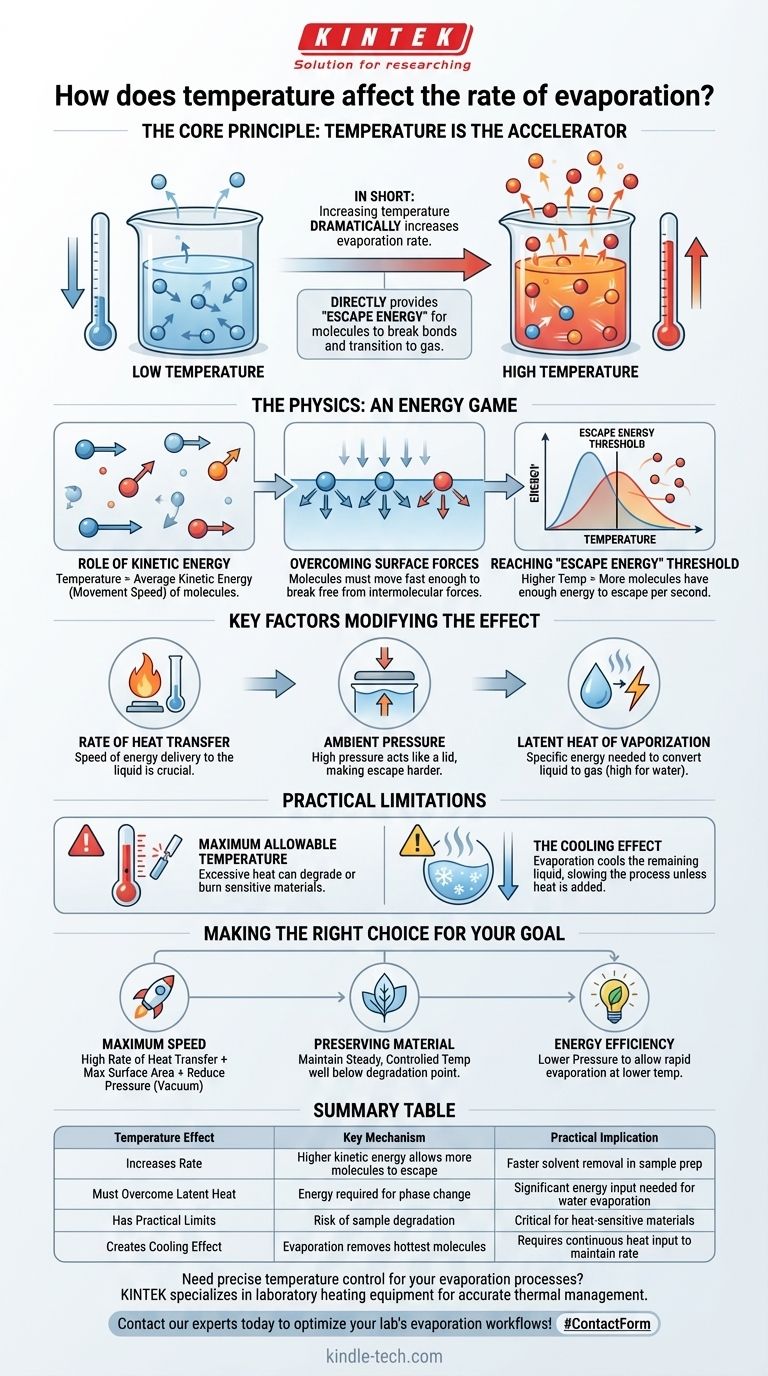
In short, increasing the temperature of a liquid dramatically increases its rate of evaporation. This occurs because heat is a form of energy. When you add heat to a liquid, you are increasing the kinetic energy of its molecules, causing them to move faster and making it easier for them to escape from the liquid's surface into the air as a gas.
The core principle is this: Temperature is the accelerator for evaporation. It directly provides the "escape energy" that individual molecules need to break their bonds with the liquid and transition into a gaseous state.

The Physics of Evaporation: An Energy Game
Evaporation is not just about boiling; it's a continuous process that happens at the surface of a liquid. Temperature's role is best understood by looking at what's happening on a molecular level.
The Role of Kinetic Energy
Temperature is fundamentally a measure of the average kinetic energy—or movement speed—of the molecules in a substance. In a glass of water, some molecules are moving slowly, some are average, and some are moving very fast.
Overcoming Surface Forces
Molecules in a liquid are held together by intermolecular forces. For a molecule at the surface to evaporate, it must be moving fast enough to break free from these attractive forces pulling it back into the liquid.
Reaching the "Escape Energy" Threshold
Increasing the temperature raises the average kinetic energy of all molecules. This means a much larger percentage of the molecules now have enough individual energy to overcome the surface forces and escape. The higher the temperature, the more molecules cross this "escape energy" threshold per second, resulting in a faster rate of evaporation.
Key Factors That Modify Temperature's Effect
While temperature is the primary driver, its effectiveness is influenced by several other critical factors. A true understanding of the system requires looking beyond temperature alone.
Rate of Heat Transfer
The speed at which you can deliver heat energy to the liquid is crucial. A large body of water heated by a small flame will not evaporate quickly, because the heat isn't being transferred efficiently to all the molecules.
Ambient Pressure
Evaporation happens when molecules escape into the surrounding air. If the air pressure above the liquid is high, it acts like a lid, making it physically harder for molecules to leave the surface. This is why water boils at a lower temperature at high altitudes where pressure is lower.
Latent Heat of Vaporization
This is the specific amount of energy required to convert one kilogram of a liquid into a gas at a constant temperature. Water has a very high latent heat, meaning it takes a significant amount of energy to make it evaporate, which is why sweating is an effective cooling mechanism.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
You cannot simply increase the temperature indefinitely to speed up evaporation. Real-world applications have constraints that must be respected.
Maximum Allowable Temperature
Many substances change or decompose when heated too much. For example, when evaporating water from a food product, excessive heat can burn the food, altering its chemical structure and ruining the final product. Every process has a temperature ceiling.
The Cooling Effect of Evaporation
A fascinating and critical trade-off is that evaporation itself is a cooling process. The molecules with the most energy are the ones that escape, leaving the lower-energy (cooler) molecules behind. This means rapid evaporation will actively cool the remaining liquid, which in turn slows down further evaporation unless you continuously supply more heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Controlling evaporation is about balancing these factors to meet a specific objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum speed: You must provide a high rate of heat transfer to maintain a high temperature, while also maximizing surface area and, if possible, reducing ambient pressure (creating a vacuum).
- If your primary focus is preserving a sensitive material: Your goal is to maintain a steady, controlled temperature well below the material's degradation point, accepting a potentially slower evaporation rate for a higher quality result.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: The most effective strategy is often to lower the pressure. This allows for rapid evaporation at a much lower temperature, significantly reducing the energy required for the process.
Ultimately, mastering evaporation is about precisely managing the energy of the system to achieve your desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Effect | Key Mechanism | Practical Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Increases Rate | Higher kinetic energy allows more molecules to escape | Faster solvent removal in sample prep |
| Must Overcome Latent Heat | Energy required for phase change | Significant energy input needed for water evaporation |
| Has Practical Limits | Risk of sample degradation at high temperatures | Critical for heat-sensitive materials |
| Creates Cooling Effect | Evaporation removes hottest molecules | Requires continuous heat input to maintain rate |
Need precise temperature control for your evaporation processes? KINTEK specializes in laboratory heating equipment, including evaporation systems, hot plates, and ovens designed for accurate thermal management. Our solutions help you achieve faster evaporation rates while protecting sensitive samples. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your lab's evaporation workflows!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What materials can evaporate? Master Thin-Film Deposition with the Right Materials
- Why is an alumina boat selected for catalyst precursors? Ensure Sample Purity at 1000 °C
- What is the vacuum evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition & PVD
- What were the 4 factors that affect the rate of evaporation? Master Control for Lab & Industrial Processes
- What is the evaporation method of e-beam? Achieve High-Purity Thin Film Coatings
- What are thin films deposited by evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Coating
- Why is sputtering deposition much slower than evaporation deposition? The Trade-Off Between Speed and Quality
- What is the electron beam evaporation technique? Achieve High-Purity Thin Film Deposition



















