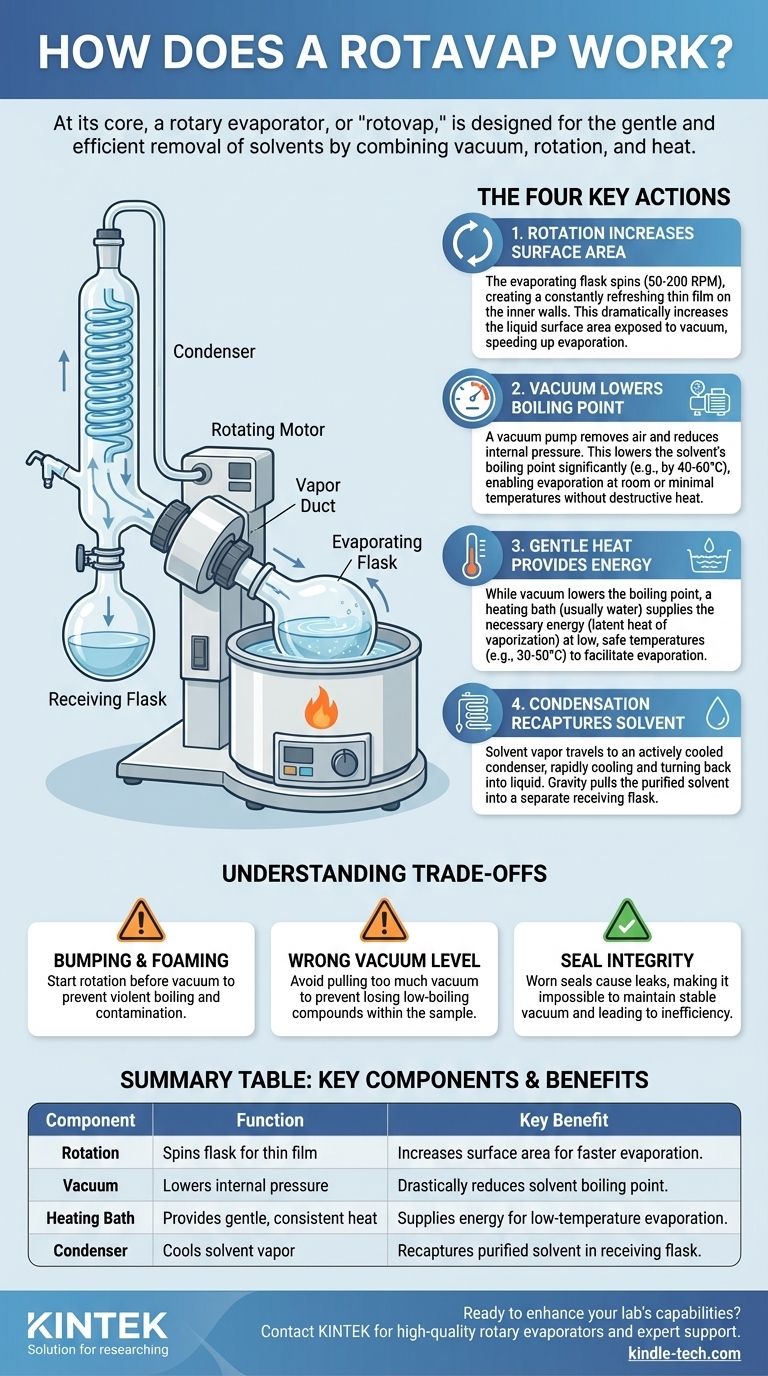
At its core, a rotary evaporator, or "rotovap," is a device designed for the gentle and efficient removal of solvents from a sample. It accomplishes this by combining three key principles: reducing the pressure with a vacuum to lower the solvent's boiling point, rotating the sample to increase its surface area, and applying gentle heat to facilitate evaporation.
The true purpose of a rotovap isn't merely to boil off a liquid. It is a precision instrument for separating a volatile solvent from a non-volatile sample without damaging or degrading the target compound by using low-temperature, high-surface-area evaporation under vacuum.

The Goal: Why Not Just Boil It?
The primary challenge in many chemical processes is isolating a desired compound from the solvent it's dissolved in. Simply heating the mixture to boil off the solvent is often a poor choice, as high temperatures can easily destroy or alter delicate organic molecules, rendering your work useless.
The rotovap was invented to solve this exact problem. It allows for rapid evaporation at room temperature or with only minimal heat, preserving the integrity of the compound you want to keep.
Breaking Down the Process: The Four Key Actions
A rotovap's effectiveness comes from four distinct actions working in perfect harmony. Understanding each one allows you to control the process with precision.
1. Rotation Increases Surface Area
The process begins with your sample in a round-bottom flask. This evaporating flask is attached to the rotovap and spun by a motor, typically between 50-200 RPM.
This rotation is critical. It forces the liquid up and around the inner walls of the flask, creating a constantly refreshing thin film. This dramatically increases the surface area of the liquid exposed to the vacuum, making evaporation far faster and more efficient than it would be in a static pool.
2. Vacuum Lowers the Boiling Point
This is the central scientific principle behind the rotovap. A vacuum pump is connected to the system, which removes air and reduces the internal pressure.
Pressure and boiling point are directly linked. At sea level, water boils at 100°C (212°F). On a high mountain, where the air pressure is lower, water boils at a lower temperature. The vacuum in a rotovap creates an environment of extremely low pressure, which can lower a solvent's boiling point by 40-60°C or more. This is what enables evaporation without destructive heat.
3. Gentle Heat Provides Energy
While the vacuum lowers the boiling point, evaporation still requires energy (the latent heat of vaporization). This energy is supplied by a heating bath, usually filled with water.
The rotating flask is partially submerged in this bath, which provides a gentle, consistent, and low-level heat. Because the boiling point has already been drastically reduced by the vacuum, the bath temperature can be kept low, often around 30-50°C, which is safe for most organic compounds.
4. Condensation Recaptures the Solvent
As the solvent evaporates from the thin film inside the rotating flask, the vapor travels up into a condenser. This is a coil of glass with a large surface area that is actively cooled by a circulating fluid (like cold tap water or a dedicated chiller).
When the warm solvent vapor hits the cold surface of the condenser, it rapidly cools and turns back into a liquid. Gravity then pulls the condensed, purified solvent down into a separate receiving flask, effectively separating it from your original sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While highly effective, a rotovap requires skill to operate correctly. Misunderstanding the interplay of its components can lead to poor results or sample loss.
Bumping and Foaming
If the vacuum is applied too aggressively or the rotation is not started first, the solvent can boil violently in a phenomenon called bumping. This can splash your unpurified sample directly into the condenser and collection flask, contaminating everything and causing significant loss. Always start the rotation before applying the vacuum.
Setting the Wrong Vacuum Level
A common mistake is applying too much vacuum ("pulling a hard vac"). While this lowers the boiling point most, it can also cause low-boiling-point compounds within your sample to evaporate along with the solvent. The key is to find a vacuum level that is low enough for efficient solvent removal but not so low that you lose your product.
Seal Integrity is Everything
The entire system relies on maintaining a consistent vacuum. Worn or dirty seals on the rotating joint or glass connections will cause leaks. A leak forces the vacuum pump to work harder and makes it impossible to maintain a stable, low boiling point, leading to a slow and inefficient process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Mastering the rotovap is about balancing the variables—rotation speed, heat, and vacuum depth—to match your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is speed: Use a moderate vacuum and a bath temperature roughly 20°C warmer than your solvent's target boiling point. A faster rotation will also increase the evaporation rate.
- If your primary focus is protecting a highly sensitive compound: Use a weaker vacuum and the lowest possible bath temperature, even if the process takes longer. The goal is gentleness above all else.
- If your primary focus is high-purity solvent recovery: Ensure your condenser is very cold (at least 20°C colder than the solvent's boiling point under vacuum) to guarantee efficient recapture of all vapor.
By understanding how these components work together, you transform the rotovap from a simple machine into a powerful tool for precision separation.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Rotation | Spins the flask to create a thin film | Increases surface area for faster evaporation |
| Vacuum | Lowers the internal pressure | Drastically reduces solvent boiling point |
| Heating Bath | Provides gentle, consistent heat | Supplies energy for evaporation at low temperatures |
| Condenser | Cools the solvent vapor | Recaptures purified solvent into a separate flask |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precision separation?
A rotary evaporator is essential for any laboratory focused on gentle, efficient solvent removal for sensitive compounds. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including reliable rotary evaporators, designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern research and production.
We provide:
- Durable and efficient rotovaps for consistent, reliable performance.
- Expert support and guidance to help you select the perfect system for your specific application, whether your priority is speed, sample protection, or high-purity solvent recovery.
Let KINTEK be your partner in achieving superior results.
Contact our experts today to find the ideal rotary evaporator for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- Why is a water circulating vacuum pump suitable for handling flammable or explosive gases? Inherent Safety Through Isothermal Compression
- How does the impeller rotation affect the gas flow in a water circulating vacuum pump? A Guide to the Liquid Ring Principle
- How does a water circulating vacuum pump operate? Discover the Efficient Liquid Piston Principle
- What is the purpose of the compression chamber in a vacuum pump? The Heart of Vacuum Generation
- What types of gases can a water circulating vacuum pump handle? Safely Manage Flammable, Condensable & Dirty Gases



















