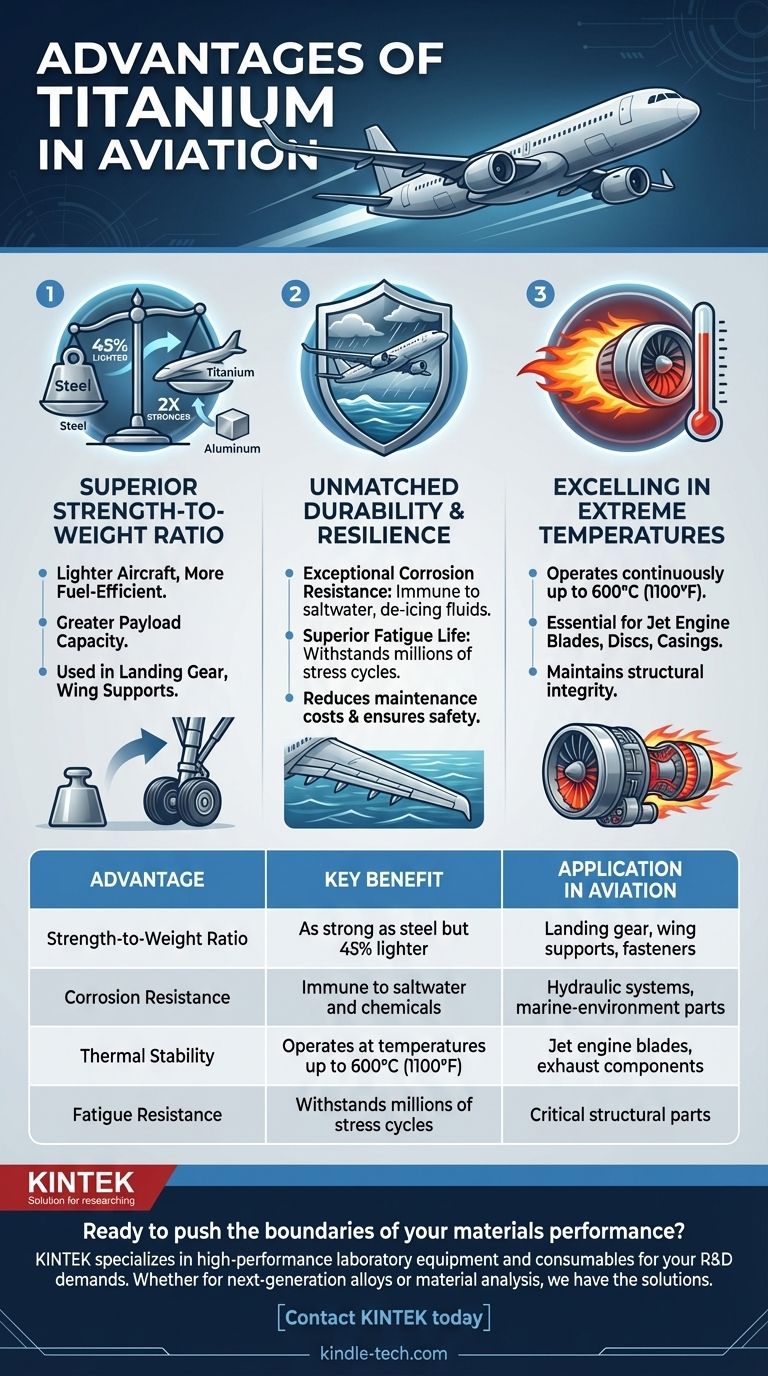
The primary advantages of titanium in aviation are its superior strength-to-weight ratio, exceptional corrosion resistance, and its ability to withstand extreme temperatures. These properties allow for the construction of lighter, more fuel-efficient, and more durable aircraft that can perform reliably under the immense stresses of flight.
Titanium is not chosen because it is the strongest or the cheapest material, but because it delivers the best balance of strength, low weight, and thermal stability for critical aerospace applications where performance and safety are non-negotiable.

The Core Advantage: Strength-to-Weight Ratio
One of the most critical metrics in aerospace engineering is the strength-to-weight ratio. Every kilogram saved on the aircraft's structure translates directly into increased fuel efficiency or greater payload capacity.
A Direct Comparison with Steel and Aluminum
Titanium alloys are as strong as many high-strength steels but are approximately 45% lighter. While aluminum is even lighter, titanium is roughly twice as strong, allowing for the use of smaller, lighter components in high-stress areas.
Impact on Aircraft Performance
This high strength-to-weight ratio is a key enabler of modern aircraft design. It allows engineers to build robust structures, like landing gear and wing supports, that can handle immense forces without adding excessive weight to the airframe.
Unmatched Durability and Resilience
An aircraft is subjected to constant stress, from pressurization cycles to extreme weather. Titanium's inherent durability ensures long-term operational integrity and safety.
Exceptional Corrosion Resistance
Titanium naturally forms a stable, passive layer of titanium dioxide on its surface. This layer makes it virtually immune to corrosion from saltwater, de-icing fluids, and other atmospheric or chemical agents, significantly reducing maintenance costs over the aircraft's lifespan.
Superior Fatigue Life
Fatigue is the weakening of a material caused by repeated, cyclical loads, such as those experienced during takeoff, flight, and landing. Titanium exhibits an outstanding resistance to fatigue cracking, making it the ideal choice for critical structural parts that must endure millions of stress cycles.
Excelling in Extreme Temperatures
Both high-speed flight and jet engines generate immense heat. Materials used in these environments must retain their structural integrity at temperatures that would cripple other metals.
Where Aluminum Fails
Conventional aluminum alloys, the primary material for most of an aircraft's fuselage, begin to lose their strength significantly at temperatures above 150°C (300°F).
Titanium's Thermal Stability
Titanium alloys, by contrast, can operate continuously at temperatures up to 600°C (1100°F). This property makes them indispensable for components in and around the engine, such as compressor blades, discs, and casings, as well as for firewalls.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its clear advantages, titanium is not used for the entire airframe. Its application is strategic, guided by a clear understanding of its limitations.
The Primary Hurdle: High Cost
The extraction and refinement process for titanium is far more complex and energy-intensive than for aluminum or steel. This results in a significantly higher raw material cost.
Difficult Manufacturing and Machining
Titanium is a challenging material to machine and weld. It requires specialized equipment, techniques, and slower processing speeds, which adds to the final component cost. These factors mean it is used only where its specific properties are absolutely necessary.
Where Titanium is Deployed in Modern Aircraft
The decision to use titanium is driven entirely by the operational demands of a specific aircraft component.
- If your primary focus is high-stress structures: Titanium is the premier choice for landing gear, wing boxes, and critical fasteners where maximum strength and low weight are essential.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature environments: It is the only viable option for fan and compressor blades in jet engines, as well as for nacelles and exhaust structures.
- If your primary focus is corrosion and pressure resistance: Titanium is used for hydraulic tubing and components in marine environments where other metals would quickly degrade.
Ultimately, titanium is the enabling material that allows engineers to push the boundaries of aviation performance and safety.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit | Application in Aviation |
|---|---|---|
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | As strong as steel but 45% lighter | Landing gear, wing supports, fasteners |
| Corrosion Resistance | Immune to saltwater and chemicals | Hydraulic systems, marine-environment parts |
| Thermal Stability | Operates at temperatures up to 600°C (1100°F) | Jet engine blades, exhaust components |
| Fatigue Resistance | Withstands millions of stress cycles | Critical structural parts |
Ready to push the boundaries of your materials performance?
Just as titanium's unique properties are essential for aviation innovation, having the right lab equipment is critical for developing and testing advanced materials. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance laboratory equipment and consumables that deliver the precision, durability, and thermal control your R&D demands.
Whether you are working on next-generation alloys or need reliable tools for material analysis, we have the solutions to enhance your lab's efficiency and accuracy.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our specialized equipment can support your critical projects and help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Ultra-High Vacuum Flange Aviation Plug Glass Sintered Airtight Circular Connector for KF ISO CF
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina (Al₂O₃) Ceramic Positioning Pin Straight Bevel for Precision Applications
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are the pros and cons of laser sintering? Unlock Complex, Functional Parts
- What is the principle of wiped film molecular still? Preserve and Purify Heat-Sensitive Compounds
- Is biomass electricity cheap? The True Cost of Dispatchable Renewable Power
- How does debinding work? A Guide to Binder Removal for MIM and 3D Printed Parts
- At what temperature does THC distillate degrade? A Guide to Preserving Potency and Purity
- What role does a laboratory constant temperature shaker play in the fungal strain cultivation stage? Boost Mycelium Growth
- What is the temperature and time for ashing? Achieve Accurate Results with the Right Parameters
- What is the activated carbon regeneration method? Find the Right Process for Your Needs















