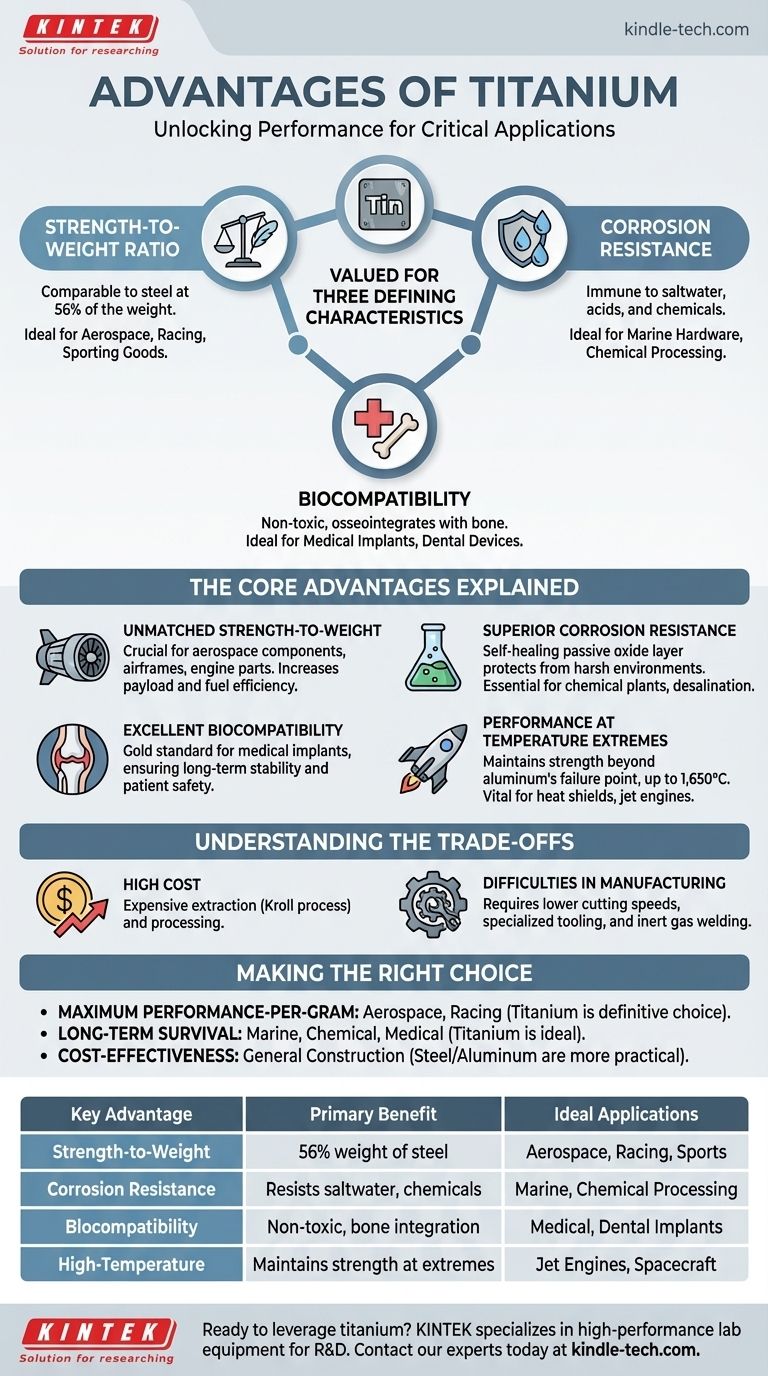
At its core, titanium is valued for three defining characteristics. It possesses an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, is extraordinarily resistant to corrosion, and is highly biocompatible, meaning it is not harmful or toxic to living tissue. These properties make it a premier material for high-performance applications where failure is not an option.
The decision to use titanium is rarely about a single attribute. Instead, it is chosen for its unique and powerful combination of strength, lightness, and resilience, which allows for engineering solutions that are impossible with conventional metals like steel or aluminum.

The Core Advantages of Titanium Explained
To understand why titanium is specified for critical applications, we must look at its fundamental material properties in more detail. Each one solves a distinct engineering challenge.
Unmatched Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Titanium alloys offer strength comparable to many common types of steel but at only 56% of the weight. This makes it the material of choice when every gram counts.
This property is the primary reason for its widespread use in the aerospace industry for components like airframes, landing gear, and high-performance engine parts. Reducing weight directly translates to increased payload capacity, better fuel efficiency, and higher performance.
Superior Corrosion Resistance
Titanium naturally forms a thin, stable, and highly adherent layer of titanium dioxide on its surface when exposed to air or moisture. This passive oxide layer is self-healing and protects the underlying metal from a vast range of corrosive agents.
It is virtually immune to degradation from saltwater, marine environments, and a wide variety of industrial chemicals, including chlorides and acids. This makes it indispensable for marine hardware, chemical processing equipment, and desalination plants.
Excellent Biocompatibility
Titanium is one of the few metals the human body does not reject. It is non-toxic, non-allergenic, and has the ability to osseointegrate, meaning bone can grow directly onto its surface.
This makes it the gold standard for medical implants, including hip and knee replacements, bone screws, dental implants, and pacemaker cases. Its non-reactive nature ensures long-term stability and patient safety inside the body.
Performance at Temperature Extremes
Titanium and its alloys maintain their strength exceptionally well at elevated temperatures, far beyond the point where aluminum alloys would fail. Its high melting point (over 3,000°F or 1,650°C) is key to this performance.
This characteristic is critical for applications like jet engine components and spacecraft heat shields that must operate reliably under extreme thermal stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and choosing titanium involves accepting a clear set of compromises. Its advantages are balanced by significant challenges, primarily related to cost and fabrication.
The Challenge of High Cost
The primary barrier to wider titanium use is its cost. It is significantly more expensive than steel or aluminum.
This high price is driven by the complex and energy-intensive Kroll process required to extract the metal from its ore. The difficulty in processing adds to the final component cost.
Difficulties in Manufacturing
Titanium is a notoriously difficult material to machine and weld. It requires lower cutting speeds, specialized tooling, and a constant flow of coolant to manage heat.
Welding must be done in an inert gas environment (like argon) to prevent contamination from oxygen, which can make the joint brittle and prone to failure. These manufacturing complexities add both time and expense to any project.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a material requires a clear understanding of your project's primary objective. Titanium is a specialized tool, not a universal solution.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance-per-gram: Titanium is the definitive choice for applications in aerospace, racing, and high-end sporting goods where minimizing weight is critical.
- If your primary focus is long-term survival in harsh environments: Titanium's corrosion resistance makes it ideal for marine, chemical, and medical applications where reliability and longevity are paramount.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for structural applications: Steel or aluminum will almost always be the more practical and economical choice for general construction or consumer products.
Ultimately, you choose titanium when the operational demands of the application justify its premium cost.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Primary Benefit | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Strength of steel at 56% of the weight | Aerospace, racing, sporting goods |
| Corrosion Resistance | Resists saltwater, chemicals, and acids | Marine hardware, chemical processing |
| Biocompatibility | Non-toxic, allows for bone integration (osseointegration) | Medical implants, dental devices |
| High-Temperature Performance | Maintains strength at extreme temperatures | Jet engines, spacecraft components |
Ready to leverage the superior properties of titanium for your critical projects? The right equipment is essential for processing advanced materials. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of R&D and quality control laboratories. Whether you are developing new aerospace components, medical implants, or testing materials for extreme environments, our solutions can help you achieve accurate and reliable results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your laboratory's challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Non-Standard Insulator Customization
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hydrothermal Synthesis Reactor Polytetrafluoroethylene Carbon Paper and Carbon Cloth Nano-growth
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Corrosion Resistant Cleaning Rack Flower Basket
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Etching Flower Basket ITO FTO Developing Glue Removal
People Also Ask
- How does RF sputtering work? Deposit Thin Films on Insulating Materials
- Is it fitting the mould or mold? A Guide to Correct Spelling by Region
- How thick is carbon coating for SEM? Optimize Sample Conductivity & Analysis Accuracy
- Which is a disadvantage of the carburizing process? High Costs, Complex Control, and Post-Processing Demands
- What role does an alumina-supported substrate play in CCD? Unlock the 'Gate' Effect for MFI Zeolite Membranes
- What are the types of centrifuges and their applications? Find the Right Tool for Your Separation Needs
- What machine is used for pyrolysis? Choose the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Goals
- How is powder metallurgy different from other manufacturing processes? Build Parts with Minimal Waste



















