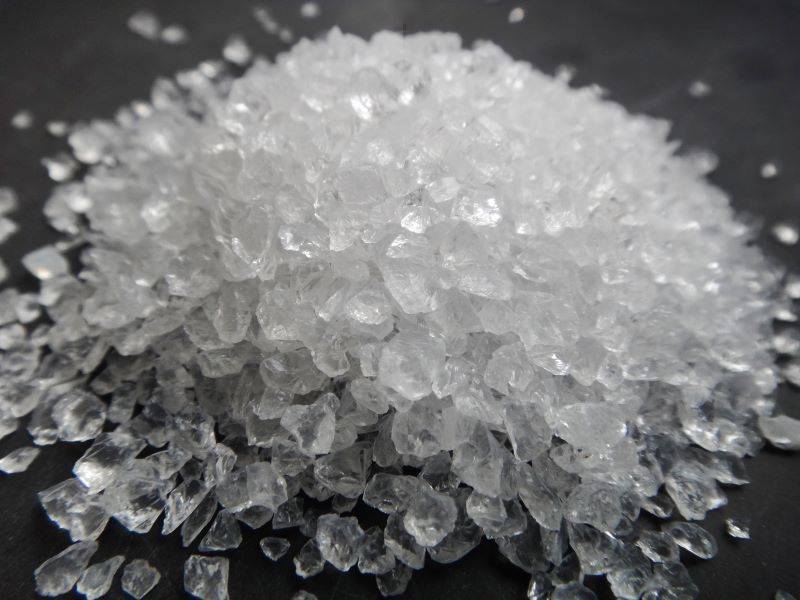
Definition and Formation
Natural Quartz
Natural quartz is a naturally occurring mineral that is ubiquitous in various forms of rocks. Its formation is deeply influenced by geological conditions, which vary significantly across different regions and environments.
Quartz is primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO₂), a compound that is widespread in the Earth's crust. The mineral's crystalline structure, which is characterized by its hexagonal symmetry, is a result of complex geological processes that include crystallization from magma, precipitation from hydrothermal solutions, and transformation from other minerals under high pressure and temperature conditions.
The color and clarity of natural quartz can vary widely, ranging from clear and colorless to shades of pink, purple, yellow, and even black, depending on the presence of trace elements and impurities. These variations in color and clarity are often exploited in the gemstone industry, where quartz is used to create beautiful and valuable pieces such as amethyst, citrine, and rose quartz.
In addition to its aesthetic appeal, natural quartz is valued for its physical and chemical properties. It possesses a high degree of hardness, making it resistant to scratching and abrasion, and it exhibits good thermal stability, which allows it to withstand high temperatures without significant degradation. These properties, along with its natural abundance, make natural quartz a versatile material with applications in various industries, including electronics, optics, and construction.
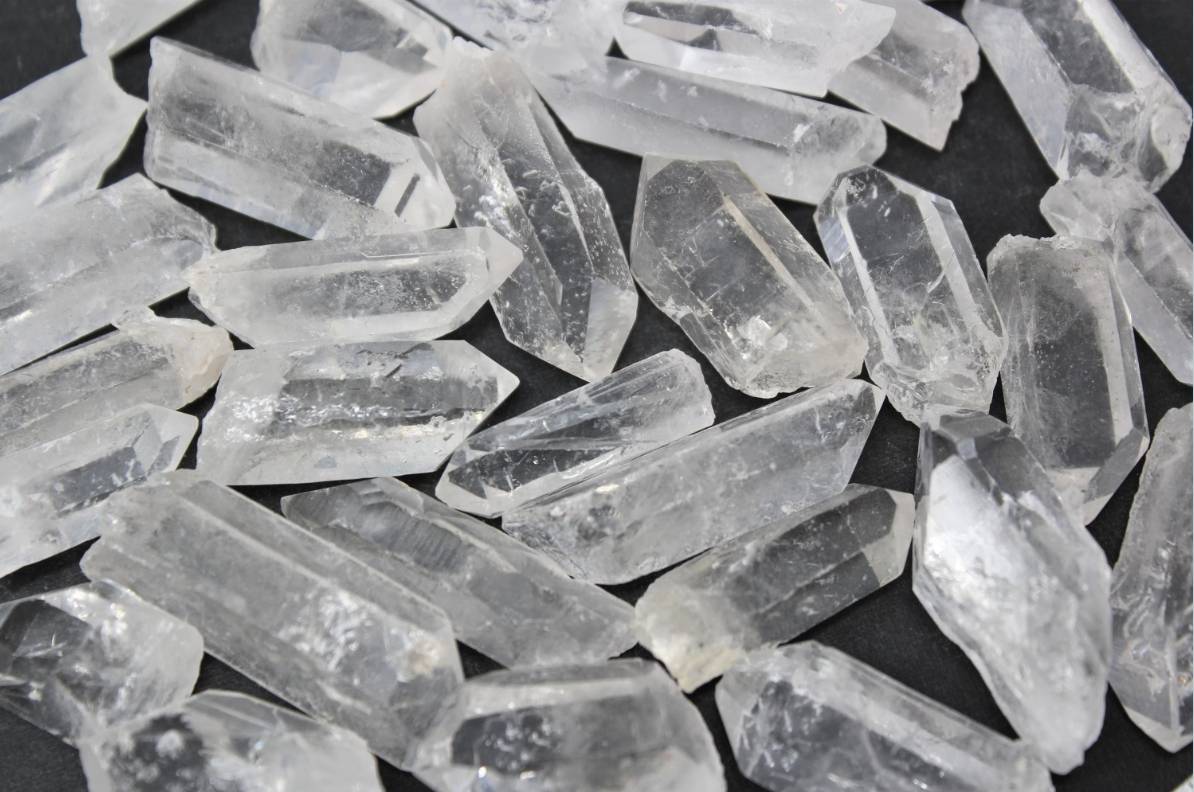

The geological conditions that influence the formation of natural quartz also play a crucial role in determining its physical and chemical properties. For instance, quartz formed in different geological settings may exhibit variations in its thermal expansion, thermal conductivity, and density. These variations, while they can complicate the use of quartz in certain applications, also provide opportunities for tailoring its properties to meet specific industrial needs.
In summary, natural quartz is a fascinating and versatile mineral whose properties and characteristics are shaped by a combination of its chemical composition and the geological conditions under which it forms. Its wide range of colors and forms, coupled with its robust physical and chemical properties, make it a valuable resource in both industrial and ornamental contexts.
Fused Quartz
Fused quartz is a specialized glass meticulously crafted by heating and melting natural pure quartz to achieve a controlled composition and structure. This process involves the fusion of crystalline silica, a substance that constitutes nearly one-third of the Earth's crust, including materials like sand and rock crystal. The manufacturing techniques for fused quartz can be categorized into two primary methods: electrically fused, which utilizes electrical energy, and flame fused, which employs a combination of gas and oxygen.
The resulting material can exhibit varying degrees of transparency, ranging from completely transparent to opaque or translucent, enabling a diverse array of applications. Notably, fused silica, often referred to as synthetic fused quartz, is produced from silica sand of exceptionally high purity, rendering it translucent. This synthetic variant is particularly valued for its superior optical and thermal properties, which far exceed those of conventional glass types.
For instance, the production of fused quartz tubes involves the high-temperature fusion of naturally occurring quartz crystals, typically at temperatures exceeding 2000°C. These tubes are predominantly transparent and are prized for their exceptional optical clarity and thermal stability, making them ideal for a multitude of industrial and scientific applications.
Appearance Characteristics
Fused Silica
Fused silica, often referred to as synthetic fused quartz, is a highly purified form of silica glass, derived from silica sand of exceptional purity. This material is typically colorless and transparent, although it can also appear as opaque or translucent depending on the manufacturing process. The production of fused silica involves melting crystalline silica, which includes natural sources like sand and rock crystal. This melting process can be achieved through electrical fusion, where the material is heated using electric arcs, or through flame fusion, where a gas-oxygen flame is employed. The resulting fused silica can be found in various forms, including lumps, granules, or even as a fine white powder, each with its unique applications and properties.

Natural Quartz
Natural quartz is a diverse mineral, exhibiting a wide array of colors that range from clear and transparent to vibrant hues such as purple, pink, and yellow. This variability in color is primarily due to the presence of trace elements and impurities within the crystal structure. Typically, natural quartz forms in a crystalline structure, characterized by its specific shape and distinct crystal surface. The crystal lattice of quartz is composed of a repeating pattern of silicon and oxygen atoms, which gives it its unique optical and physical properties.
The formation of natural quartz is influenced by various geological processes, including the metamorphism of pre-existing rocks and the crystallization of magma. These processes can lead to the development of different quartz varieties, such as amethyst, citrine, and rose quartz, each with its own distinct appearance and properties. The crystalline nature of quartz is further enhanced by its ability to grow in well-defined, geometric shapes, which are often sought after for their aesthetic and functional qualities in various applications.
In summary, natural quartz is not only known for its varied colors and crystalline structure but also for its formation through geological processes that contribute to its unique and diverse properties.
Physical Properties
Fused Silica
Fused silica, also known as synthetic fused quartz, is a material of exceptional purity, derived from silica sand. This synthetic variant of quartz is produced through the controlled melting of crystalline silica, which includes natural sources like sand and rock crystal. The fusion process can be achieved either electrically or through the use of gas and oxygen, resulting in a material that can be transparent, opaque, or translucent, depending on the specific manufacturing method and conditions.
One of the standout features of fused silica is its low thermal expansion coefficient. This property ensures that the material remains stable under varying temperature conditions, making it ideal for applications where thermal shock resistance is crucial. Additionally, fused silica exhibits high thermal stability, allowing it to withstand extreme temperatures without degrading. Despite these thermal advantages, fused silica has a relatively low thermal conductivity, which helps in maintaining a stable internal environment even when exposed to external heat sources.
In terms of mechanical properties, fused silica boasts high hardness, which contributes to its durability and resistance to scratching. This makes it suitable for use in environments where abrasion is a concern. Furthermore, the high purity of fused silica, typically exceeding 99.9% SiO₂, endows it with excellent chemical stability and resistance to both high temperatures and chemical erosion. These characteristics collectively position fused silica as a versatile and robust material for a wide array of industrial andscientific applications.
Natural Quartz
Natural quartz exhibits several distinct physical properties that set it apart from other materials like fused silica. One of its most notable characteristics is its higher thermal expansion. This means that natural quartz expands more significantly when heated compared to fused silica, which has a lower thermal expansion rate. This property is crucial in applications where thermal stability is a key consideration.
Another significant attribute is its variable thermal conductivity. Unlike fused silica, which has a consistently low thermal conductivity, natural quartz's thermal conductivity can vary. This variability is often influenced by the presence of impurities within the quartz. These impurities can create microstructural variations that affect how heat is conducted through the material.
Natural quartz also boasts high hardness and density. Its Mohs hardness rating is 7, which is quite high, making it resistant to scratching and wear. This hardness, combined with its density, contributes to its durability and suitability for various industrial applications.
However, it's important to note that the properties of natural quartz can fluctuate due to impurities. These impurities, which can include various minerals or elements, can alter the quartz's physical and chemical characteristics. For instance, the presence of iron can give quartz a pink or purple hue, while other impurities can affect its optical properties or thermal behavior. Understanding these fluctuations is essential for predicting how natural quartz will perform in different environments and applications.
Chemical Properties
Fused Silica
Fused silica, also referred to as synthetic fused quartz, is a highly refined form of silica glass, primarily composed of silica (SiO₂). This material is derived from high-purity silica sand, which undergoes a meticulous melting process to achieve its vitreous state. The production methods include electrical fusion, where the sand is melted using electrical currents, and flame fusion, which involves heating the material with gas and oxygen. These processes result in a versatile substance that can be transparent, opaque, or translucent, enabling the creation of a wide array of products.
Fused silica is renowned for its exceptional chemical stability, largely due to its high SiO₂ content, which exceeds 99.9%. This high purity imparts remarkable resistance to acids, high temperatures, and chemical erosion. Unlike natural quartz, which may contain impurities that affect its properties, fused silica maintains consistent chemical behavior across various conditions. Its ability to withstand extreme environments makes it indispensable in industries requiring materials that can endure harsh conditions, such as in the production of precision instruments, high-temperature furnaces, and chemical reactors.
Natural Quartz
Natural quartz is a naturally occurring mineral found in various forms of rocks, influenced by geological conditions. This mineral exhibits good chemical stability, which is a significant advantage in many industrial applications. However, the presence of impurities can significantly affect its properties. These impurities can range from trace elements to inclusions of other minerals, which can alter the quartz's thermal, optical, and mechanical characteristics.
For instance, impurities can lead to variations in thermal conductivity, affecting the material's performance in high-temperature environments. Additionally, the presence of certain elements can alter the optical properties of quartz, making it less transparent or introducing color variations. This variability in properties due to impurities necessitates careful selection and processing of natural quartz for specific applications.
In summary, while natural quartz boasts excellent chemical stability, its properties can be influenced by the presence of impurities, necessitating meticulous handling and selection for optimal performance in various industrial contexts.
Applications
Fused Silica
Fused silica, also known as synthetic fused quartz, is a versatile material derived from silica sand of exceptional purity. This material is produced through the melting of crystalline silica, which includes natural substances like sand and rock crystal. The melting process can be achieved either through electrical means, known as electrically fused silica, or by using gas and oxygen, referred to as flame-fused silica. The resulting products can appear transparent, opaque, or translucent, offering a wide range of applications.
In the industrial sector, fused silica finds extensive use due to its unique properties. It is a key component in precision casting processes, where its high purity and thermal stability are crucial. Additionally, it plays a significant role in the production of glass ceramics, contributing to the development of materials with enhanced durability and thermal resistance.
In the realm of electronics and optics, fused silica's transparency and chemical stability make it indispensable. It is used in the manufacturing of high-precision optical components and electronic devices, where even the slightest impurities can compromise performance. Furthermore, its application in aerospace is driven by its lightweight yet robust nature, making it ideal for use in space-bound equipment.
Beyond these high-tech applications, fused silica also serves as a filler in various chemical industries. Its inertness and resistance to chemical erosion ensure that it can be safely used in a multitude of chemical processes without degrading or reacting with other substances. This versatility underscores why fused silica is a material of choice across multiple industries, each leveraging its distinct properties to achieve superior results.
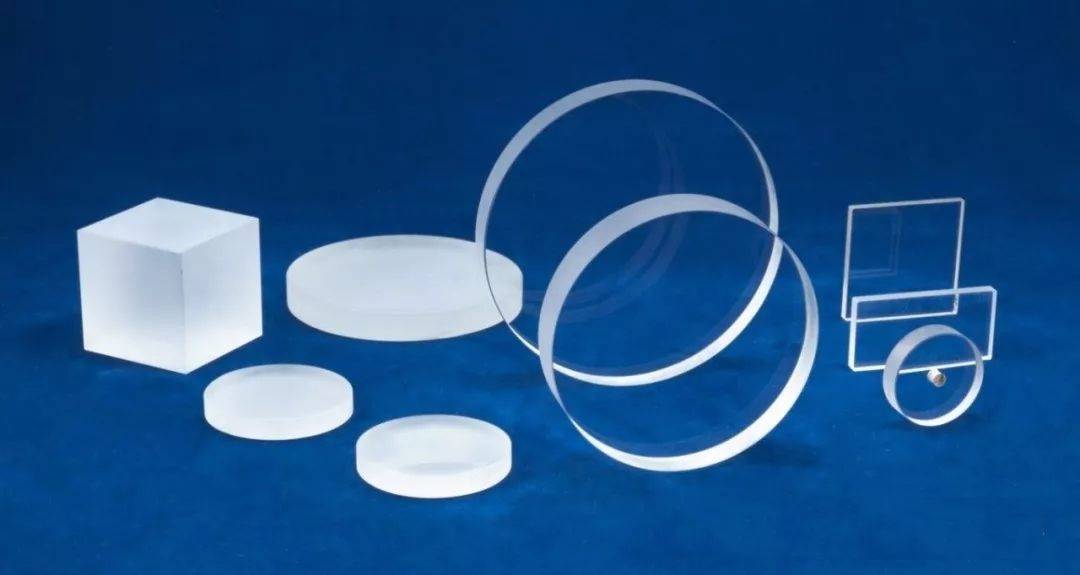

Natural Quartz
Natural quartz finds extensive usage across various industries due to its unique properties and versatility. One of its primary applications is in the production of quartz glass, which is renowned for its high transparency and thermal resistance. This glass is often utilized in high-tech applications such as semiconductor manufacturing and photovoltaic cells.
In addition to glass production, natural quartz is integral to the creation of oscillators, which are crucial components in electronic devices. These oscillators provide precise timing signals, essential for the functioning of everything from watches to communication systems.
Natural quartz also serves as a key material in construction, where it is processed into sand. This quartz sand is used in a variety of construction applications, including as an aggregate in concrete and mortar, and for creating durable, high-quality building materials.
Moreover, natural quartz is prized for its aesthetic appeal and is often used as a decorative element. Its natural crystalline structure and varied colors make it a popular choice for jewelry, sculptures, and interior design elements.
Overall, the diverse applications of natural quartz highlight its importance in both technological advancements and everyday life.
Related Products
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Quartz Plate JGS1 JGS2 JGS3
- Infrared High Resistance Single Crystal Silicon Lens
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer CaF2 Substrate Window Lens
- CF Ultra-High Vacuum Observation Window Window Flange High Borosilicate Glass Sight Glass
Related Articles
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Cleaning Laboratory Glassware
- Glassware vs. Plasticware - Which is the Better Choice for Your Needs?
- Technological Innovations in the Fused Silica Industry
- Understanding Quartz Electrolytic Cells: Applications, Mechanisms, and Advantages
- Unlocking the Power of Optical Quartz Plates: Applications and Benefits











