied too quickly or the temperature difference is too great. This results in the loss of valuable product into the condenser and receiving flask.
Always start the rotation before applying the vacuum or heat to minimize this risk.
Setting the Right Parameters
Achieving efficient evaporation is a balancing act between three variables: bath temperature, vacuum pressure, and rotation speed. There is no single setting for all applications.
The goal is to find a rate of evaporation where the solvent condenses efficiently without overwhelming the system or causing bumping. A common rule of thumb is to set the bath temperature 20°C higher than the boiling point of the solvent at the target pressure.
Glassware and Seal Integrity
The entire system relies on maintaining a vacuum. Any cracks in the glassware or worn-out seals will cause leaks, preventing the system from reaching the necessary low pressure.
Always inspect glassware for star cracks before use and ensure all seals and joints are clean and properly greased (if necessary) to ensure a perfect seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific goal will dictate how you operate the rotary evaporator.
- If your primary focus is protecting a delicate, heat-sensitive compound: Use the lowest possible bath temperature and achieve a deeper vacuum to compensate.
- If your primary focus is quickly removing a high-boiling-point solvent (like water or DMF): You will need a higher bath temperature and a more powerful vacuum pump to lower the boiling point sufficiently.
- If your primary focus is maximizing sample recovery for analysis: Be extremely vigilant about preventing bumping by gradually increasing temperature and vacuum, and ensure your flask isn't more than half full.
Understanding these core principles transforms the rotary evaporator from a piece of machinery into a precision tool under your complete control.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Rotating Flask | Holds the sample; rotation increases surface area for evaporation. |
| Heating Bath | Provides gentle, controllable heat to the flask. |
| Vacuum System | Lowers pressure to reduce the solvent's boiling point. |
| Condenser | Cools solvent vapor, turning it back into liquid for collection. |
| Receiving Flask | Collects the purified, condensed solvent. |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with a precision rotary evaporator? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including reliable rotary evaporators designed for safe and effective solvent removal. Our experts can help you select the perfect system for your specific application, ensuring you get the performance and durability your laboratory needs. Contact us today to find your ideal solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- 30T 40T Split Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What are the common configurations and typical performance specifications of Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps? Expert Guide
- Why is a gas ballast valve necessary on a rotary vane vacuum pump? Protect Your Oil and Extend Pump Life
- How do you inspect a vacuum pump? A Step-by-Step Guide to Ensure Peak Performance
- Why is a rotary vane mechanical vacuum pump necessary for sub-surface etching? Ensure Precision in ALD/ALE Experiments
- What are the advantages of rotary vane pumps? Unlock Cost-Effective, High-Performance Vacuum



















