At its core, a hydrogen stove operates on a very simple chemical principle. It works by directly combusting hydrogen gas with oxygen drawn from the surrounding air. This controlled reaction produces a flame for cooking, with the primary byproduct being water vapor, making it a potentially clean alternative to traditional natural gas stoves.
A hydrogen stove functions much like a natural gas stove, burning a piped-in fuel to generate a flame. The key difference is the fuel itself—hydrogen—which upon combustion, produces heat and water, fundamentally altering the environmental and safety considerations.

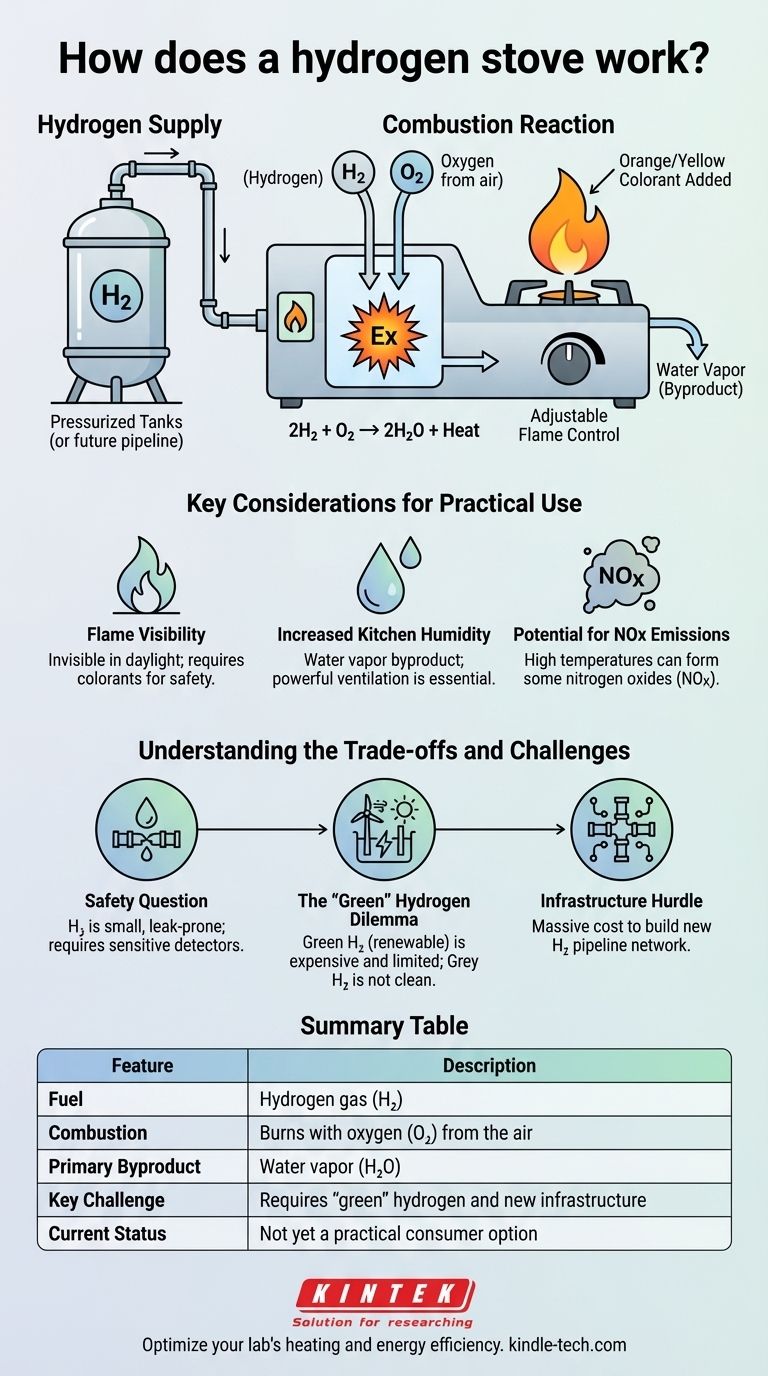
The Core Mechanism: From Gas to Flame
A hydrogen stove's operation is straightforward, but it relies on a sophisticated system to manage the fuel safely and effectively. The process involves delivering the gas, mixing it with air, and igniting it to produce a controllable flame.
How Hydrogen is Supplied
Unlike electricity, hydrogen is a gas fuel that must be stored and delivered to the appliance. In current prototypes and test homes, this is typically done via pressurized tanks located outside the building. For widespread adoption, it would require a dedicated pipeline infrastructure similar to the one used for natural gas today.
The Combustion Reaction
The chemical reaction is the centerpiece of the technology. When ignited, hydrogen (H₂) combines with oxygen (O₂) from the air. This exothermic reaction releases significant energy in the form of heat, and the molecules recombine to form water (H₂O). The ideal, simplified equation is 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O + Heat.
Creating a Controllable Flame
A burner, visually similar to one on a gas stove, is designed to mix the hydrogen fuel with the optimal amount of air. An electronic igniter sparks this mixture, creating a stable flame. The user can then adjust the flow of hydrogen gas with a dial, instantly controlling the flame's size and heat output, offering the same responsiveness prized by chefs who use natural gas.
Key Considerations for Practical Use
While the science is simple, the practical application of cooking with hydrogen introduces unique characteristics and challenges that differ significantly from cooking with gas or electricity.
Flame Visibility and Color
A pure hydrogen flame is nearly invisible in daylight, which presents a major safety hazard. To solve this, manufacturers add agents—often sodium-based compounds—to the system. These additives give the flame a familiar orange or yellow color, making it easy to see if the stove is on.
Increased Kitchen Humidity
Because the primary byproduct is water vapor, using a hydrogen stove will noticeably increase the humidity in your kitchen. This makes powerful and effective ventilation an absolute necessity to prevent issues with condensation, mold, and excess moisture.
Potential for NOx Emissions
While the ideal reaction only produces water, the reality is more complex. Air is nearly 80% nitrogen. When any fuel is burned at very high temperatures in the presence of air, some nitrogen oxides (NOx), which are pollutants, can be formed. While emissions are expected to be far lower than natural gas, it is not perfectly emission-free in a real-world kitchen environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
The viability of hydrogen stoves extends far beyond the appliance itself. The primary obstacles are related to safety, cost, and the immense challenge of building a new energy infrastructure.
The Overarching Safety Question
Hydrogen is a much smaller molecule than natural gas, making it more difficult to contain and more prone to leaking from pipes and fittings. It is also flammable over a much wider range of concentrations in air. Consequently, any hydrogen appliance requires extremely sensitive leak detectors and automatic shut-off systems that exceed the standards for natural gas.
The "Green" Hydrogen Dilemma
Not all hydrogen is created equal. The vast majority of hydrogen produced today is "grey hydrogen," made from natural gas in a process that releases significant carbon dioxide. Using it would defeat the climate goal.
The truly clean alternative is "green hydrogen," produced by splitting water (electrolysis) using renewable energy like wind or solar. This process is currently very expensive and the supply is extremely limited, making it the single biggest barrier to a hydrogen-powered future.
The Infrastructure Hurdle
Replacing the existing, extensive natural gas network with a new pipeline system capable of safely transporting hydrogen would be a monumental and costly undertaking. The technical and financial challenges of building out this infrastructure are the primary reasons you cannot buy a hydrogen stove today.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
While hydrogen cooking technology is a fascinating field of research, it is not yet a practical option for consumers. Understanding its context helps inform your decisions today.
- If your primary focus is immediate sustainability: The best choice available now is an electric induction cooktop paired with a renewable electricity plan from your utility.
- If your primary focus is cooking performance: A modern natural gas stove still offers the responsive flame control many prefer, while high-end induction offers faster and more precise temperature control.
- If your primary focus is future-proofing your home: Do not plan for a hydrogen stove. Instead, ensure your kitchen has robust electrical wiring to support powerful induction cooktops, as electrification is the most likely path for residential decarbonization.
Ultimately, understanding how a hydrogen stove works reveals that the true challenge is not the appliance, but the massive industrial and energy systems required to support it.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuel | Hydrogen gas (H₂) |
| Combustion | Burns with oxygen (O₂) from the air |
| Primary Byproduct | Water vapor (H₂O) |
| Key Challenge | Requires 'green' hydrogen and new infrastructure |
| Current Status | Not yet a practical consumer option |
Optimize your lab's heating and energy efficiency with KINTEK
While hydrogen stoves represent a future direction for clean energy, your laboratory's current needs for precise, reliable, and efficient heating are our top priority. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including furnaces and ovens, designed for superior performance and control.
Let our experts help you select the perfect heating solution for your specific applications. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's goals with our high-quality equipment and consumables.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Hydrogen Determination Probe for Quickly Measuring Hydrogen Content with High Success Rate
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE wire used for hanging metal specimens in biodiesel corrosion tests? Ensure Pure Experimental Results
- What are the advantages of using PTFE molds for epoxy resin flame retardant samples? Ensure High-Purity Material Testing
- What are the specific applications of PTFE in micro-batch slug flow systems? Enhance Your Microfluidic Reaction Purity
- What are alloys in simple words? Unlock the Power of Engineered Materials
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type




