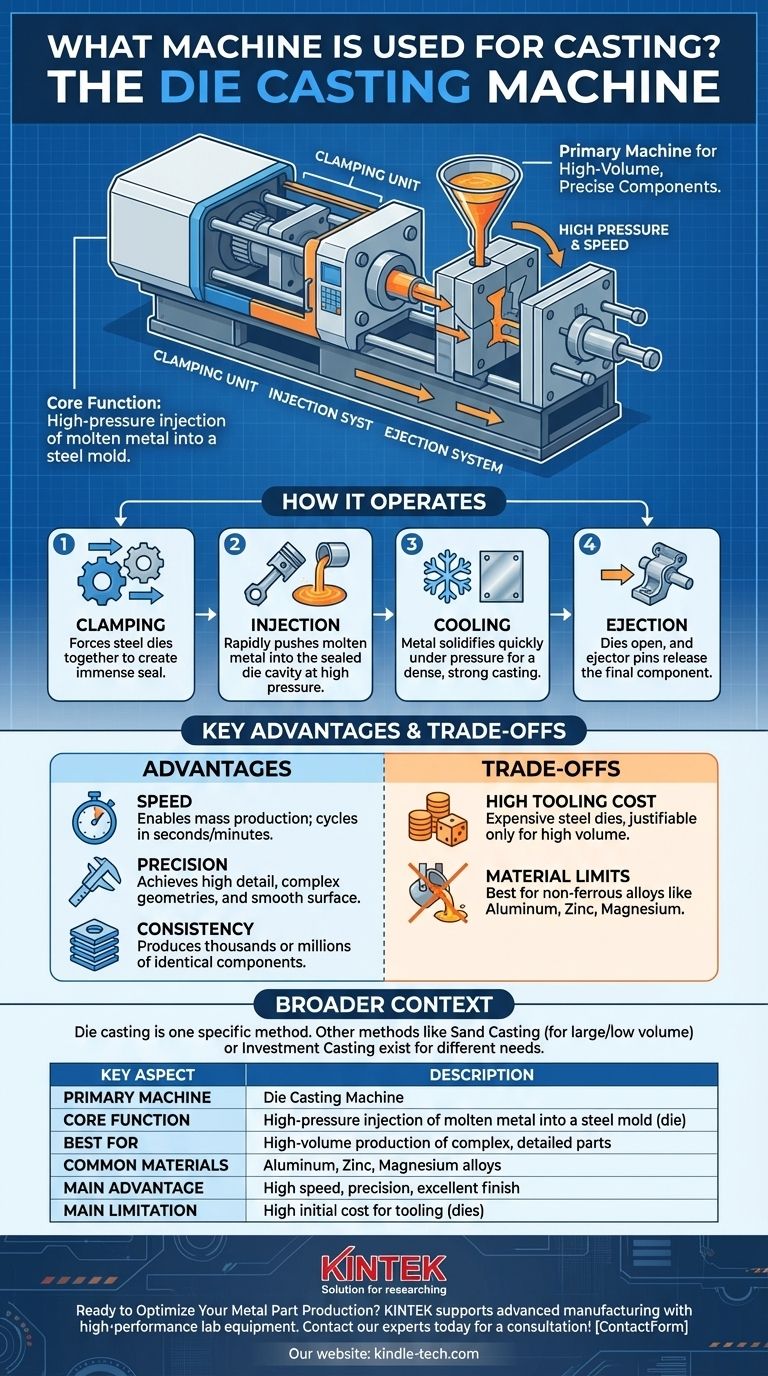
The primary machine used for a specific, high-volume type of casting is the die casting machine. This equipment operates by using a pneumatic or hydraulic system to inject molten metal into a steel mold, known as a die, under extremely high pressure and speed. The metal then solidifies within the mold cavity, forming a precise and highly detailed component.
While "casting" is a broad manufacturing category with many methods, the high-pressure machine you are asking about is a die casting machine. Its core function is to produce highly detailed, consistent metal parts at great speed by forcing liquid metal into a hardened steel mold.

How a Die Casting Machine Operates
A die casting machine executes a precise, rapid, and repeatable cycle to turn molten metal into a finished part. The process is defined by its use of high pressure at nearly every stage.
The Clamping Unit
Before any metal is injected, the machine's powerful clamping unit forces the two halves of the steel die together. This creates an immense seal, necessary to contain the high-pressure injection that follows and to ensure the final part's dimensional accuracy.
The Injection System
This is the heart of the machine. A hydraulic or pneumatic actuator rapidly pushes a plunger forward, forcing a "shot" of molten metal from a chamber into the sealed die cavity. This injection occurs at extremely high speeds and pressures, ensuring the liquid metal fills every intricate detail of the mold.
Cooling and Ejection
The molten metal cools and solidifies very quickly while still held under pressure inside the die. Maintaining pressure during this phase prevents shrinkage porosity and results in a denser, stronger casting. Once solid, the machine's clamping unit opens the die, and an ejector pin mechanism pushes the finished casting out.
The Purpose of a Die Casting Machine
Die casting is not used for all types of metal forming. It is a specialized process chosen for its unique advantages in speed and precision for high-volume production.
Achieving High Precision and a Smooth Finish
The immense pressure used in die casting forces the metal into every microscopic feature of the mold. This results in parts with exceptionally fine detail, complex geometries, and a very smooth surface finish, often requiring little to no secondary machining.
Enabling Mass Production
The entire die casting cycle—from closing the mold to ejecting the part—can take just a few seconds to a couple of minutes, depending on the part's size. This incredible speed makes it the go-to process for manufacturing thousands or millions of identical components efficiently.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the die casting process has specific limitations and is not the right choice for every application. Understanding these trade-offs is critical for making an informed manufacturing decision.
High Initial Tooling Cost
The steel dies used in these machines are complex, hardened tools that must withstand immense pressure and thermal shock. Their design and fabrication are extremely expensive, often costing tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars. This high upfront investment is only justifiable for high-volume production runs.
Limitations on Materials
The process is primarily suited for non-ferrous alloys with relatively low melting points, such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. Casting high-temperature metals like steel or iron is generally not feasible with this method due to the extreme toll it would take on the molds.
A Note on "Casting" as a Broader Term
It is crucial to recognize that die casting is just one type of casting. Other methods, like sand casting (for very large parts or low volumes) and investment casting (for highly complex shapes in a wider range of alloys), use entirely different equipment and principles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for volume, material, and complexity.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing complex, precise parts: The die casting machine is the definitive technology to investigate due to its unmatched speed and ability to create net-shape components.
- If your primary focus is a low-volume prototype or a very large part: You should explore other methods like sand casting or 3D printing, as the high initial tooling cost of die casting would be prohibitive.
By understanding the specific function of a die casting machine, you can better align your design and production goals with the most effective manufacturing technology.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Machine | Die Casting Machine |
| Core Function | High-pressure injection of molten metal into a steel mold (die) |
| Key Components | Clamping Unit, Injection System, Ejection System |
| Best For | High-volume production of complex, detailed parts |
| Common Materials | Aluminum, Zinc, Magnesium alloys |
| Main Advantage | High speed, precision, and excellent surface finish |
| Main Limitation | High initial cost for tooling (dies) |
Ready to Optimize Your Metal Part Production?
Understanding the right machinery is the first step. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-performance lab equipment and consumables needed to support advanced manufacturing processes like die casting. Whether you're in R&D, quality control, or process optimization, our solutions help ensure material integrity and production efficiency.
Let's discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
People Also Ask
- What is short capacity of injection Moulding machine? Optimize Your Shot Size for Flawless Parts
- What is the difference between injection molding and pressure molding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Process
- What are the parameters to be considered for selecting the thin wall molding machine? Key Specs for High-Speed Production
- What can you make with an injection moulding machine? Mass-Produce High-Quality Plastic Parts Efficiently
- What are the three 3 differences between compression molding and injection molding? Choose the Right Process for Your Project



















