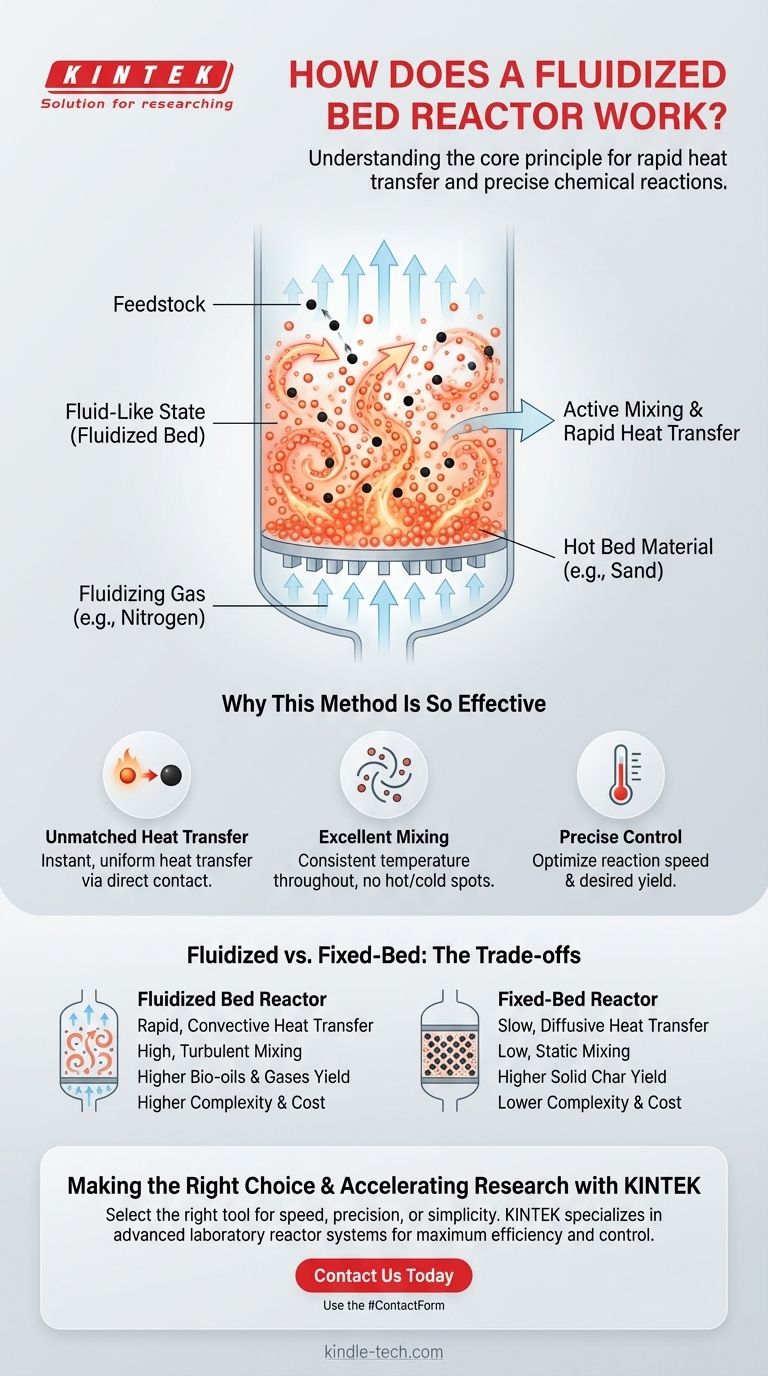
At its core, a fluidized bed reactor works by using an upward flow of gas to suspend solid particles, making them behave like a turbulent, boiling fluid. This "fluidized" bed of hot material, typically sand, then surrounds the feedstock (the material being processed), enabling extremely rapid and uniform heat transfer that drives the desired chemical reaction.
The fundamental advantage of a fluidized bed reactor is not just containing a reaction, but creating a dynamic, well-mixed environment. This active mixing overcomes the slow, inefficient heat transfer common in static reactors, leading to more control, speed, and a higher yield of desired products.

The Core Principle: Achieving Fluidization
A fluidized bed reactor is a highly dynamic system. Its effectiveness comes from creating and controlling a unique physical state where solid particles exhibit fluid-like properties.
The Setup: Bed Material and Fluidizing Gas
The reactor vessel contains a layer of fine, solid particles, known as the bed material. Sand is a common choice due to its high heat tolerance and inertness.
A fluidizing gas, often an inert gas like nitrogen, is continuously pumped into the bottom of the reactor through a distributor plate.
The "Fluid-Like" State
As the gas flows upward through the bed material, it exerts a drag force on the particles. Once the gas velocity is high enough, this force counteracts gravity, and the particles become suspended and churned within the gas flow.
The result is a turbulent mixture of gas and solids that looks and behaves remarkably like a boiling liquid. This is the fluidized bed.
The Dual Role of the Gas
The fluidizing gas serves two critical functions. Its primary mechanical job is to suspend the particles.
In many applications, like pyrolysis, its chemical job is equally important. Using an inert gas like nitrogen creates an oxygen-free atmosphere, preventing unwanted side reactions such as combustion and ensuring the feedstock decomposes through the intended chemical pathway.
Why This Method Is So Effective
The fluid-like state is not just a novelty; it provides significant advantages for heat and mass transfer, which are the cornerstones of process engineering.
Unmatched Heat Transfer
When feedstock (e.g., small particles of woody biomass) is introduced into the reactor, it is immediately engulfed by the hot, churning bed material.
This direct contact with thousands of hot particles transfers heat to the feedstock almost instantaneously and with exceptional uniformity.
Excellent Mixing and Temperature Control
The constant, turbulent motion ensures the temperature throughout the reactor is extremely consistent. This eliminates hot spots and cold spots, which can lead to inconsistent product quality or unwanted byproducts in less-agitated systems.
This high degree of control allows engineers to run reactions at precise temperatures, optimizing for speed and the desired outcome.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Fluidized vs. Fixed-Bed
To fully appreciate the fluidized bed reactor, it helps to compare it to a simpler alternative: the fixed-bed reactor.
Fixed-Bed Reactor: The Simple Baseline
In a fixed-bed reactor, the solid feedstock or catalyst is stationary, or "fixed." Heat is typically applied to the reactor walls and must slowly diffuse inward from particle to particle.
This process is slow and often results in a significant temperature gradient, where particles near the wall are much hotter than those in the center.
Fluidized-Bed Reactor: Complexity for Performance
A fluidized bed reactor is more complex, requiring precise control over gas flow rates to maintain the fluidized state.
However, this complexity is justified by its superior performance. It transforms heat transfer from a slow, diffusive process into a rapid, convective one, leading to far more efficient and controllable reactions.
The Consequence on Product Yield
This difference directly impacts the final output. For processes like pyrolysis, the rapid heating in a fluidized bed favors the production of valuable liquids (bio-oils) and gases.
The slow, uneven heating in a fixed bed often results in a higher proportion of solid char, which may be less desirable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct reactor type depends entirely on the specific requirements of your process, balancing performance needs with operational simplicity.
- If your primary focus is rapid and uniform reactions: The fluidized bed's superior heat and mass transfer make it the definitive choice for processes that demand speed and precision.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the yield of specific products (e.g., bio-oils): The controlled, uniform environment of a fluidized bed reactor is essential for steering chemical reactions toward a desired output and away from unwanted byproducts.
- If your primary focus is design simplicity and lower cost: A fixed-bed reactor may be sufficient for slower reactions where perfect temperature uniformity is not a critical factor.
Ultimately, understanding the principle of fluidization empowers you to select the right tool to achieve precise control over your chemical process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Fluidized Bed Reactor | Fixed Bed Reactor |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer | Rapid, uniform, convective | Slow, diffusive, uneven |
| Temperature Control | Excellent (no hot/cold spots) | Poor (significant gradients) |
| Mixing | High, turbulent | Low, static |
| Typical Product Yield | Higher bio-oils & gases | Higher solid char |
| Complexity & Cost | Higher | Lower |
Ready to Optimize Your Chemical Process with Superior Reactor Technology?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced laboratory equipment, including reactor systems designed for maximum efficiency and control. Whether your goal is rapid pyrolysis, precise temperature management, or maximizing bio-oil yield, our expertise can help you select and implement the right solution.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our reactor technologies can enhance your lab's performance and accelerate your research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a PTFE-lined stainless steel high-pressure autoclave in ZrW2O8 synthesis? Achieve High Purity
- Why are stainless steel autoclaves key to PCL-TPE preparation? Mastering High-Vacuum Polycondensation
- What is the function of a high-pressure static autoclave in biomass HTL? Optimize Your Biomass Conversion Research
- What is the role of a high-pressure reactor in h-BN magnetic nanocomposite synthesis? Master Precision Deposition
- What environment does a PTFE-lined autoclave provide for TiO2-GQD synthesis? Achieve Superior Nanocomposite Results



















