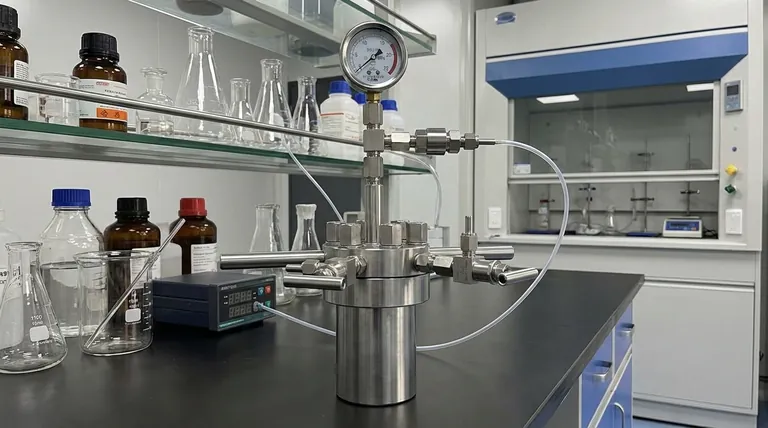
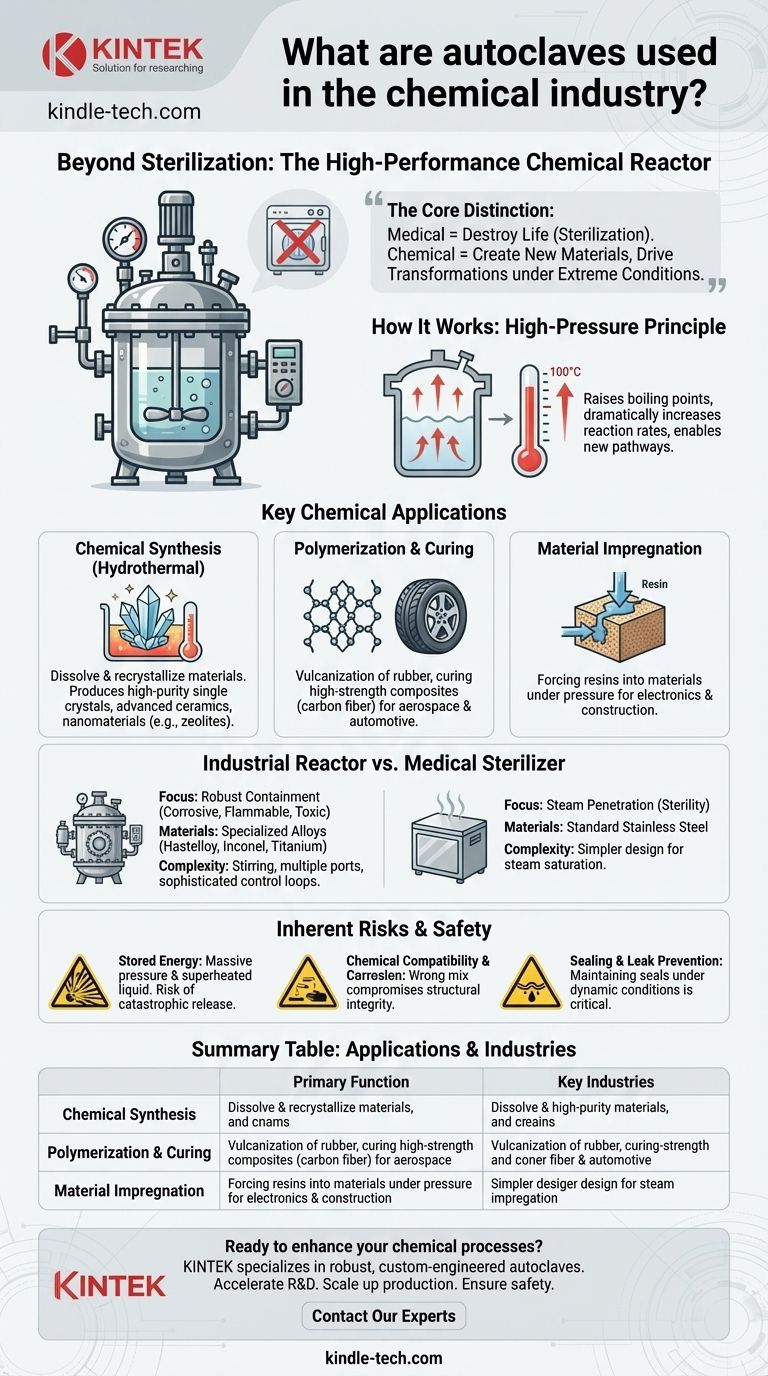
In the chemical industry, an autoclave is far more than a simple sterilizer. While it operates on the same principles of high pressure and high temperature, its primary function shifts from decontamination to serving as a high-performance chemical reactor. It is a critical vessel for synthesizing materials, curing composites, and forcing chemical reactions that would be impossible under normal atmospheric conditions.
The core distinction is one of purpose. In a medical or lab setting, an autoclave's goal is to destroy life (sterilization). In the chemical industry, an autoclave's goal is to create new materials or drive chemical transformations under precisely controlled extreme conditions.

The Autoclave as a High-Pressure Reactor
In chemical applications, the term "autoclave" is often used interchangeably with "high-pressure reactor" or "reaction vessel." The device leverages physics to alter the rules of chemistry.
The Core Principle: Overcoming Limitations
At standard atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). By sealing a vessel and increasing the pressure, an autoclave can raise the boiling point of water or other solvents significantly. This allows chemical reactions to be conducted in a liquid phase at much higher temperatures, dramatically increasing the reaction rate and enabling new chemical pathways.
Key Application: Chemical Synthesis
Many modern materials owe their existence to autoclave-based synthesis. This process, often called hydrothermal synthesis, uses a heated and pressurized aqueous solution to dissolve and recrystallize materials that are otherwise insoluble. This is essential for producing high-purity single crystals, advanced ceramics, and nanomaterials like zeolites, which are critical catalysts in the petroleum industry.
Key Application: Polymerization and Curing
The production of specialized polymers and composites relies heavily on autoclaves. For example, the vulcanization of rubber (as used in car tires) involves heating it with sulfur under pressure in an autoclave to create a more durable, cross-linked material. Similarly, manufacturing high-strength aerospace components from carbon fiber involves curing the resin matrix inside a large autoclave under strict temperature and pressure cycles.
Industrial Reactors vs. Medical Sterilizers
While they share a name, the design and function of an industrial autoclave and a medical autoclave are fundamentally different.
Design Focus: Containment vs. Sterility
A medical autoclave is optimized for steam penetration to ensure all surfaces of an instrument are sterilized. A chemical autoclave is designed for robust containment. It must safely manage potentially corrosive, flammable, or toxic chemicals at extreme pressures and temperatures for extended periods.
Materials of Construction
Medical sterilizers are typically made of standard stainless steel. Industrial autoclaves must be constructed from highly specialized alloys (like Hastelloy, Inconel, or titanium) chosen specifically to resist corrosion from the chemicals being used in the reaction.
Operational Complexity and Control
A chemical reactor autoclave is a complex system. It often includes features absent in a sterilizer, such as:
- Stirring mechanisms (magnetic drives or mechanical agitators) to ensure the reaction mixture is homogenous.
- Multiple ports for introducing reactants, inert gases, or extracting samples during the reaction.
- Sophisticated sensors and control loops for precisely managing temperature, pressure, and reaction kinetics.
Understanding the Inherent Risks
The power of an autoclave also makes it a significant operational hazard if not managed correctly.
The Danger of Stored Energy
An autoclave contains a massive amount of stored energy in the form of compressed gas and superheated liquid. A vessel failure or improper depressurization can result in a catastrophic, explosive release. Strict adherence to safety protocols, regular inspection, and certified pressure relief systems are non-negotiable.
Chemical Compatibility and Corrosion
The wrong combination of chemicals, temperature, and vessel material can lead to rapid corrosion, compromising the structural integrity of the autoclave. Material selection is one of the most critical design decisions and requires deep expertise.
Sealing and Leak Prevention
Maintaining a perfect seal under dynamic temperature and pressure conditions is a major engineering challenge. Failure of gaskets or seals can lead to the release of hazardous materials, creating a significant safety and environmental risk.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When specifying or evaluating an autoclave for a chemical process, your decision must be guided by the specific application.
- If your primary focus is hydrothermal synthesis or catalysis research: Prioritize a reactor with precise temperature/pressure controls, options for different corrosion-resistant alloys, and a robust agitation system.
- If your primary focus is curing composites or impregnating materials: You need a large-volume autoclave capable of executing complex, multi-stage temperature and pressure profiles, often with integrated vacuum systems.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure polymerization: Look for a vessel rated for extreme pressures with specialized safety features like burst discs and advanced monitoring for runaway reactions.
Ultimately, choosing the right industrial autoclave is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts process efficiency, product quality, and operational safety.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Function | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Synthesis | Hydrothermal synthesis of crystals, ceramics, and nanomaterials | Petrochemicals, Nanotechnology |
| Polymerization & Curing | Vulcanizing rubber, curing carbon fiber composites | Aerospace, Automotive, Plastics |
| Material Impregnation | Forcing resins/polymers into materials under pressure | Electronics, Construction |
Ready to enhance your chemical processes with a high-performance autoclave?
KINTEK specializes in robust, custom-engineered autoclaves and high-pressure reactors designed for the demanding needs of the chemical industry. Whether you are synthesizing advanced materials, curing composites, or developing new catalysts, our reactors offer precise control, superior safety features, and corrosion-resistant construction.
We help you:
- Accelerate R&D with reliable, high-pressure reaction vessels.
- Scale up production with autoclaves built for industrial durability.
- Ensure safety with engineered solutions for hazardous processes.
Let's discuss your specific application. Contact our experts today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your laboratory or production facility.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- Why is a PTFE-lined stainless steel autoclave required for Ag@N-TiO2? Ensure Purity and Performance in Synthesis
- How does an autoclave work in simple words? Sterilize with High-Pressure Steam
- How long does it take to vent an autoclave? A Guide to Safe and Efficient Sterilization Cycles
- What are the steps to prepare instruments for autoclaving? Ensure Sterility and Protect Your Equipment
- How do you test the quality of an autoclave? Ensure Sterilization with Biological Indicators
- Why must Zircaloy-4 components undergo high-pressure autoclave steam oxidation? Ensure Critical Corrosion Resistance
- What are the sizes of autoclaves? A Guide to Choosing the Right Capacity for Your Lab
- How does autoclave work inside? Mastering the Science of Steam Sterilization



















