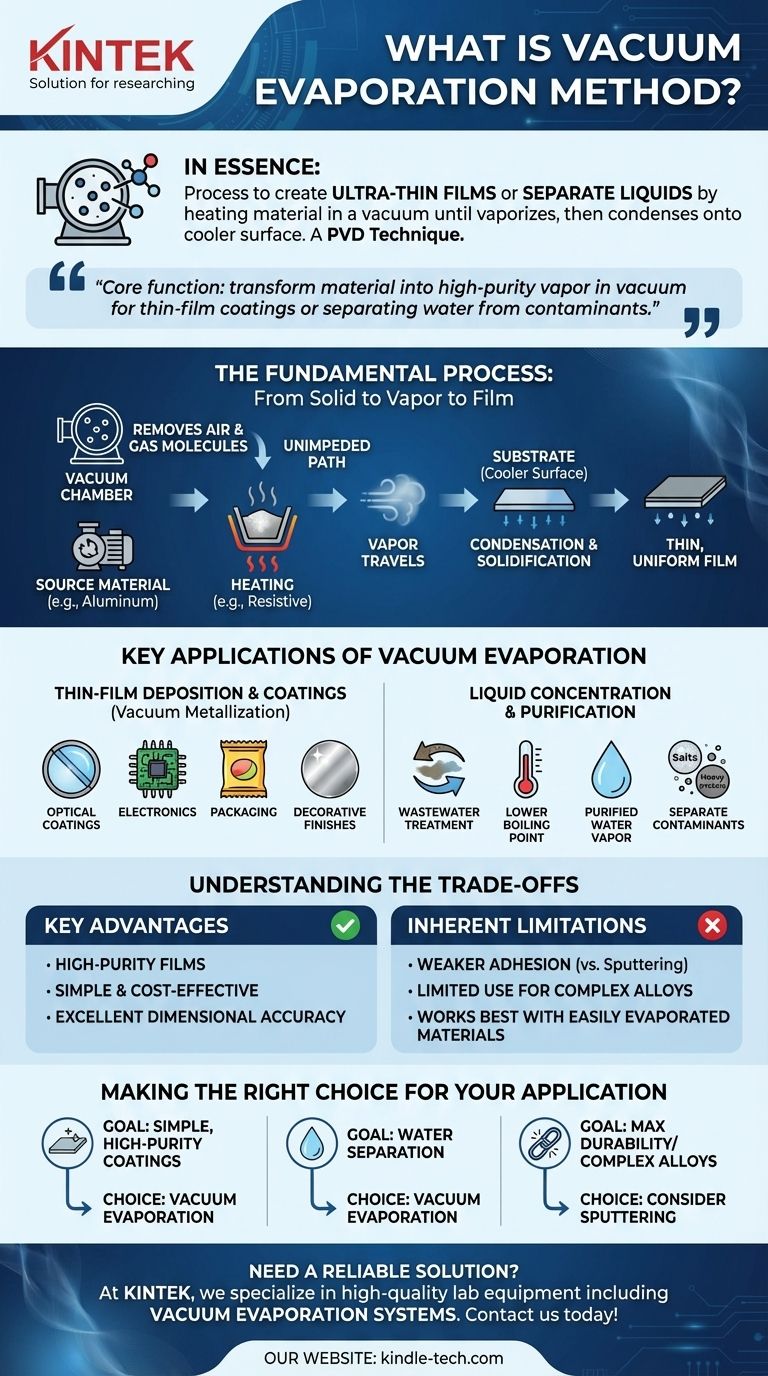
In essence, the vacuum evaporation method is a process used to create ultra-thin films or to separate liquids by heating a material in a vacuum until it turns into a vapor. This vapor then travels unimpeded and condenses onto a cooler surface, forming a solid coating or leaving behind a concentrated solution. It is a foundational technique in the family of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) processes.
The core function of vacuum evaporation is to transform a material into a high-purity vapor within a vacuum. This allows it to be used for two distinct purposes: depositing precise, thin-film coatings onto a surface or efficiently separating water from contaminants.

The Fundamental Process: From Solid to Vapor to Film
Vacuum evaporation operates on a simple, elegant principle, closely resembling how steam from a boiling kettle condenses on a cold window. The process, however, is executed with atomic-level precision inside a highly controlled vacuum chamber.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
The entire process takes place in a vacuum chamber, which is pumped down to remove almost all air and other gas molecules. This vacuum is essential because it provides a clear, unobstructed path for the vaporized material to travel from its source to the target.
Without a vacuum, the vaporized atoms would collide with air molecules, scattering them and preventing a uniform, pure film from forming on the substrate.
Heating the Source Material
The source material—the substance to be deposited, such as aluminum or a specific optical compound—is placed inside the chamber. It is then heated using methods like resistive heating, where an electrical current passes through it.
This energy input causes the material's atoms or molecules to gain enough energy to break their bonds and transition directly into a gaseous or vapor phase.
Condensation on the Substrate
This vapor travels through the vacuum and eventually reaches the substrate—the object to be coated, which is kept at a cooler temperature. Upon contact with this cooler surface, the vapor rapidly loses its energy, condenses, and solidifies back into a thin, uniform film.
Key Applications of Vacuum Evaporation
The versatility of this principle allows it to be applied in fields that seem unrelated, from high-tech optics to industrial wastewater treatment.
Thin-Film Deposition and Coatings
This is the most common application. By carefully selecting the source material, vacuum evaporation can create highly functional layers for a variety of purposes.
When used to deposit metals like aluminum, it is often called vacuum metallization. Key applications include:
- Optical Coatings: Creating anti-reflection layers on lenses or highly reflective mirror coatings.
- Electronics: Forming electrically conductive films for circuits and components.
- Packaging: Applying permeation barrier films on flexible packaging to protect food and medicine.
- Decorative Finishes: Producing shiny, metallic coatings on plastics and other materials.
Liquid Concentration and Purification
The same principle can be used to separate substances with different boiling points. In wastewater treatment, a vacuum is used to lower the boiling point of water.
The contaminated water is heated, causing the pure water to evaporate while leaving behind contaminants with higher boiling points (like salts, heavy metals, and oils). The purified water vapor is then condensed and collected separately.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, vacuum evaporation is one of several deposition techniques, and its selection depends on specific project requirements. It is known for its simplicity and quality but has inherent limitations.
Key Advantages
The primary benefit is its ability to produce very high-purity films because the process is so clean and direct. It offers excellent dimensional accuracy and is a relatively simple and well-understood PVD method, making it cost-effective for many applications.
Inherent Limitations
Compared to more energetic PVD methods like sputtering, films created by vacuum evaporation can sometimes have weaker adhesion to the substrate. The process also works best with materials that can be easily evaporated, which can limit its use for complex alloys or high-temperature ceramics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right manufacturing or treatment process requires aligning the method's strengths with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is creating simple, high-purity metallic or optical coatings: Vacuum evaporation is an excellent, cost-effective, and highly reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is separating water from non-volatile contaminants: Vacuum evaporation provides an energy-efficient method for purification and concentration.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex alloy or requires maximum film durability: You may need to compare vacuum evaporation with other PVD methods like sputtering to ensure the best adhesion.
Ultimately, vacuum evaporation is a foundational and powerful technique for manipulating materials at the atomic level to achieve a specific functional outcome.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Creates thin films or separates liquids by vaporizing a material in a vacuum. |
| Core Principle | Material is heated to vapor, travels unimpeded in a vacuum, and condenses on a cooler surface. |
| Main Applications | Thin-film deposition for electronics/optics, liquid purification (e.g., wastewater treatment). |
| Key Advantage | Produces high-purity films; simple and cost-effective for many applications. |
| Main Limitation | Films can have weaker adhesion compared to other methods like sputtering. |
Need a reliable solution for your thin-film or purification challenges?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment, including vacuum evaporation systems tailored for research and industrial applications. Whether you are developing advanced optical coatings, electronic components, or require efficient purification processes, our expertise ensures you get the precision and performance your laboratory needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your project's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a magnetron sputtering work? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- What is liquid phase sintering and how is it different from solid state sintering? A Guide to Faster, Denser Materials
- What is the role of the hydraulic system in hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Material Density and Strength



















