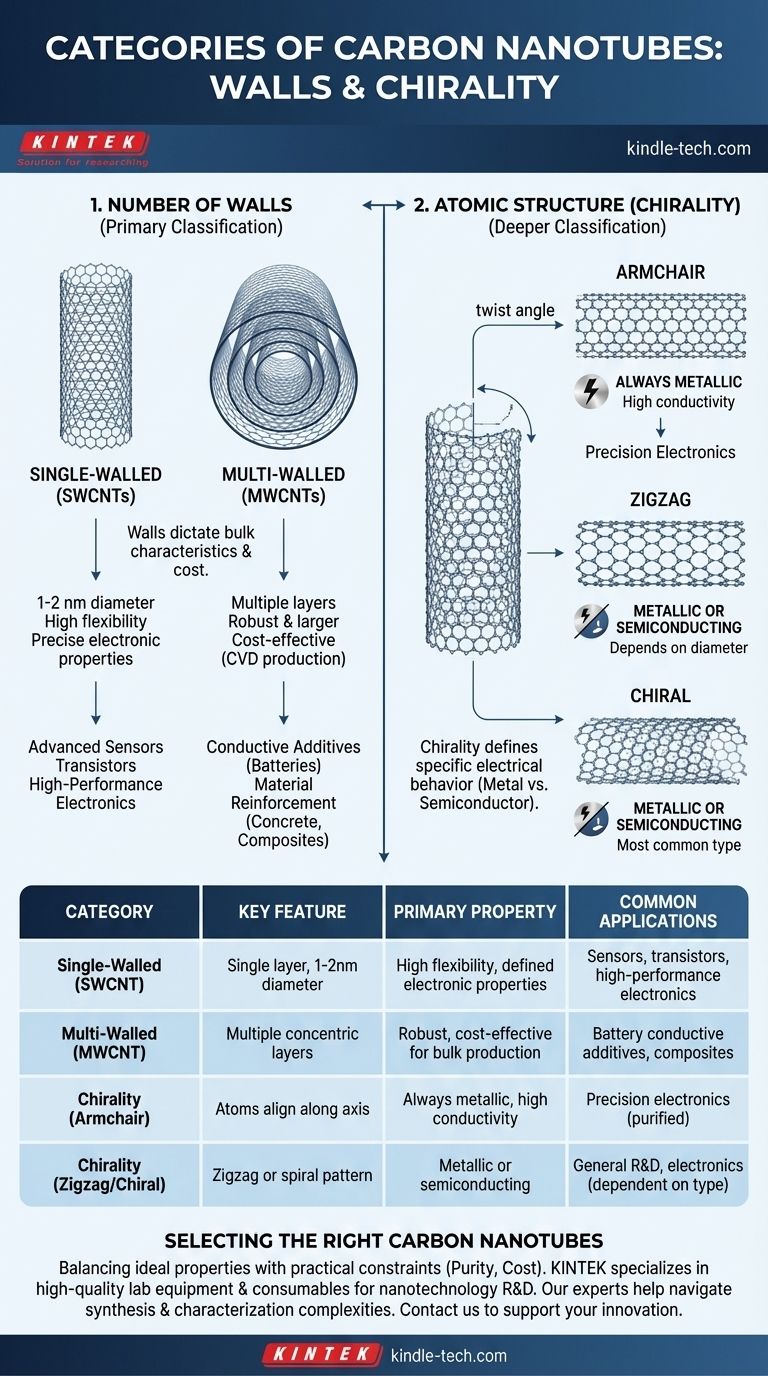
Carbon nanotubes are primarily categorized in two fundamental ways: first by the number of concentric walls they possess, and second by their atomic structure, known as chirality. These structural differences directly determine the nanotube's unique electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties.
The most critical distinction to understand is that the number of walls (single vs. multi-walled) dictates the nanotube's bulk characteristics and cost, while its specific atomic arrangement (chirality) defines its precise electrical behavior, determining if it acts like a metal or a semiconductor.
The Primary Classification: Number of Walls
The most straightforward way to classify carbon nanotubes (CNTs) is by counting the layers of rolled-up graphene that form the tube's structure.
Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWCNTs)
A single-walled carbon nanotube is the simplest form, consisting of a single sheet of graphene seamlessly rolled into a cylindrical tube.
These tubes have exceptionally small diameters, typically 1-2 nanometers, which gives them remarkable and precisely defined properties. SWCNTs are prized for their high flexibility and unique electronic characteristics.
Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs)
Multi-walled carbon nanotubes consist of multiple, concentric cylinders of graphene nested inside one another, much like the rings of a tree trunk.
MWCNTs are larger and more robust than SWCNTs. Because they are generally easier and cheaper to produce in large quantities through methods like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), they are more common in commercial applications today.
The Deeper Classification: Atomic Structure (Chirality)
The second, more nuanced classification is based on chirality, which describes the angle at which the graphene sheet is "rolled" to form the tube. This angle dictates the pattern of carbon atoms along the tube's surface and is the single most important factor in determining its electrical properties.
What is Chirality?
Imagine a flat sheet of chicken wire (representing graphene). You can roll it up straight, at a slight angle, or at a sharper angle. Each method creates a different pattern where the edges meet. This "twist" is its chirality.
Armchair Nanotubes
In an armchair configuration, the carbon atoms align perfectly along the axis of the tube. This structure creates a clear path for electrons to flow without resistance.
As a result, armchair nanotubes are always metallic and exhibit extremely high electrical conductivity.
Zigzag Nanotubes
In a zigzag structure, the pattern of carbon atoms forms a zigzag pattern at the open end of the tube.
Depending on the exact diameter of the tube, zigzag nanotubes can be either metallic or semiconducting.
Chiral Nanotubes
Most nanotubes fall into this category, where the carbon atoms spiral around the axis of the tube at an angle.
Like zigzag nanotubes, chiral tubes can be either metallic or semiconducting, depending on their specific angle of twist and diameter.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Practical Realities
While these classifications are precise, the reality of producing and using CNTs involves significant practical challenges and trade-offs.
Purity and Separation
Current synthesis methods, including the dominant commercial process of CVD, typically produce a mixture of different chiralities and diameters.
Separating these nanotubes to isolate a single type (e.g., only metallic armchair SWCNTs) is an expensive and complex process, which is a major barrier to their use in precision electronics.
SWCNTs vs. MWCNTs in Application
For applications requiring bulk material enhancement, MWCNTs are the dominant choice. Their lower production cost and robustness make them ideal as conductive additives in lithium-ion batteries or as a reinforcing agent in materials like concrete.
SWCNTs are reserved for high-performance applications where their unique, precisely defined properties are critical, such as in advanced sensors, transistors, and transparent conductive films.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right category of CNT depends entirely on balancing the ideal properties required for an application with the practical constraints of manufacturing and cost.
- If your primary focus is bulk conductivity or mechanical reinforcement: Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) are the standard choice due to their lower cost and robust production.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or specific optical properties: Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) with a specific, purified chirality are required, though this remains a significant technical and financial challenge.
- If you are exploring general research and development: It is critical to characterize the mixture of nanotube types produced by your synthesis method to correctly interpret experimental results.
Ultimately, understanding these fundamental categories is the first step toward harnessing the extraordinary potential of these materials for your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Category | Key Feature | Primary Property | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Walled (SWCNT) | Single graphene layer, small diameter (1-2 nm) | High flexibility, defined electronic properties | Advanced sensors, transistors, high-performance electronics |
| Multi-Walled (MWCNT) | Multiple concentric graphene layers | Robust, cost-effective for bulk production | Conductive additives (batteries), material reinforcement (composites) |
| Chirality (Armchair) | Atoms align along tube axis | Always metallic, high conductivity | Precision electronics (when purified) |
| Chirality (Zigzag/Chiral) | Atoms form zigzag or spiral pattern | Metallic or semiconducting | General R&D, electronics (dependent on type) |
Struggling to select the right carbon nanotubes for your project? The choice between SWCNTs and MWCNTs is critical for achieving optimal performance in applications like battery materials, composite reinforcement, or advanced electronics. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for nanotechnology research and development. Our experts can help you navigate the complexities of CNT synthesis and characterization to ensure your materials meet your specific goals. Contact us today to discuss your application needs and discover how KINTEK can support your innovation. Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Conductive Carbon Fiber Brush for Static Removal and Cleaning
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Magnetic Stirring Bar
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- What is the process of thin film optical coating? Precision Light Control for Lenses & Mirrors
- What is an ITO target? The Key to Transparent, Conductive Coatings for Displays and Solar Panels
- What are the importance of carbon nanotubes? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What is the evaporation process in semiconductors? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- Which material is used in thin film? Discover the Right Material for Your Application
- What are the methods of synthesis for carbon nanotubes? A Guide to Arc Discharge, Laser Ablation & CVD
- What makes nanotubes special? Discover the Revolutionary Material Combining Strength, Conductivity & Lightness
- How can nanotubes be used as a catalyst? Enhance Performance and Durability of Metal Catalysts



















