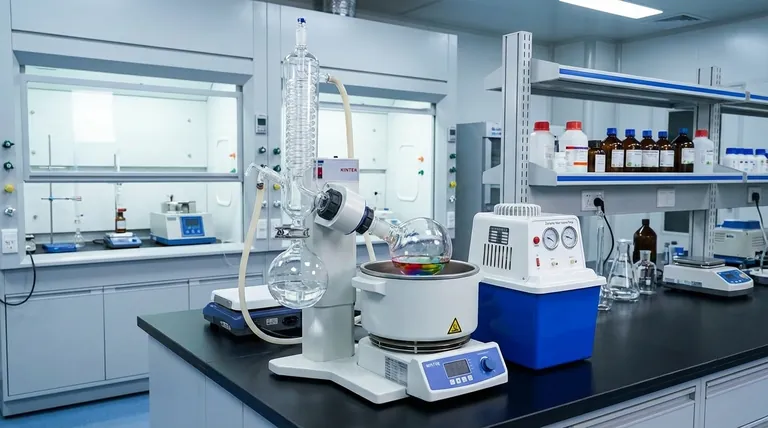
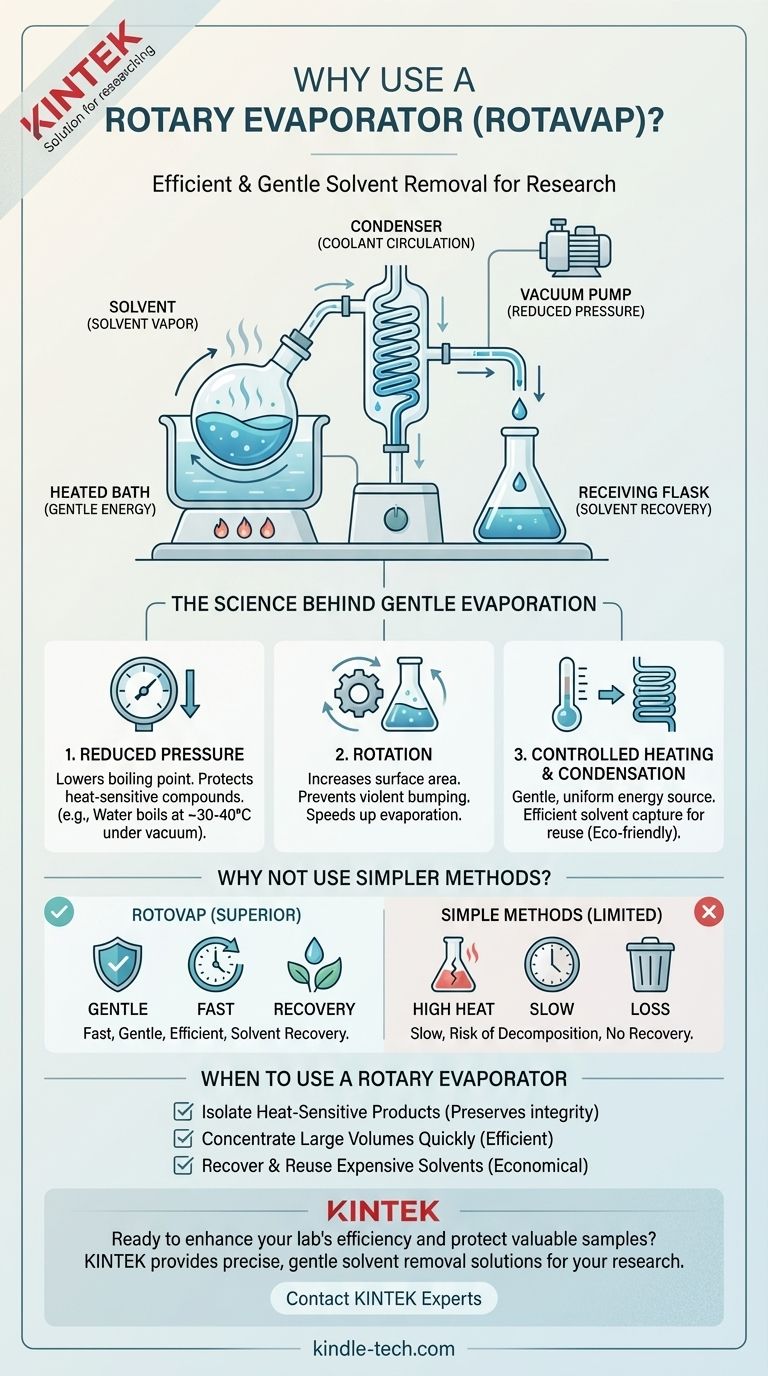
At its core, a rotary evaporator (rotovap) is used to efficiently and gently remove volatile solvents from a sample by evaporation. It achieves this by reducing the pressure inside the apparatus, which lowers the solvent's boiling point, while simultaneously rotating the sample to increase its surface area. This combination allows for rapid solvent removal at low temperatures, protecting heat-sensitive compounds from decomposition.
A rotovap solves a critical problem in chemistry: how to separate a desired, non-volatile compound from its solvent quickly and without destroying it. It achieves this by combining reduced pressure and rotation, enabling fast evaporation at temperatures far below the solvent's normal boiling point.

The Science Behind Gentle Evaporation
To understand why a rotovap is so essential in a modern lab, we must look at the physical principles it masterfully combines. Its design isn't arbitrary; each component addresses a specific challenge in the separation process.
Principle 1: Reduced Pressure Lowers the Boiling Point
A liquid boils when its vapor pressure equals the pressure of the environment around it. At sea level, water boils at 100°C (212°F).
However, if you lower the environmental pressure—for instance, by using a vacuum pump—the liquid needs far less energy (and thus a lower temperature) to start boiling.
This is the rotovap's most critical function. By applying a vacuum, a solvent like water can be made to boil at 30-40°C instead of 100°C. This prevents the thermal degradation of delicate organic molecules, proteins, or natural products that would be destroyed by excessive heat.
Principle 2: Rotation Increases Surface Area and Prevents Bumping
Evaporation is a surface phenomenon. By constantly rotating the flask, the rotovap spreads the sample into a thin, moving film on the inner wall of the glass.
This action dramatically increases the surface area of the liquid exposed to the vacuum and heat, which significantly speeds up the rate of evaporation.
Furthermore, the rotation provides gentle, continuous agitation. This prevents "bumping"—the violent, sudden boiling that can occur when a liquid is heated without stirring, which can cause sample to splash out of the flask and be lost.
Principle 3: Controlled Heating and Condensation
The rotovap doesn't just rely on a vacuum. The rotating flask is partially submerged in a heated water or oil bath, which provides a gentle and uniform source of energy to drive the evaporation.
As the solvent evaporates, the vapor travels into a condenser coil, which is cooled by circulating water or another coolant.
Here, the vapor is cooled back down into a liquid and collects in a separate receiving flask. This allows for the efficient recovery of the solvent for reuse or proper disposal, which is both economical and environmentally responsible.
Why Not Use Simpler Methods?
The rotovap's utility becomes clear when compared to more basic laboratory techniques for solvent removal.
The Problem with Simple Evaporation
Simply heating a beaker on a hot plate is an uncontrolled and inefficient process. It is slow, offers no way to recover the solvent, and creates "hot spots" that can easily overheat and decompose the sample.
The Limits of Standard Distillation
Standard distillation can separate liquids, but it requires heating the entire solution to the solvent's atmospheric boiling point. For many applications in organic chemistry and biochemistry, these temperatures are far too high and would destroy the desired product. The rotovap is essentially a much more gentle and efficient form of distillation under vacuum.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Best Practices
While indispensable, a rotovap is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Not for Highly Volatile Products
The rotovap is designed to separate a non-volatile or low-volatility solute from a volatile solvent. If your desired compound is also volatile, it will evaporate along with the solvent and be lost or co-collected in the receiving flask.
The Risk of Bumping and Foaming
While rotation minimizes bumping, it can still occur, especially with superheated solvents or when the vacuum is applied too quickly. Likewise, some solutions (like those containing proteins or soaps) have a tendency to foam, which can carry the sample over into the condenser and receiving flask. Careful control of vacuum and rotation speed is essential.
Proper Solvent and Temperature Matching
Effective use requires matching the bath temperature and vacuum level to the specific solvent being removed. Using too much heat or too strong a vacuum for a low-boiling-point solvent (like dichloromethane) can cause violent bumping and sample loss. Nomographs are often used to find the ideal settings.
When to Use a Rotary Evaporator
The decision to use a rotovap is based on the need for speed, gentleness, and efficiency in solvent removal.
- If your primary focus is isolating a heat-sensitive product: The rotovap is the standard tool, as it allows you to remove solvents at low temperatures, preserving your compound's integrity.
- If your primary focus is quickly concentrating a large volume of solution: The rotovap's combination of rotation and vacuum makes it far more efficient than open-air evaporation or simple distillation.
- If your primary focus is recovering and reusing expensive solvents: The integrated condenser efficiently captures nearly all evaporated solvent, making the process economical and environmentally friendly.
Ultimately, the rotary evaporator is an indispensable instrument for any chemist who needs precise, efficient, and gentle control over solvent removal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Reduced Pressure | Lowers solvent boiling point, preventing thermal degradation of samples. |
| Rotating Flask | Increases evaporation surface area and prevents violent bumping. |
| Controlled Heating | Provides gentle, uniform energy to drive the evaporation process. |
| Integrated Condenser | Efficiently recovers solvent for reuse or disposal, saving costs. |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency and protect your valuable samples?
A KINTEK rotary evaporator provides the precise, gentle solvent removal your research demands. Our rotovaps are designed for reliability and performance, helping you concentrate solutions and isolate heat-sensitive compounds faster and more effectively.
Contact us today to find the perfect rotary evaporator for your laboratory needs. Let KINTEK, your trusted partner in lab equipment, help you optimize your workflow.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a water circulating vacuum pump operate? Discover the Efficient Liquid Piston Principle
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments
- What can I use a vacuum pump for? Powering Industrial Processes from Packaging to Automation
- What determines the vacuum degree achievable by a water circulating vacuum pump? Unlock the Physics of Its Limits
- How is a circulating water vacuum pump utilized for hydrogen production residues? Optimize Your Solid-Liquid Separation



















