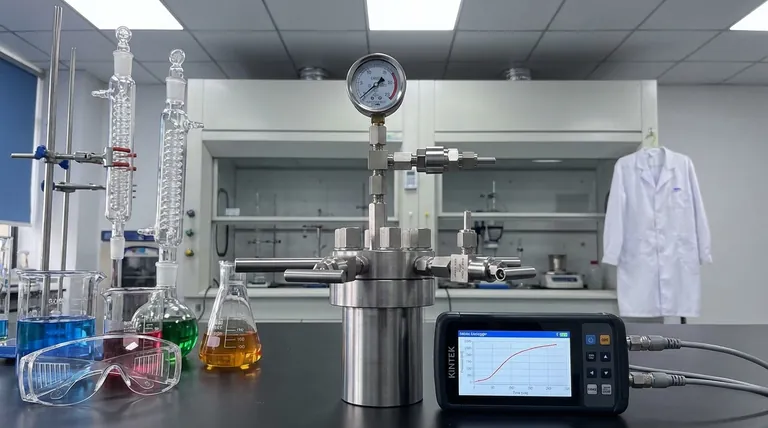
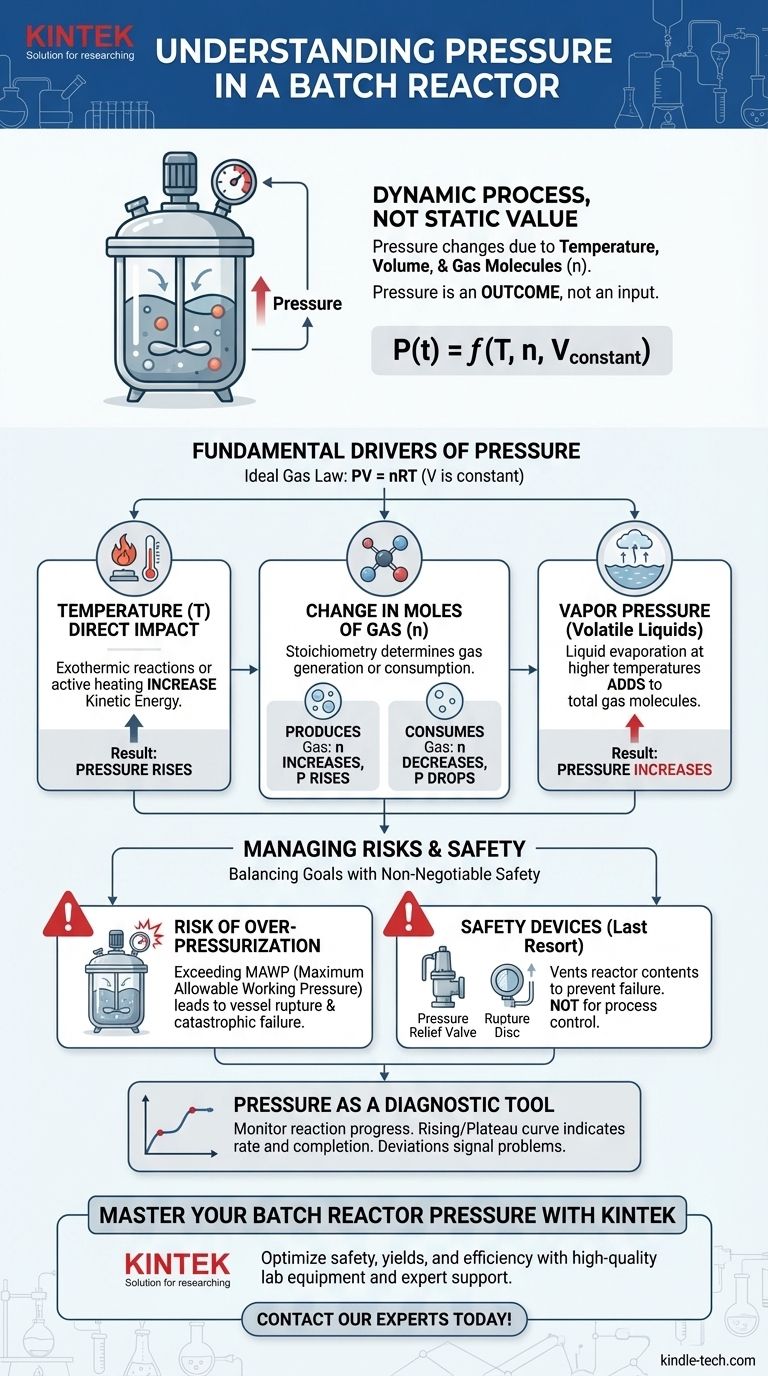
In a batch reactor, pressure is not a static value. It is a dynamic process variable that changes over the course of a reaction, driven by the interplay between temperature, the volume of the vessel, and the number of gas molecules present. Understanding these drivers is fundamental to designing, operating, and ensuring the safety of any batch process.
The central takeaway is this: Pressure is an outcome, not an independent input. It is the direct result of the chemical and physical changes occurring within the fixed volume of your reactor, making its management essential for both process safety and efficiency.

The Fundamental Drivers of Pressure
To control the pressure within a batch reactor, you must first understand the core principles that govern it. The behavior of gases in the reactor's headspace is the primary determinant.
The Ideal Gas Law as a Foundation
The relationship between pressure (P), volume (V), moles of gas (n), and temperature (T) is best described by the Ideal Gas Law: PV = nRT.
Because a batch reactor is a sealed vessel, its volume (V) is constant. This simple fact has a profound consequence: any change in the temperature (T) or the number of moles of gas (n) must result in a change in pressure (P).
Temperature's Direct Impact
As the temperature inside the reactor increases, gas molecules gain kinetic energy and move faster, colliding with the vessel walls more forcefully and frequently.
This means that if a reaction is exothermic (releases heat) or if you are actively heating the reactor, the pressure will rise, even if the number of gas molecules remains the same.
The Change in Moles of Gas (n)
The chemistry of your reaction is a critical factor. You must analyze the stoichiometry to see if the reaction generates or consumes gas.
If a reaction produces more moles of gas than it consumes (e.g., A(liquid) → B(gas) + C(gas)), the total number of gas molecules (n) increases, causing the pressure to rise.
Conversely, if a reaction consumes gas (e.g., A(gas) + B(gas) → C(liquid)), the value of 'n' decreases, and the pressure will drop.
The Role of Vapor Pressure
Never forget the contribution of volatile liquids. Any liquid in your reactor (solvents, reactants, or products) will exert a vapor pressure that is highly dependent on temperature.
As you heat the reactor, more of the liquid will evaporate into the headspace, adding to the total number of gas molecules and thus increasing the total pressure. In some low-temperature processes involving volatile solvents, vapor pressure can be the dominant contributor.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Managing reactor pressure is a balance between operational goals and non-negotiable safety requirements. Misunderstanding this balance can have severe consequences.
The Risk of Over-pressurization
This is the most critical safety concern. Every reactor is rated for a Maximum Allowable Working Pressure (MAWP).
If the pressure from a runaway exothermic reaction or unexpected gas generation exceeds the MAWP, the vessel can rupture. This is a catastrophic failure that can lead to explosions and the release of hazardous materials.
The Function of Safety Devices
Because of this risk, batch reactors are equipped with safety systems like pressure relief valves and rupture discs.
These are not process control devices; they are last-resort safety mechanisms designed to vent the reactor's contents and prevent a catastrophic failure if all other controls fail.
Using Pressure as a Diagnostic Tool
While a risk, pressure is also an invaluable source of information. By tracking the pressure profile over time, you can monitor the reaction's progress.
A pressure curve that rises and then plateaus can indicate the reaction rate and its completion. A deviation from the expected pressure profile can signal a problem, such as a side reaction or a cooling system failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to reactor pressure depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is safety: You must calculate the maximum potential pressure under worst-case failure scenarios (like a total loss of cooling) and ensure it is safely below your vessel's MAWP.
- If your primary focus is process monitoring and optimization: Treat the pressure-time profile as a key performance indicator to determine reaction endpoints, identify deviations, and optimize batch cycle times.
- If your primary focus is reaction design: You must first analyze the stoichiometry to determine if the reaction is net gas-generating or gas-consuming, as this will fundamentally shape your equipment and safety system requirements.
By treating pressure not as a simple setting but as a dynamic result of chemistry and thermodynamics, you gain precise control over your process's safety, efficiency, and outcome.
Summary Table:
| Driver | Effect on Pressure | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Increase | Increases | Critical for exothermic reactions or heating phases. |
| Gas-Generating Reaction | Increases | Must analyze reaction stoichiometry for safety. |
| Gas-Consuming Reaction | Decreases | Can lead to under-pressure if not managed. |
| Vapor Pressure (Volatile Liquids) | Increases | Often the dominant pressure source at higher temperatures. |
Master the dynamics of your batch reactor pressure with KINTEK.
Understanding and controlling pressure is not just about safety—it's about optimizing your entire process for better yields and efficiency. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing the reactors and expert support you need to design and run safe, effective batch processes.
Let's enhance your lab's capabilities together. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific reactor requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of a high-pressure reactor in SFE? Optimize Hesperidin Extraction with Precision Control
- Why must high-grade corrosion-resistant reaction vessels be used during the strong acid pretreatment of biomass?
- What role does a high-pressure autoclave play in NiFe oxide synthesis? Optimize Your Catalytic Efficiency
- What role does a high-pressure hydrothermal reactor play in material synthesis? Engineering Mesoporous Nanomaterials
- What is the function of high-pressure reactors in MOF synthesis? Unlock High-Quality Crystalline Structures
- Why are high-pressure stainless steel reactors required for PE pre-treatment? Ensure Safe & Effective Acidic Oxidation
- What role does a high-temperature reactor perform in pyrohydrolysis? Transform Waste into Pure Acid & Oxides
- How does a fluidized bed reactor work? Achieve Rapid, Uniform Heat Transfer



















