In optics, thin films are specialized coatings used to precisely control how a surface reflects, transmits, or absorbs light. These layers, often just nanometers thick, are the reason your glasses have less glare, your camera lens produces a sharper image, and a solar panel can efficiently convert sunlight into energy. Their applications range from everyday consumer electronics and architectural glass to advanced scientific instruments and photovoltaics.
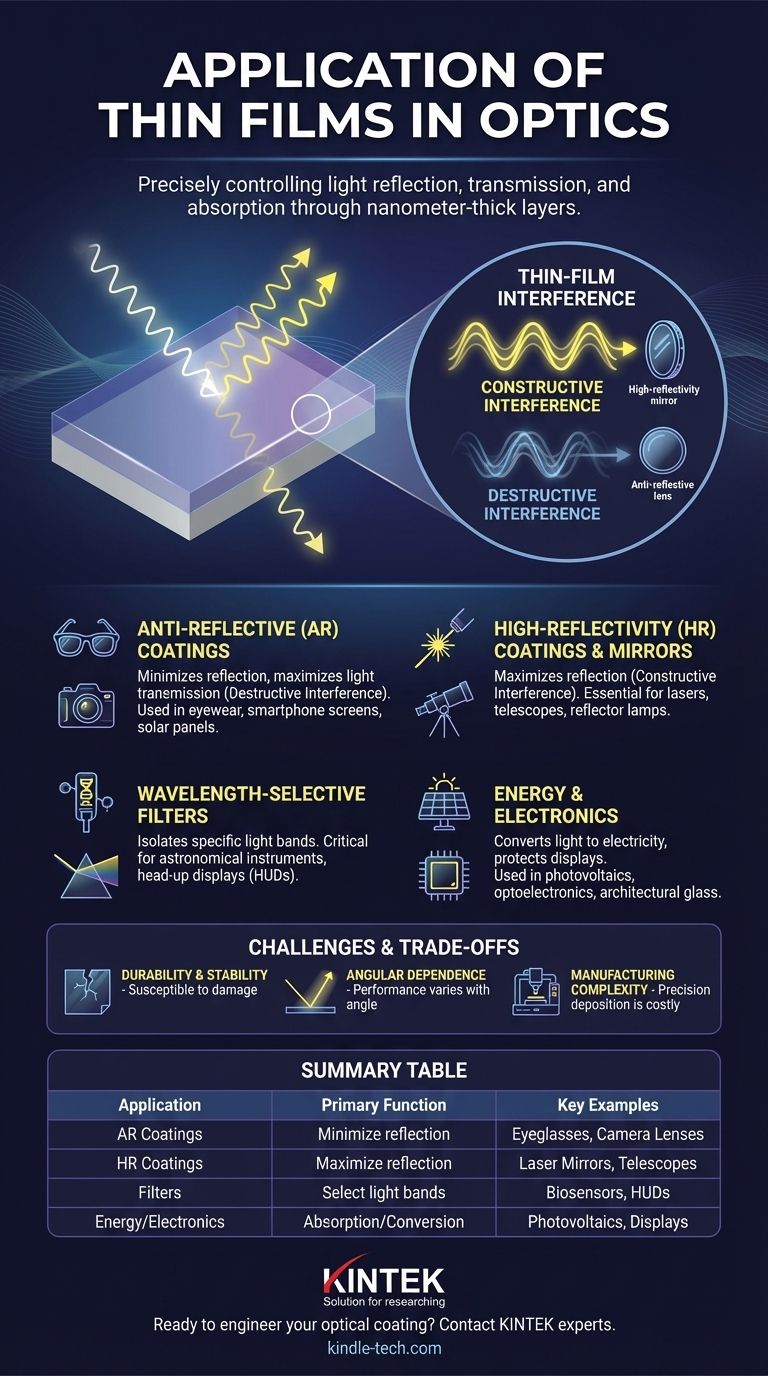
The essential purpose of a thin film in optics is not to act as a simple barrier, but to manipulate light waves through a principle called thin-film interference. By controlling the thickness and refractive index of these atomically thin layers, we can dictate whether light waves cancel each other out or reinforce one another, fundamentally altering the optical properties of any surface.
The Core Principle: Manipulating Light with Interference
The function of an optical thin film is rooted in wave physics. It’s not about the bulk properties of the material, but what happens when the film's thickness is comparable to the wavelength of light itself.
How a Nanometer-Thick Layer Changes Everything
When light hits a coated surface, some of it reflects from the top surface of the thin film, and some reflects from the bottom surface (at the film-substrate interface).
Because the film has a specific thickness, the light wave traveling to the bottom surface travels a slightly longer path than the one reflecting from the top.
Constructive vs. Destructive Interference
These two reflected light waves then interact with each other.
If the waves are in sync (in-phase), they combine and strengthen each other, a phenomenon called constructive interference. This is used to create highly reflective surfaces.
If the waves are out of sync (out-of-phase), they cancel each other out, a phenomenon called destructive interference. This is the principle behind anti-reflective coatings.
Material and Thickness are the Levers
Engineers have two primary controls: the material of the film (which determines its refractive index) and its precise thickness. By carefully selecting these two variables, they can "tune" the interference effect to control specific wavelengths (colors) of light.
Key Applications Driven by Interference
This ability to control light provides a powerful toolkit for a vast range of optical applications. Different goals simply require designing for different interference outcomes.
Anti-Reflective (AR) Coatings
AR coatings are designed for destructive interference, canceling out reflected light and allowing more light to pass through the material. This improves clarity and efficiency.
You find them on ophthalmic lenses, smartphone screens, camera lenses, and the glass on solar panels to maximize the light reaching the active cells.
High-Reflectivity (HR) Coatings & Mirrors
These coatings use constructive interference to create surfaces that are far more reflective than a simple polished metal. By stacking multiple layers, it's possible to achieve nearly 100% reflectivity for specific wavelengths.
This technology is critical for mirrors used in lasers, telescopes, reflector lamps, and other high-performance optical instruments.
Wavelength-Selective Filters
By stacking multiple thin films with different properties, it's possible to create complex filters that only transmit or reflect very specific bands of light.
These are essential in astronomical instrumentation to isolate light from distant stars, in biosensors, and in head-up displays (HUDs) for the automotive industry.
Energy and Electronics
In photovoltaics, thin films serve a dual purpose. They are used as AR coatings to maximize light absorption and as the active semiconductor layer itself, converting photons into electrons.
They are also foundational in optoelectronics, protective coatings for displays, and even thermal insulation on architectural glass, which reflects infrared (heat) radiation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, thin film technology is not without its challenges. The performance of a coating depends on a delicate balance of physics, material science, and manufacturing precision.
Durability and Stability
Thin films are, by definition, thin. They can be susceptible to mechanical abrasion, scratches, and damage from environmental factors like humidity and temperature shifts, which can alter their thickness and degrade optical performance.
Angular Dependence
The performance of many interference-based coatings is highly dependent on the angle of incidence. An anti-reflective coating on a camera lens may work perfectly for light coming straight on but become noticeably reflective for light hitting it at a steep angle.
Manufacturing Complexity and Cost
Achieving atomic-level precision across a surface requires sophisticated deposition techniques in vacuum chambers. This process can be complex, slow, and costly, especially for large or uniquely shaped optics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct thin film strategy is dictated entirely by your desired optical outcome. The design process always starts by defining what you want light to do at the surface.
- If your primary focus is maximizing light transmission: You need an anti-reflective (AR) coating designed for destructive interference across your target wavelength range.
- If your primary focus is creating a highly efficient mirror: You need a multi-layer dielectric stack designed for constructive interference to build reflectivity for specific wavelengths.
- If your primary focus is converting light into electricity: Your solution is a system of films, including AR coatings to capture light and active semiconductor layers to perform the conversion.
- If your primary focus is filtering specific colors: Your approach will involve a complex multi-layer design that uses both constructive and destructive interference to pass or block narrow bands of the spectrum.
Ultimately, mastering thin film technology allows us to command the flow of light at the most fundamental level.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Function | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Reflective (AR) Coatings | Destructive interference to minimize reflection | Eyeglasses, camera lenses, solar panels |
| High-Reflectivity (HR) Coatings | Constructive interference to maximize reflection | Laser mirrors, telescope optics |
| Wavelength-Selective Filters | Transmit or reflect specific light bands | Biosensors, astronomical instruments, HUDs |
| Energy & Electronics | Light absorption & conversion, protection | Photovoltaics, display coatings, architectural glass |
Ready to engineer the perfect optical coating for your application? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced thin film solutions for laboratories and industry. Whether you need to develop anti-reflective coatings for sensitive instruments, high-reflectivity mirrors for laser systems, or custom filters for research, our expertise in precision deposition and material science ensures optimal performance. Let us help you control light with nanometer precision—contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Barium Fluoride BaF2 Substrate Window
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
People Also Ask
- What are the components of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition Systems
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- What is the temperature of PECVD deposition? Achieve High-Quality Films at Low Temperatures
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition













