In short, argon is the industry standard for sputtering because it perfectly balances the three factors essential for the process: it is chemically inert, it has sufficient mass for efficient energy transfer, and it is overwhelmingly cost-effective. This unique combination ensures a pure, physical deposition process without unwanted chemical reactions, at a price point suitable for both research and large-scale manufacturing.
The choice of gas in sputtering is not arbitrary; it is the primary tool for controlling the deposition environment. Argon is chosen because it acts as a perfect medium, providing the energetic ions needed to physically eject material from a target without chemically interfering with the process itself, all while being economically viable.
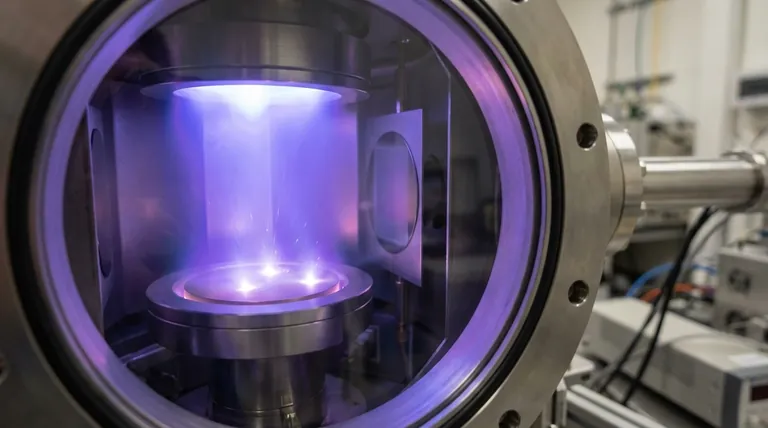
The Fundamental Role of Gas in Sputtering
To understand why argon is used, you must first understand the role any gas plays in the sputtering process. The gas is not a bystander; it is the engine of deposition.
Creating the Plasma
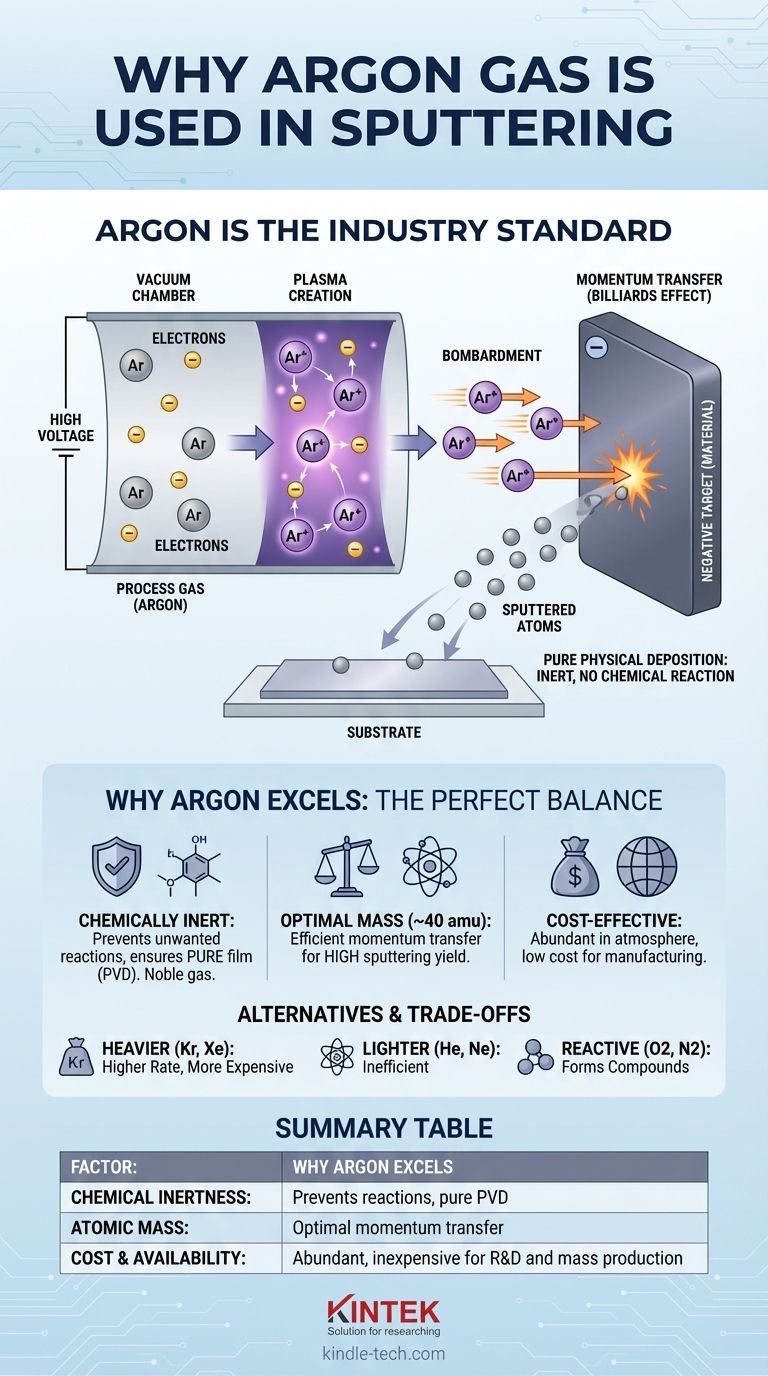
Sputtering begins in a vacuum chamber, which is backfilled with a small amount of a process gas, such as argon. A high voltage is applied between the material to be deposited (the target) and the substrate.
This voltage accelerates free electrons, which then collide with the neutral argon gas atoms. These high-energy collisions knock electrons off the argon atoms, creating positively charged argon ions (Ar+) and a glowing, ionized gas known as plasma.
The Bombardment Process
The sputtering chamber is configured so the target holds a strong negative charge. The newly formed, positively charged argon ions are therefore aggressively accelerated toward the face of this negatively charged target.
These ions strike the target surface with significant kinetic energy. This is the core mechanism of sputtering: a purely physical bombardment.
Momentum Transfer, Not Chemical Reaction
When an argon ion strikes the target, it transfers its momentum to the atoms of the target material. This is like a subatomic game of billiards.
If the momentum transfer is great enough, it can knock or "sputter" an atom 그룹 of the target material loose. These sputtered atoms then travel through the chamber and deposit onto your substrate, building a thin film. Because argon is a noble gas, it is chemically inert and will not react with the target, ensuring the deposited film is a pure layer of the target material.
Why Argon Is the Ideal Candidate
While other gases can be used, argon consistently provides the best balance of physical performance and economic reality for the vast majority of applications.
Critical Inertness
The primary goal of most sputtering processes is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), meaning the film is formed by the physical transfer of atoms. Argon's chemical inertness is non-negotiable for this.
Using a reactive gas would result in Reactive Sputtering, forming a chemical compound. This is a useful process for specific goals (like creating titanium nitride), but it is a different process entirely. For depositing pure metals or other elements, inertness is paramount.
An Optimal Mass for Efficiency
The efficiency of the sputtering process, known as the sputtering yield, is highly dependent on the mass of the bombarding ion.
Argon's atomic mass (around 40 amu) is heavy enough to effectively sputter most common materials. It provides a highly effective momentum transfer, dislodging target atoms at a practical rate for industrial and research purposes.
Economic Practicality
Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere (~1%). This abundance makes it inexpensive to isolate and purify.
For any process intended for manufacturing, cost is a primary driver. Argon's low cost and high availability make it the only economically sensible choice for the overwhelming majority of sputtering applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
Argon is the standard, but it is not the only option. Understanding the alternatives clarifies why argon's balance is so effective.
Heavier Gases for Higher Rates (Krypton & Xenon)
Heavier noble gases like Krypton (Kr) and Xenon (Xe) will produce a higher sputtering yield than argon because their greater mass allows for more efficient momentum transfer.
However, these gases are far rarer and thus significantly more expensive. Their use is reserved for niche applications where the highest possible deposition rate is critical and cost is a secondary concern.
Lighter Gases (Helium & Neon)
Lighter noble gases like Helium (He) and Neon (Ne) are generally poor choices for sputtering. Their low atomic mass results in very inefficient momentum transfer.
The bombardment from these ions is often insufficient to dislodge target atoms effectively, leading to extremely low or non-existent deposition rates.
The Exception: Reactive Sputtering
Sometimes, the goal is to create a compound film, such as a metal oxide or nitride. In this case, a reactive gas like oxygen (O2) or nitrogen (N2) is intentionally introduced into the chamber along with argon.
The argon ions still do the physical sputtering, but the reactive gas combines with the sputtered target atoms in-flight or on the substrate surface to form the desired compound.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the choice of gas is determined by the desired properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is depositing a pure, elemental film at a reasonable cost: Argon is the default and most logical choice due to its perfect balance of inertness, efficiency, and low price.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the deposition rate for a specific material: Consider a heavier, more expensive noble gas like Krypton (Kr) or Xenon (Xe) for its superior momentum transfer.
- If your primary focus is creating a compound film (e.g., a ceramic oxide or nitride): You will use reactive sputtering, introducing a gas like oxygen or nitrogen in addition to the primary sputtering gas, argon.
Understanding these factors allows you to select a process gas not just by convention, but by deliberately engineering the outcome of your thin-film deposition.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Why Argon Excels |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents unwanted reactions, ensuring a pure Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) process. |
| Atomic Mass (~40 amu) | Provides optimal momentum transfer for a high sputtering yield on most materials. |
| Cost & Availability | Highly abundant and inexpensive, making it practical for both R&D and mass production. |
Ready to optimize your sputtering process with the right equipment and consumables?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's thin-film deposition needs. Whether you are conducting research or scaling up for manufacturing, our expertise ensures you achieve precise, reliable, and cost-effective results.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your sputtering applications and drive your projects forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the uses of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells



















