At its core, vacuum evaporation is a versatile process with two distinct, primary applications. It is used to either create ultra-pure thin film coatings for industries like optics and electronics, or to efficiently separate and purify liquids, most notably in industrial wastewater treatment. This dual utility stems from a single physical principle: lowering pressure to reduce a material's boiling point.
The fundamental advantage of vacuum evaporation is its ability to induce a phase change (from solid or liquid to gas) with less energy. This allows for either the precise deposition of a material onto a surface as a thin film or the efficient separation of clean water from dissolved contaminants.
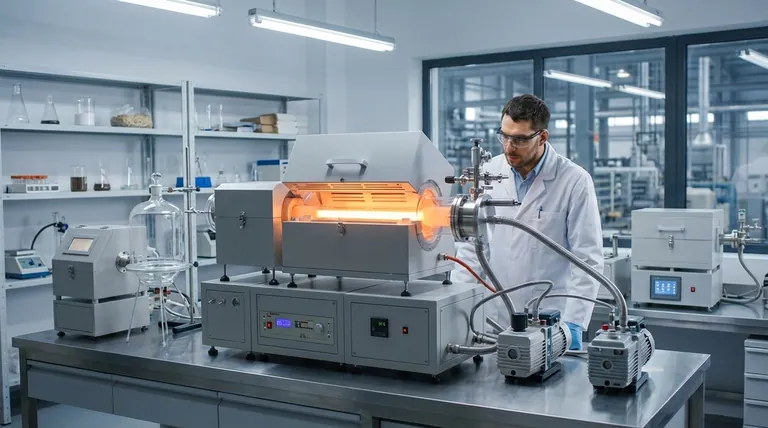

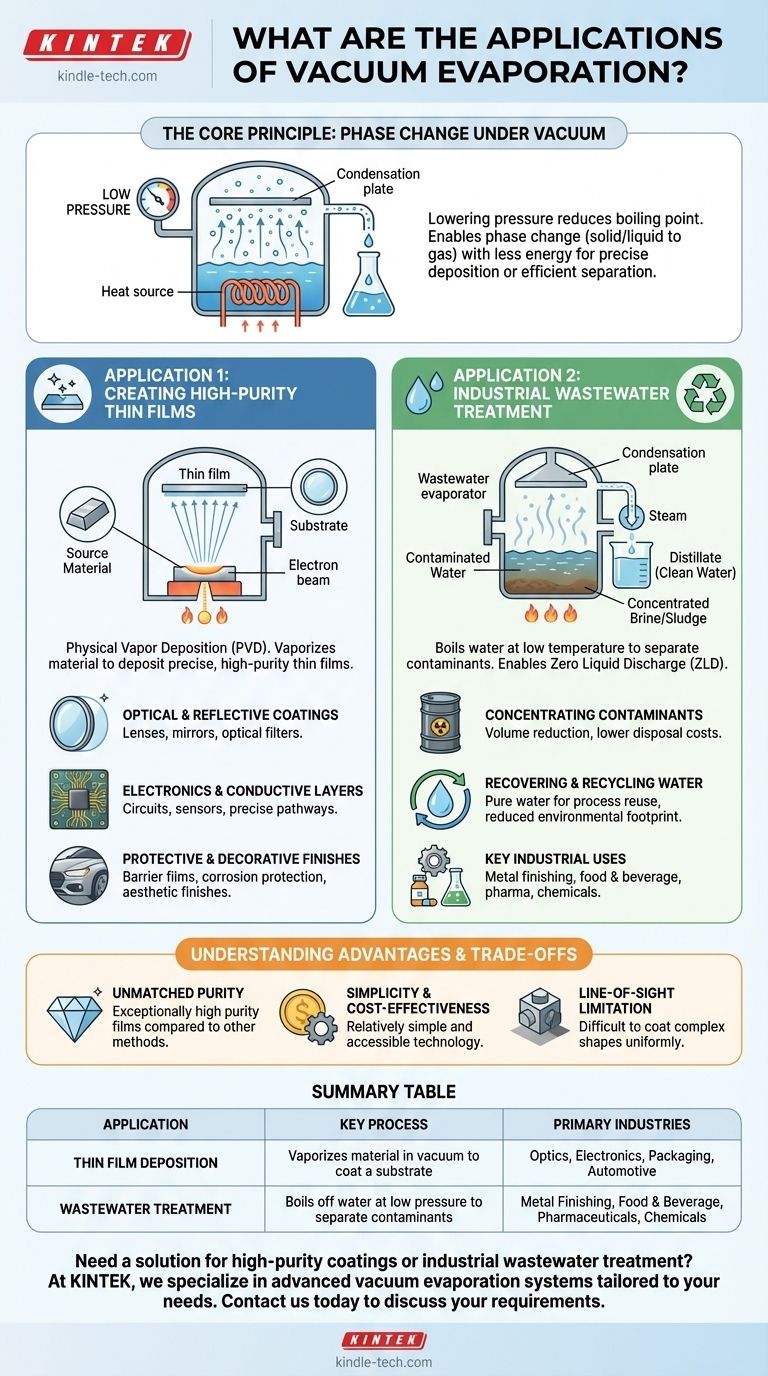
The Core Principle: Phase Change Under Vacuum
Vacuum evaporation leverages the direct relationship between pressure and a substance's boiling point. By removing air from a chamber, we create a low-pressure environment where materials can be vaporized at much lower temperatures than they would require at normal atmospheric pressure.
The Mechanism of Deposition
In thin film deposition, a source material (like a metal) is heated inside a vacuum chamber. Because of the low pressure, it evaporates into a vapor, travels in a straight line, and then condenses onto a cooler target object (the substrate), forming a solid, thin, and highly pure film.
The Mechanism of Separation
In wastewater treatment, the contaminated water is placed under a vacuum and heated. The water boils at a low temperature, turning into vapor (steam), while the contaminants with higher boiling points are left behind. This vapor is then collected and condensed back into purified liquid water, called distillate.
Application 1: Creating High-Purity Thin Films
This process, a type of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), is foundational for manufacturing a wide range of advanced products. When used with metals, it is often called vacuum metallization.
Optical and Reflective Coatings
Vacuum evaporation is used to apply precise layers of material onto lenses and mirrors. These layers can create anti-reflective properties, specific filtering capabilities (optical interference coatings), or highly reflective surfaces for mirrors and telescopes.
Electronics and Conductive Layers
Thin, electrically conductive films are deposited onto circuits and components. This is a critical step in manufacturing various electronic devices where precise, pure conductive pathways are required.
Protective and Decorative Finishes
The process creates barrier films on flexible packaging materials, protecting contents from oxygen and moisture. It is also widely used for durable, corrosion-protective coatings and for applying shiny, metallic decorative finishes on everything from automotive parts to consumer goods.
Application 2: Industrial Wastewater Treatment
This is one of the most effective methods for managing complex industrial waste streams, enabling a "zero liquid discharge" approach in many facilities.
Concentrating Contaminants
By boiling off the water, the process leaves behind a highly concentrated brine or sludge. This dramatically reduces the volume of hazardous waste that needs to be handled, transported, and disposed of, leading to significant cost savings.
Recovering and Recycling Water
The clean water vapor, once condensed, is a valuable resource. This distilled water is often pure enough to be recycled directly back into the industrial process, reducing a facility's overall water consumption and environmental footprint.
Key Industrial Uses
This technology is critical in sectors that produce challenging wastewater, including metal forming and finishing, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing. It effectively separates water from salts, heavy metals, oils, and other contaminants.
Understanding the Advantages and Trade-offs
Choosing vacuum evaporation depends on balancing its benefits against the requirements of the specific application.
Unmatched Purity
Because the process occurs in a vacuum and the source material is directly vaporized, it is possible to create films of exceptionally high purity. This is a major advantage over chemical or electroplating methods.
Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to more complex PVD methods like sputtering, vacuum evaporation is a relatively simple, mature, and inexpensive process, making it a highly accessible technology for many coating applications.
The "Line-of-Sight" Limitation
A key consideration for deposition is that the vapor travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. While excellent for coating flat surfaces, this makes it difficult to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional objects with hidden areas or undercuts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if vacuum evaporation is the right solution, clarify your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is creating high-performance coatings: Vacuum evaporation offers a cost-effective and reliable method for depositing simple, high-purity films onto direct-facing surfaces.
- If your primary focus is managing complex industrial wastewater: This process is an exceptional choice for separating pure water from dissolved contaminants, enabling water recycling and waste volume reduction.
- If your primary focus is increasing the concentration of a solution: The technology efficiently removes water to increase the concentration of valuable or hazardous substances for recovery or disposal.
Ultimately, vacuum evaporation is a powerful tool precisely because it masters a fundamental physical principle to solve critical industrial challenges.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Process | Primary Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Thin Film Deposition | Vaporizes material in a vacuum to coat a substrate | Optics, Electronics, Packaging, Automotive |
| Wastewater Treatment | Boils off water at low pressure to separate contaminants | Metal Finishing, Food & Beverage, Pharmaceuticals, Chemicals |
Need a solution for high-purity coatings or industrial wastewater treatment?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced vacuum evaporation systems tailored to your specific laboratory and industrial needs. Whether you're developing next-generation electronics, creating precise optical coatings, or aiming for zero liquid discharge in your facility, our expertise and equipment can help you achieve superior results with efficiency and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss how our lab equipment and consumables can enhance your processes and deliver the purity and performance you require.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating


















