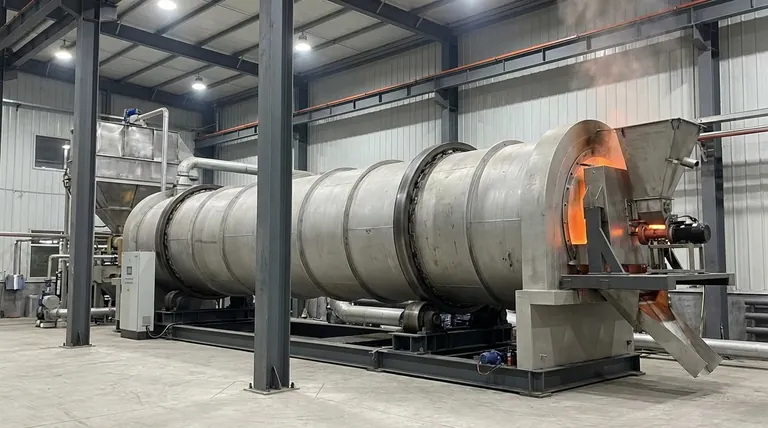
At its core, a rotary extractor is a simple and robust machine designed for the continuous processing of solid materials. It consists of a large, rotating cylindrical tube, often called a kiln or reactor, which is slightly inclined. As raw material is fed into the higher end, the tube's slow rotation and incline work together to transport, mix, and heat the material until it exits at the lower end.
The fundamental purpose of a rotary extractor is not just to heat material, but to do so with exceptional uniformity. The constant tumbling action ensures that every particle is processed under nearly identical conditions, which is critical for consistent chemical reactions and phase changes in industrial settings.

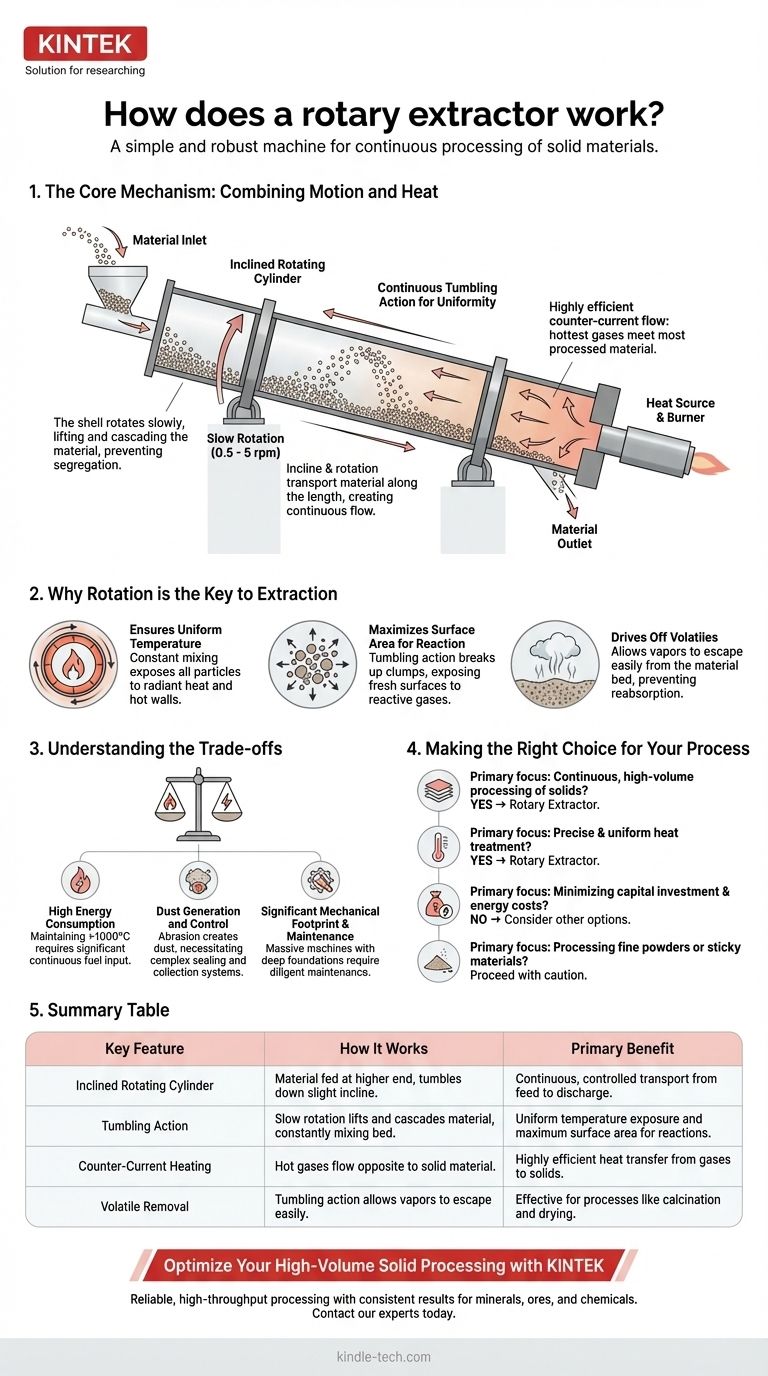
The Core Mechanism: Combining Motion and Heat
A rotary extractor’s effectiveness comes from the elegant interplay of simple mechanical and thermal principles. Understanding these individual components reveals why the design is so widely used.
The Inclined Rotating Cylinder
The main body is a long, hollow steel cylinder lined with refractory material to withstand high internal temperatures. This cylinder, or shell, is mounted on rollers and tilted at a slight angle, typically between 1 and 4 degrees from horizontal.
The Role of Rotation
The shell rotates slowly, usually between 0.5 and 5 revolutions per minute. This rotation lifts the solid material partway up the interior wall of the cylinder. Gravity then causes it to cascade, or tumble, back down to the bottom of the bed.
This continuous tumbling is the key to the extractor's function. It is a highly effective mixing method, preventing segregation and ensuring the material bed remains homogenous.
Material Transport
The combination of the rotational tumbling and the slight downward incline of the cylinder forces the material to move gradually along the length of the extractor. This creates a continuous flow from the feed inlet to the discharge outlet. The speed of this transport, known as residence time, can be controlled by adjusting the rotation speed and the angle of inclination.
The Heat Transfer Process
The reference to a "furnace" indicates a high-temperature process. Heat is typically introduced via a large burner or lance at the lower, discharge end of the cylinder. This creates a counter-current flow, where the hot gases move up the kiln in the opposite direction of the solid material moving down.
This counter-current design is highly efficient. The hottest gases encounter the most processed material, while the cooler gases encounter the fresh, cold feed, maximizing thermal transfer along the entire length of the machine.
Why Rotation is the Key to Extraction
The simple act of rotation is what elevates this device from a simple heated tube to a sophisticated chemical reactor. The benefits are directly tied to the tumbling motion it creates.
Ensuring Uniform Temperature
Without tumbling, material at the bottom of the bed would be insulated and under-heated, while material on top could be overheated. The constant mixing exposes all particles to the radiant heat from the flame and the hot refractory walls, ensuring a uniform temperature profile throughout the solid bed.
Maximizing Surface Area for Reaction
Many extraction processes involve a chemical reaction between a gas and a solid (gas-solid reaction). The tumbling action continuously breaks up clumps and exposes fresh particle surfaces to the reactive gases within the extractor's atmosphere, dramatically increasing the rate and completeness of the reaction.
Driving Off Volatiles
In processes like calcination or drying, the goal is to drive off water or other volatile compounds. Tumbling allows these vapors to escape the material bed easily and be carried away by the kiln's gas flow, preventing them from being reabsorbed and driving the process to completion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary extractor design is not without its challenges. Objectively evaluating these trade-offs is critical for proper application.
High Energy Consumption
Maintaining temperatures often exceeding 1000°C in such a large, unsealed piece of equipment requires a significant and continuous input of fuel. Heat loss through the shell and exhaust gases can be substantial, making energy a primary operational cost.
Dust Generation and Control
The tumbling action, while beneficial for mixing, inevitably creates dust as particles abrade against each other and the shell. This necessitates complex sealing systems at both ends of the kiln and large dust collection systems (like baghouses or electrostatic precipitators) to prevent product loss and environmental pollution.
Significant Mechanical Footprint and Maintenance
Rotary extractors are massive, heavy machines. They require deep foundations and a robust support structure. The drive system, support rollers (trunnions), and the large girth gear that rotates the shell are all subject to immense mechanical stress and require diligent, preventative maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Use this framework to determine if a rotary extractor aligns with your primary processing goals.
- If your primary focus is continuous, high-volume processing of solids: The rotary extractor is purpose-built for this task, offering reliable throughput for materials like minerals, ores, and chemicals.
- If your primary focus is achieving precise and uniform heat treatment: The tumbling action provides unparalleled mixing, making it ideal for processes where every particle must reach a specific temperature for a specific time.
- If your primary focus is minimizing capital investment and energy costs: This technology is likely not the best fit; its large scale and high-temperature operation make it one of the more capital- and energy-intensive options.
- If your primary focus is processing fine powders or sticky materials: Proceed with caution, as high dust generation can be a major issue with fine powders, and sticky materials can build up on the shell wall, disrupting flow and heat transfer.
By understanding its core principles of motion and heat, you can effectively leverage the unique capabilities of the rotary extractor.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | How It Works | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Inclined Rotating Cylinder | Material is fed in at a higher end and tumbles down a slight incline. | Continuous, controlled transport of solids from feed to discharge. |
| Tumbling Action | Slow rotation lifts and cascades material, constantly mixing the bed. | Uniform temperature exposure and maximum surface area for reactions. |
| Counter-Current Heating | Hot gases flow opposite to the solid material moving down the kiln. | Highly efficient heat transfer from gases to solids. |
| Volatile Removal | Tumbling action allows vapors to escape the material bed easily. | Effective for processes like calcination and drying. |
Optimize Your High-Volume Solid Processing with KINTEK
A rotary extractor is a powerhouse for continuous, uniform thermal processing of materials like minerals, ores, and chemicals. If your lab or production facility requires reliable, high-throughput processing with consistent results, this robust technology is essential.
At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying high-quality lab equipment, including robust thermal processing systems tailored to your specific needs. Our expertise ensures you get the right equipment to enhance efficiency, improve product consistency, and scale your operations effectively.
Ready to achieve superior processing results? Contact our experts today to discuss how a rotary extractor can transform your workflow and meet your production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- What is a rotary kiln reactor? A Guide to Industrial Thermal Processing
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding


















