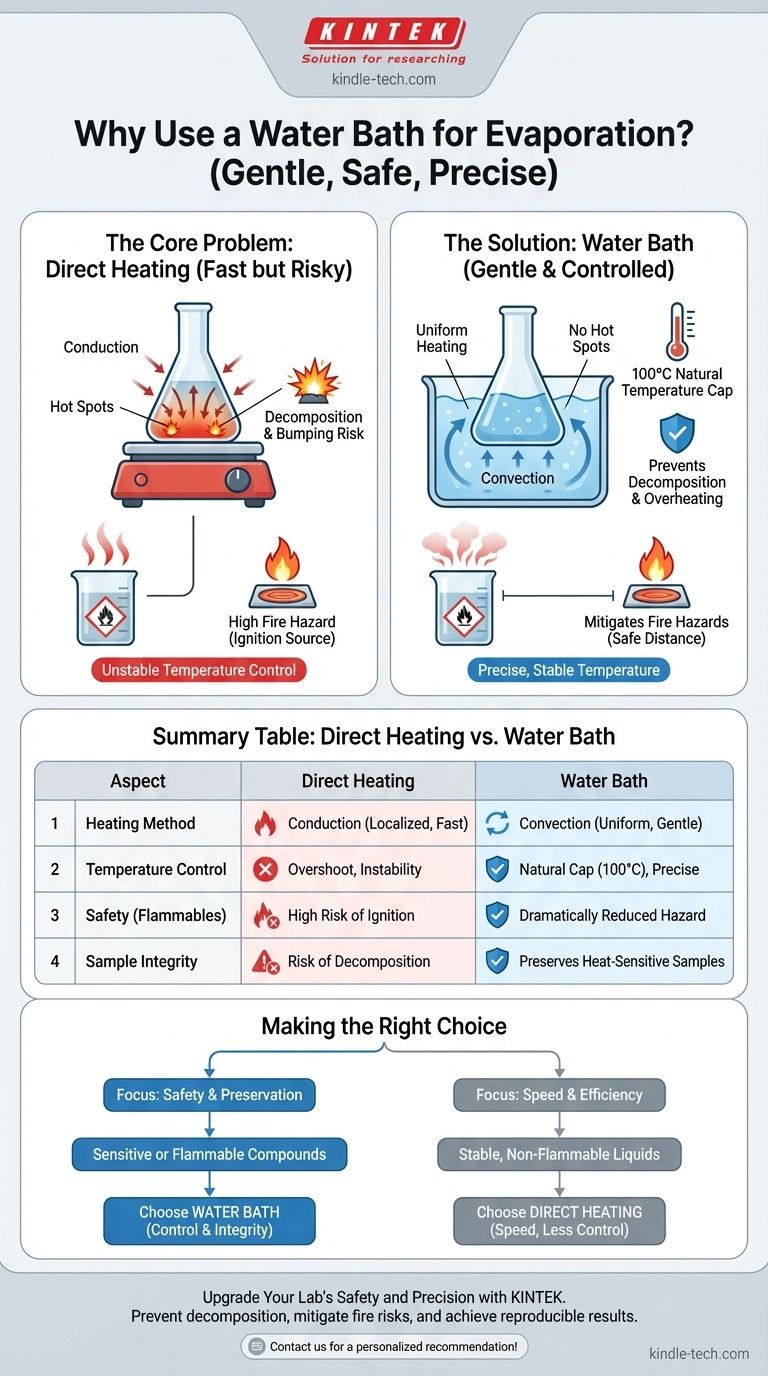
In any laboratory, the choice between direct heat and a water bath for evaporation is a critical decision based on safety and precision. A water bath is used because it provides exceptionally gentle, uniform heating and a natural temperature cap at 100°C, which prevents the decomposition of heat-sensitive compounds and dramatically reduces the fire risk associated with flammable solvents.
The decision to use a water bath is not about heating efficiency; it is about control. You are intentionally sacrificing the raw speed of direct heat to gain the thermal precision and safety required to protect your sample and your lab environment.

The Core Problem with Direct Heating
Direct heating, typically with a hot plate or Bunsen burner, is fast and simple. However, this simplicity masks significant risks related to temperature control and heat distribution.
Understanding Direct Heat Transfer
Direct heating works primarily through conduction. The hot surface of a plate or the tip of a flame transfers thermal energy to the small area of glassware it touches.
This creates an intense, localized transfer of energy.
The Danger of "Hot Spots"
This focused energy creates hot spots on the bottom of the flask or beaker. These areas can become significantly hotter than the bulk of the liquid.
For a sensitive organic compound, these hot spots can cause localized charring or decomposition, ruining your sample even if the liquid's average temperature seems correct. They can also lead to "bumping," where a pocket of liquid superheats and vaporizes violently.
Temperature Overshoot and Instability
Hot plates are notorious for temperature overshoot. The heating element's surface can easily exceed the set temperature as it cycles on and off, making it difficult to maintain a precise, stable temperature for the substance you are trying to evaporate.
How a Water Bath Solves for Precision and Safety
A water bath introduces a medium—the water—that fundamentally changes how heat is delivered to your sample, solving the problems of hot spots and temperature instability.
Gentle, Uniform Heating
A water bath heats your vessel via convection. The water circulates, delivering heat evenly to the entire submerged surface of the container.
Think of it as wrapping your flask in a warm blanket instead of touching it with a hot poker. This eliminates dangerous hot spots and ensures the entire sample is at a uniform temperature.
A Natural Temperature Ceiling
At standard atmospheric pressure, a water bath cannot exceed 100°C (212°F). This provides a natural, foolproof safety mechanism.
If you are evaporating a solvent from a compound that decomposes at 110°C, a water bath ensures you can never accidentally overheat and destroy it.
Mitigating Fire Hazards
This is the most critical safety function. When evaporating flammable solvents like ethanol or diethyl ether, their vapors are heavy and can spill over the side of the flask.
With direct heating, these flammable vapors can easily travel down to the hot surface of the plate, which can act as an ignition source. A water bath creates a safe distance between the heating element and the mouth of the flask, drastically reducing the risk of a fire.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a water bath is a deliberate decision that involves balancing speed, control, and convenience. It is not always the superior choice.
Speed vs. Control
The primary trade-off is speed. Direct heating is significantly faster.
If your goal is to simply boil a large volume of a stable, non-flammable liquid like water, direct heat is far more efficient. The water bath's gentle heating process is inherently slower.
Temperature Limitations
A standard water bath is only effective for processes that occur at or below 100°C. For higher-temperature evaporations, chemists use other media like oil or sand baths, which operate on the same principle of even heating but at higher temperature ranges.
Setup and Monitoring
A water bath requires more setup. You must fill it, wait for the water itself to heat up, and monitor the water level to ensure it doesn't evaporate completely during a long procedure. Direct heating is simpler to initiate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use the properties of your substance and the goal of your experiment to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is safety with flammable solvents: A water bath is the correct and necessary choice to minimize ignition risk.
- If your primary focus is preserving a heat-sensitive compound: A water bath provides the essential temperature control to prevent decomposition and ensure a pure final product.
- If your primary focus is speed with a stable, non-flammable substance (like an aqueous salt solution): Direct heating is often sufficient and more time-efficient.
Mastering thermal control is a fundamental step toward achieving reliable and safe experimental results.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Direct Heating | Water Bath |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Conduction (localized) | Convection (uniform) |
| Temperature Control | Prone to overshoot & instability | Natural cap at 100°C |
| Safety for Flammable Solvents | High risk of ignition | Dramatically reduced fire hazard |
| Impact on Heat-Sensitive Samples | Risk of hot spots & decomposition | Gentle heating preserves integrity |
| Best Use Case | Fast evaporation of stable, non-flammable liquids | Safe evaporation of sensitive or flammable compounds |
Upgrade Your Lab's Safety and Precision with KINTEK
Choosing the right evaporation method is critical for protecting your samples and ensuring lab safety. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including reliable water baths designed for gentle, uniform heating and precise temperature control.
Our solutions help you:
- Prevent sample decomposition with consistent, controlled heating.
- Mitigate fire risks when working with flammable solvents.
- Achieve reproducible results by eliminating hot spots and temperature instability.
Whether you're evaporating sensitive organic compounds or handling flammable solvents, KINTEK has the equipment to meet your laboratory's needs. Contact us today to find the perfect water bath or other lab essentials for your application.
#ContactForm to get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
- 10L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 5L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Achieve Precise Temperature Control for Your Experiments
- What are the post-use procedures for a five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Ensure Safety & Longevity
- What are the pre-use procedures for a five-port water bath electrolytic cell? A 4-Step Guide for Reliable Results
- When is professional repair required for a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Protect Your Lab's Precision and Safety
- How should a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell be operated? A Step-by-Step Guide for Reliable Results



















