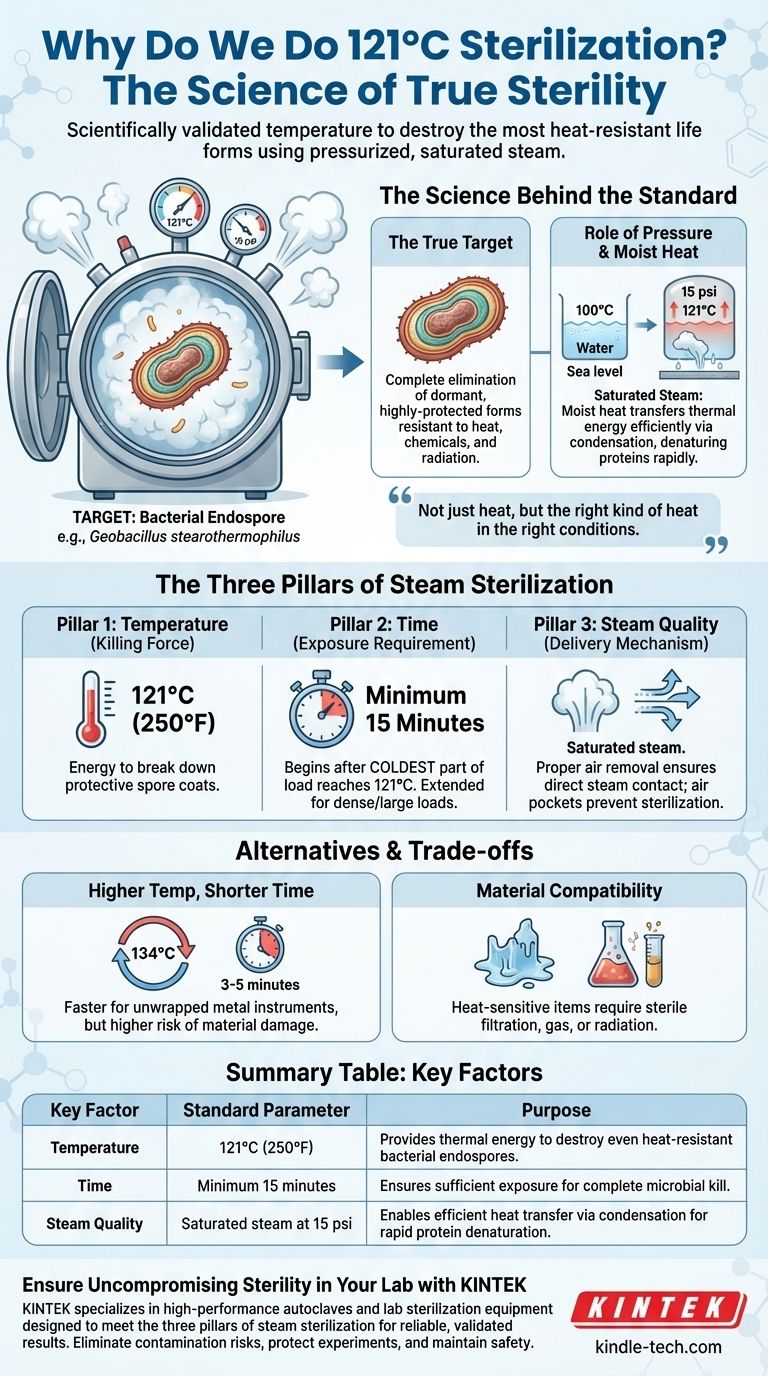
The standard of 121°C is not an arbitrary number; it is the scientifically validated temperature required to destroy the most heat-resistant life forms on Earth. Using pressurized, saturated steam at this temperature for a minimum of 15 minutes, we can reliably kill bacterial endospores, achieving a state of true sterility. This process is the cornerstone of safety in laboratories, medicine, and food production.
Achieving sterility is not just about applying heat, but about applying the right kind of heat in the right conditions. The 121°C standard represents the critical balance of temperature, pressure, and moisture needed to guarantee the destruction of even the most durable microorganisms.

The Science Behind the Standard
To understand why 121°C is the benchmark, we must first understand the true target of sterilization and the physics involved in defeating it.
The True Target: Bacterial Endospores
The goal of sterilization is the complete elimination of all microbial life. This includes not just active bacteria and viruses, but also their dormant, highly-protected forms known as endospores.
Spores produced by bacteria like Geobacillus stearothermophilus are the benchmark. They are metabolically inert and encased in tough, protective layers, making them exceptionally resistant to heat, chemicals, and radiation. Any sterilization process must be proven to kill them.
The Role of Pressure
At standard atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). This temperature is sufficient for disinfection but is not hot enough to reliably destroy bacterial endospores in a practical timeframe.
Pressure is the key to unlocking higher temperatures. Inside a sealed autoclave, as it heats, pressure builds. At approximately 15 psi (or 1 bar) above atmospheric pressure, the boiling point of water is raised to 121°C. The pressure itself does not kill the microbes; its sole purpose is to create the high-temperature steam environment.
Why Moist Heat is Superior
You could achieve 121°C with dry heat in an oven, but it would be far less effective. The presence of water in saturated steam is the critical factor.
Moist heat is incredibly efficient at transferring thermal energy. When steam makes contact with a cooler item, it condenses into water, rapidly releasing its "latent heat of vaporization." This massive energy transfer swiftly denatures the essential proteins and enzymes within microbes, leading to irreversible cell death much faster than dry heat.
The Three Pillars of Steam Sterilization
Temperature is the most famous variable, but it is only one part of a three-part system that must work in concert to ensure success.
Pillar 1: Temperature (The Killing Force)
121°C (250°F) is the established temperature that provides enough thermal energy to break down the protective coats and internal structures of bacterial endospores in a reasonable amount of time.
Pillar 2: Time (The Exposure Requirement)
A minimum exposure time of 15 minutes is the standard once the entire load has reached 121°C. It's crucial to understand this time begins only after the coldest part of the load reaches the target temperature, not when the chamber itself does.
For larger, denser, or insulated loads (like large flasks of liquid or tightly wrapped instrument packs), this time must be extended significantly to ensure full heat penetration.
Pillar 3: Steam Quality (The Delivery Mechanism)
The process relies on saturated steam, which is steam holding the maximum amount of water vapor possible at that temperature and pressure.
If air is not properly removed from the chamber, it creates insulating air pockets that prevent steam from making direct contact with surfaces. Where there is no steam contact, there is no sterilization. This is the most common cause of autoclave cycle failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
While 121°C is the gold standard, it is not the only option, and it's essential to understand the context and limitations.
Incomplete Sterilization: The Risk of Cutting Corners
Failing to meet any of the three pillars—temperature, time, or steam contact—will result in an unsterile load. This can lead to contaminated experimental results, patient infections, or food spoilage, invalidating the entire purpose of the procedure.
Higher Temperatures, Shorter Times
Many modern autoclaves also use a cycle at 134°C (273°F). At this higher temperature, sterilization can often be achieved in as little as 3-5 minutes.
This is a common choice for unwrapped metal instruments in medical settings where speed is critical. The trade-off is that this higher temperature can damage or degrade more sensitive materials like plastics, some liquids, and complex devices.
Material Compatibility
The intense heat and moisture of a 121°C cycle will destroy heat-sensitive materials. Many plastics will melt, and some chemical solutions will degrade. For these items, alternative methods like sterile filtration, ethylene oxide gas, or radiation must be used.
Applying the Correct Sterilization Cycle
Choosing the right approach depends entirely on your material and your objective.
- If your primary focus is routine sterilization of lab media, glassware, and stable instruments: The gold standard of 121°C for at least 15-20 minutes is your most reliable and well-validated choice.
- If your primary focus is speed for robust, non-porous items (like surgical tools): A higher temperature cycle, such as 134°C for 3-5 minutes, is an efficient and valid option, provided the materials are compatible.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive liquids or plastics: You must use a non-heat-based method, such as sterile filtration for liquids or gas sterilization for compatible equipment.
Understanding these core principles transforms sterilization from a routine task into a controlled, scientific process critical for safety and success.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Standard Parameter | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 121°C (250°F) | Provides thermal energy to destroy even heat-resistant bacterial endospores. |
| Time | Minimum 15 minutes (after load reaches temperature) | Ensures sufficient exposure for complete microbial kill. |
| Steam Quality | Saturated steam at 15 psi above atmospheric pressure | Enables efficient heat transfer via condensation for rapid protein denaturation. |
Ensure Uncompromising Sterility in Your Lab with KINTEK
Achieving true sterility is non-negotiable in laboratory research, medicine, and food production. The 121°C standard is a precise science, and using the right equipment is critical for reliable, validated results.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance autoclaves and lab sterilization equipment designed to meet the exacting demands of the three pillars of steam sterilization: precise temperature control, accurate timing, and optimal steam quality. Our solutions help you eliminate contamination risks, protect your experiments and products, and maintain the highest standards of safety.
Ready to enhance your lab's sterilization protocols? Contact our experts today to find the perfect autoclave for your specific materials and workflow. Let KINTEK be your partner in precision and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What types of items and materials can be processed in a laboratory autoclave? Essential Guide for Lab Safety
- Why is a laboratory autoclave necessary for Postgate Medium B (PMB)? Ensure Pure SRB Cultures & Accurate MIC Research
- What is the primary function of a laboratory Autoclave in seaweed hydrolysates? Sterilize and Optimize Fermentation



















