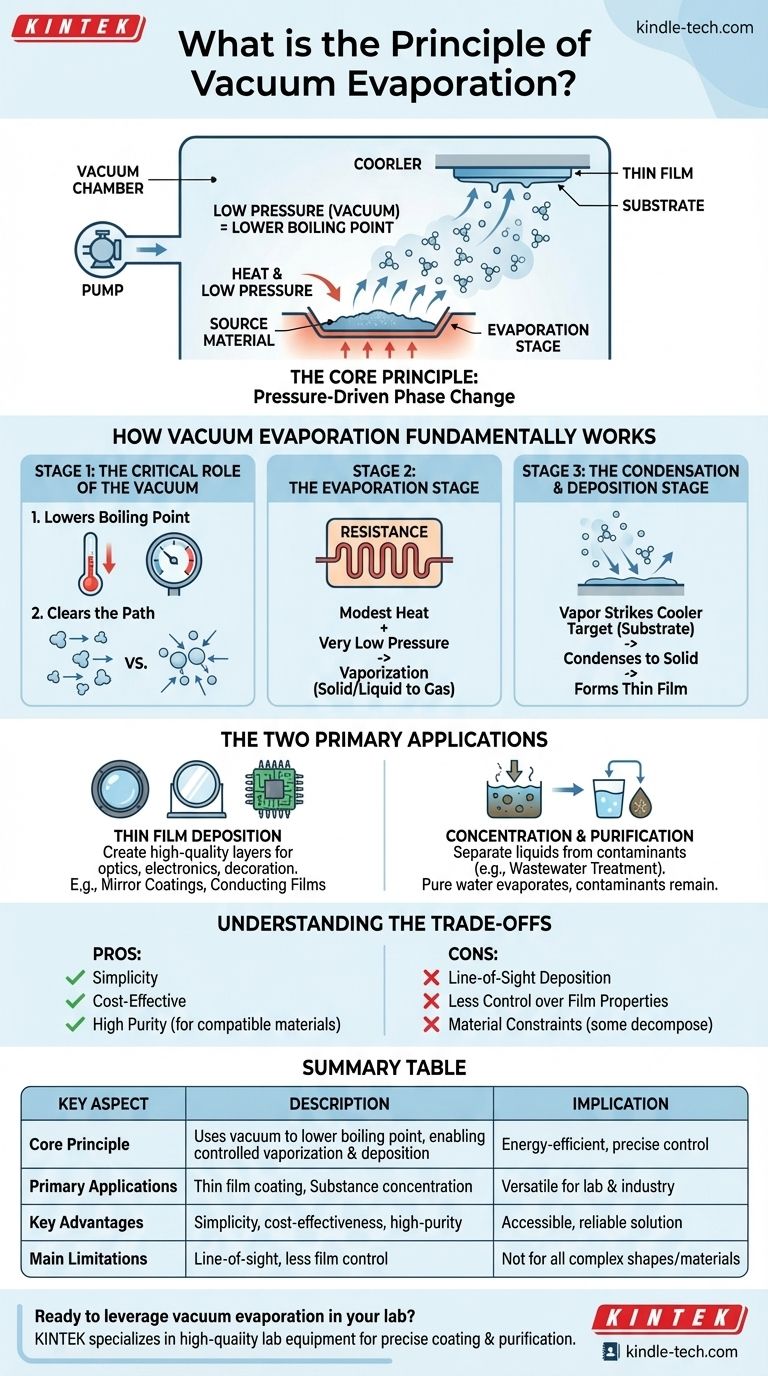
At its core, vacuum evaporation is a process that uses a vacuum to dramatically lower the boiling point of a material, causing it to turn from a solid or liquid into a vapor. This vapor then travels unimpeded through the vacuum chamber and condenses onto a cooler target surface. This fundamental technique is a type of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) used for everything from applying mirror coatings to concentrating chemical solutions.
The central principle of vacuum evaporation is not about using extreme heat, but about manipulating pressure. By creating a vacuum, we make it significantly easier for materials to vaporize, enabling their controlled transfer and deposition onto a target or their separation from a mixture.
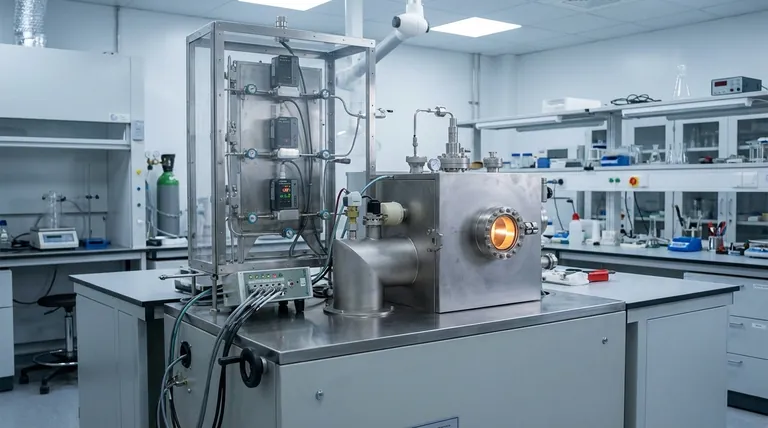

How Vacuum Evaporation Fundamentally Works
The entire process is a three-stage physical transformation orchestrated inside a vacuum chamber. Each stage is critical to the final outcome.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
The vacuum environment serves two distinct and vital purposes.
First, it lowers the boiling point of the source material. Just as water boils at a lower temperature on a high mountain, all materials evaporate more easily when the pressure around them is reduced. This allows for vaporization without needing temperatures that might damage the material itself.
Second, it clears the path for the vaporized atoms. By removing air and other gas molecules, the vacuum ensures that the evaporated material can travel directly to the substrate in a straight line without collisions, which is essential for forming a clean, high-purity film.
The Evaporation Stage
With the vacuum established, the source material is heated. A common method is resistance evaporation, where an electric current is passed through a holder (often called a "boat") containing the material, causing it to heat up.
The combination of this modest heat and the very low pressure causes the material to change phase, either boiling (liquid to gas) or sublimating (solid to gas), releasing a vapor of atoms or molecules.
The Condensation and Deposition Stage
This vapor travels through the chamber until it strikes a cooler surface, which is intentionally placed as the target. This target is known as the substrate.
Upon contact, the vaporized atoms rapidly cool, lose their energy, and condense back into a solid state, forming a thin, uniform film on the substrate's surface.
The Two Primary Applications
While the principle remains the same, vacuum evaporation is used to achieve two very different goals: coating a surface or separating substances.
Thin Film Deposition
This is the most common application, used to create high-quality layers for technical and decorative purposes. The goal is to build a new layer on top of the substrate.
Applications include optical interference coatings on lenses, reflective mirror coatings, and electrically conducting films for electronics. When used to deposit metals like aluminum, the process is often called vacuum metallization. By using multiple sources simultaneously, complex alloys and composite films can be created.
Concentration and Purification
In this context, the goal is not to coat a substrate but to separate a liquid from dissolved contaminants. This is a highly effective method for wastewater treatment.
Here, the contaminated water is heated in the vacuum, causing the pure water to evaporate easily, leaving the contaminants (which have much higher boiling points) behind. The pure water vapor is then condensed and collected elsewhere, significantly reducing the volume of waste.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum evaporation is not a universal solution. It's essential to understand its inherent limitations.
Simplicity vs. Control
Vacuum evaporation is one of the simplest and most cost-effective PVD processes. However, this simplicity comes at the cost of control. It offers less influence over film properties like density and adhesion compared to more advanced techniques like sputtering.
Line-of-Sight Deposition
The vaporized atoms travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This means the process has poor "throw," making it very difficult to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes without sophisticated rotating fixtures.
Material Constraints
The process relies on heating a material to its evaporation point. Some complex compounds can decompose or break apart when heated, making them unsuitable for this method. Others require extremely high temperatures that are impractical to achieve.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Applying this principle effectively depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is creating simple, high-purity coatings: Vacuum evaporation is a cost-effective and reliable method, especially for optical, decorative, or basic metallic layers.
- If your primary focus is wastewater reduction or substance concentration: The process offers an energy-efficient way to separate liquids from dissolved solids without the need for additional chemicals.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, durable films for high-stress applications: You should consider more advanced PVD techniques like sputtering, which provide greater control over the final film structure and properties.
Ultimately, understanding this core principle of pressure-driven phase change is the key to leveraging vacuum evaporation for both industrial-scale purification and nanoscale engineering.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Uses vacuum to lower boiling point, enabling controlled vaporization and deposition. |
| Primary Applications | Thin film coating (e.g., optics, electronics) and substance concentration (e.g., wastewater treatment). |
| Key Advantages | Simplicity, cost-effectiveness, high-purity results for compatible materials. |
| Main Limitations | Line-of-sight deposition, less control over film properties compared to advanced PVD methods. |
Ready to leverage vacuum evaporation in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including vacuum evaporation systems tailored for precise coating and purification tasks. Our solutions help you achieve superior thin films and efficient substance separation with reliability and ease. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained



















