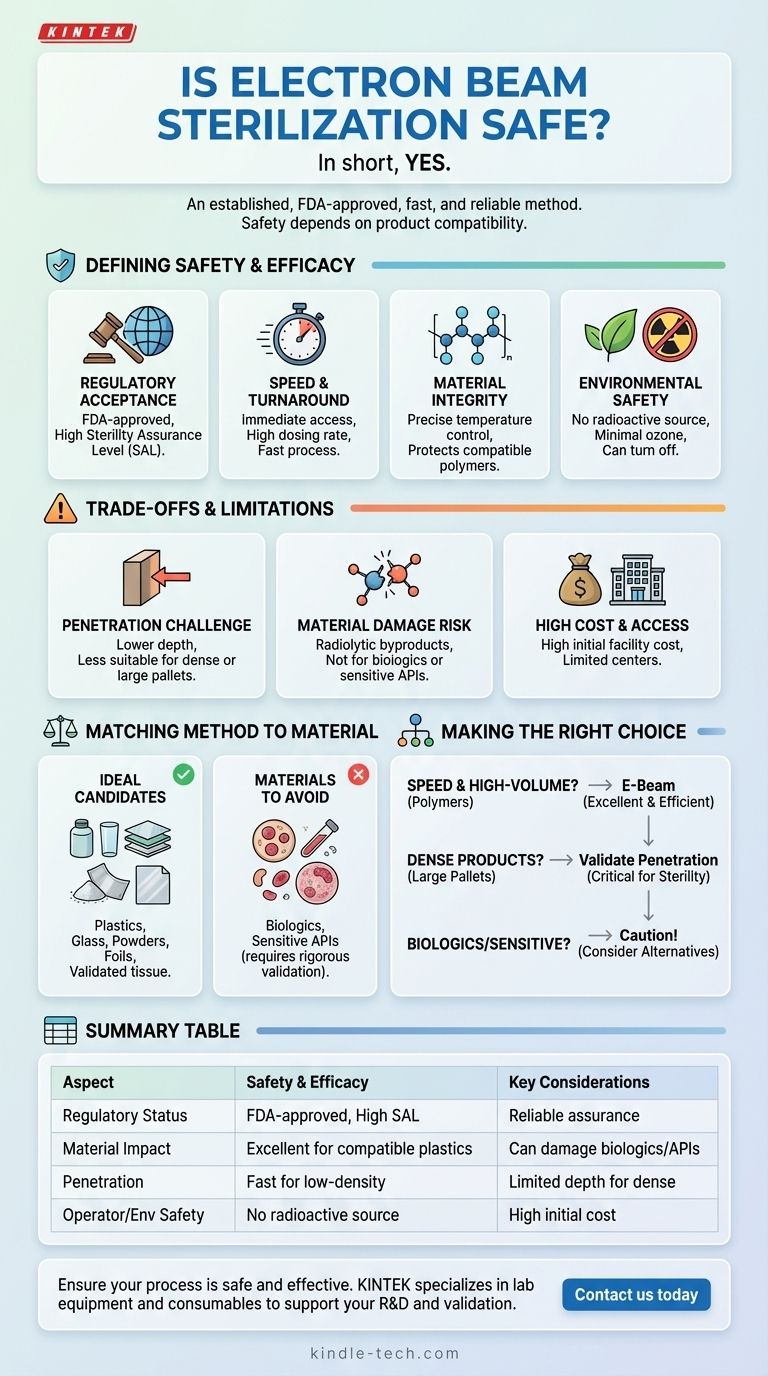
In short, yes. Electron beam (e-beam) sterilization is an established and highly safe method for sterilizing a wide range of products, particularly medical devices. It is an internationally accepted and FDA-approved process known for its speed, reliability, and minimal environmental impact.
E-beam sterilization is considered safe due to its high efficacy and lack of radioactive materials, but its overall safety for a specific application depends entirely on product compatibility. Its lower penetration depth and potential to alter sensitive materials are critical factors that must be evaluated.

What Defines E-Beam's Safety and Efficacy?
The safety of any sterilization process is judged on multiple factors: its ability to reliably kill microbes, its impact on the product, and its effect on operators and the environment. E-beam excels in several of these areas.
Regulatory Acceptance and Reliability
E-beam sterilization is an FDA-approved process trusted worldwide for medical devices and other materials.
The process provides a high sterility assurance level (SAL), reliably inactivating microorganisms to ensure the product is safe for the end-user.
Speed and Turnaround Time
As a fast process with a high dosing rate, e-beam allows for near-immediate access to fully sterilized products. This efficiency is a significant operational advantage, reducing quarantine times.
Material Integrity and Control
The process allows for precise temperature control during irradiation, which is critical for protecting heat-labile materials.
When used on appropriate polymers, it is known to protect material properties and prevent significant degradation.
Environmental and Operator Safety
Unlike gamma irradiation, e-beam systems do not require a localized radioactive source, which simplifies handling, security, and decommissioning.
The system has a minimal atmospheric effect, releasing only a slight amount of ozone, and can be simply turned off when not in use.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No sterilization method is perfect for every application. Objectively assessing e-beam requires understanding its specific limitations, which are central to using it safely and effectively.
The Challenge of Penetration
E-beam sterilization has lower penetration capability compared to other methods like gamma radiation.
This makes it less suitable for very dense products or large, fully loaded pallets where the beam cannot reach all surfaces uniformly to guarantee sterility.
Risk of Material Damage
The high-energy electrons can cause the formation of radiolytic byproducts, which could potentially damage raw materials, active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), or packaging systems.
This risk is why e-beam is not recommended for biologics, as it can damage sensitive structures like nucleoproteins.
High Cost and Accessibility
The initial capital cost of constructing e-beam sterilization facilities is extremely high.
This has resulted in a limited number of e-beam radiation centers, which can be a logistical constraint for some manufacturers.
Matching the Method to the Material
A key component of e-beam's safety profile is ensuring it is only used on compatible products. The interaction between the electron beam and the material itself is a critical consideration.
Ideal Candidates for E-Beam
E-beam is highly effective for sterilizing many common medical materials, including plastics, glass, powders, and foils.
It is also successfully used for certain tissue materials that have been validated for the process, such as bone, cardiovascular valves, and hydrogels.
Materials to Avoid
The primary contraindication for e-beam is biologics. The radiation can irreversibly damage these complex molecules, rendering them ineffective or unsafe.
Any product containing sensitive APIs must undergo rigorous validation to ensure the sterilization process does not degrade the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Product
To determine if e-beam is the safest and most effective choice for you, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is speed and high-volume sterilization for lower-density medical devices: E-beam is an excellent and highly efficient choice that is safe for many common polymers.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing dense products or large, sealed pallets: You must carefully validate that the beam's limited penetration can achieve the required sterility assurance level throughout the entire load.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing biologics or sensitive APIs: You must proceed with extreme caution, as the risk of material damage is significant, and alternative methods are often a safer choice for product integrity.
Ultimately, the safety of electron beam sterilization is a direct function of its correct application to a compatible product.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Safety & Efficacy | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Status | FDA-approved, internationally accepted | Reliable sterility assurance level (SAL) |
| Material Impact | Excellent for compatible plastics, glass, powders | Can damage sensitive biologics and some APIs |
| Penetration | Fast and efficient for low-density items | Limited penetration depth for dense products |
| Operator/Environmental Safety | No radioactive source; minimal ozone release | High initial facility cost; limited accessibility |
Ensure your sterilization process is safe and effective. Choosing the right method is critical for your product's integrity and regulatory compliance. KINTEK specializes in providing lab equipment and consumables to support your R&D and validation processes. Our experts can help you navigate the complexities of sterilization technology. Contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and how we can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Laboratory Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer Lab Microcomputer Sterilizer
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why is it important to autoclave the prepared reagents before using? Ensure Sterility and Reliable Results
- What is a lab autoclave? Your Guide to Sterilization with Pressurized Steam
- What temperature must be reached for sterilization in 10-12 minutes? Achieve Rapid, Reliable Sterility with Flash Autoclaving
- How do you sterilize glassware by autoclave? Master the 3-Step Process for Reliable Sterility
- What are the advantages of autoclaving in hospitals? Achieve Unmatched Sterilization for Patient Safety



















