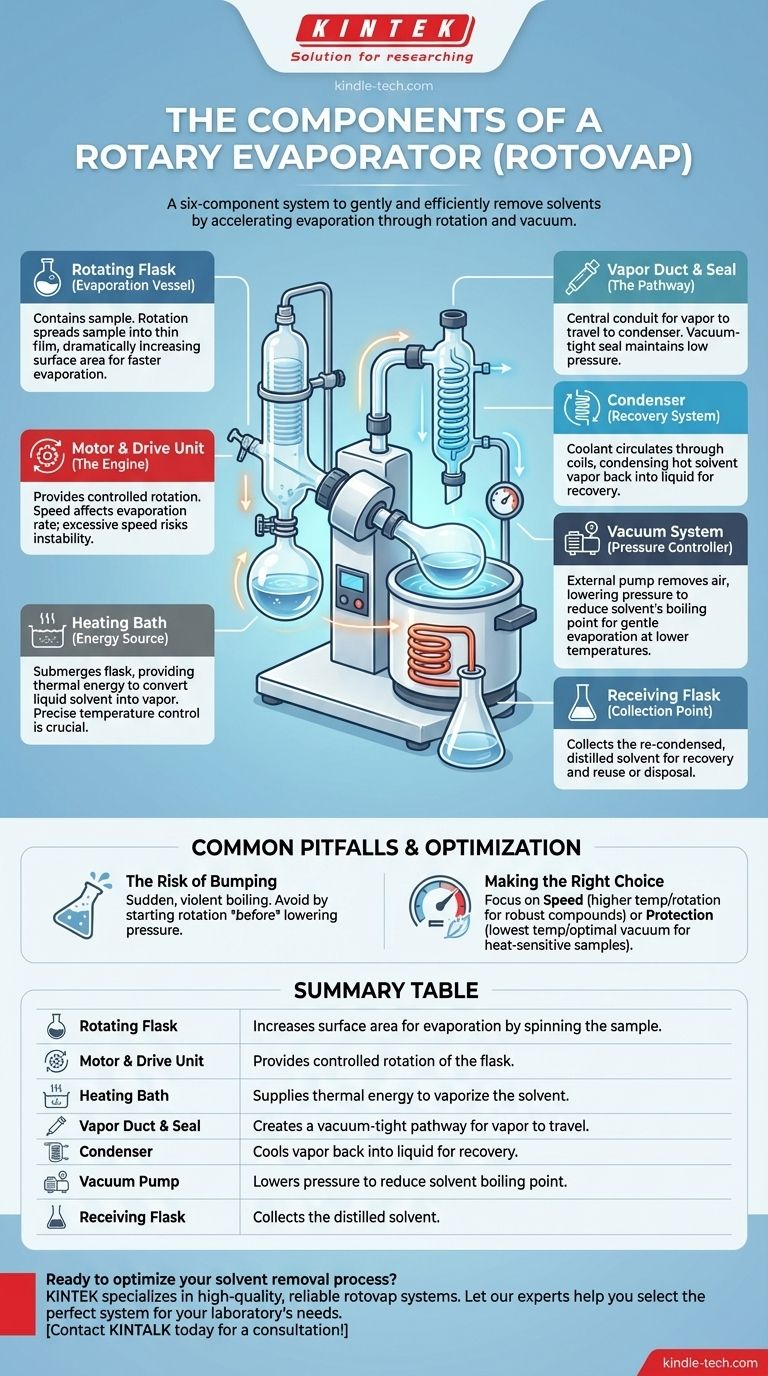
At its core, a rotary evaporator, or rotovap, is a system of six primary components working together. These are the rotating flask, a motor to turn it, a heating bath, a condenser, a receiving flask for the distilled solvent, and a vacuum pump to lower the system's pressure. The purpose of this assembly is to gently and efficiently remove solvents from a sample.
A rotovap is not just a collection of glassware; it's an integrated system designed to accelerate evaporation. It achieves this by increasing the liquid's surface area through rotation while simultaneously lowering the solvent's boiling point with a vacuum.

The Anatomy of a Rotary Evaporator
Each component of a rotovap plays a distinct and critical role in the distillation process. Understanding the function of each part is essential for operating the instrument effectively and safely.
The Rotating Flask (The Evaporation Vessel)
This is the round-bottom flask containing your sample. It is attached to the main apparatus and rotated during the process.
The rotation constantly spreads the sample into a thin film on the flask's inner surface. This dramatically increases the surface area available for evaporation, making the process much faster than static heating.
The Motor and Drive Unit (The Engine)
This is the mechanical component that provides the controlled rotation of the evaporation flask.
The speed of rotation is adjustable. A faster spin generally increases the evaporation rate, but an excessive speed can cause mechanical instability.
The Heating Bath (The Energy Source)
The rotating flask is partially submerged in a temperature-controlled bath, typically filled with water or oil.
This bath provides the thermal energy (heat) needed to convert the solvent from a liquid into a vapor. Precise temperature control is crucial, especially for heat-sensitive compounds.
The Vapor Duct and Seal (The Pathway)
This is the central glass tube that connects the rotating flask to the rest of the system. It serves as the conduit for the solvent vapor to travel from the flask to the condenser.
A critical part of this is the vacuum-tight seal, which allows the flask to rotate freely while maintaining the low pressure inside the system.
The Condenser (The Recovery System)
The condenser is a coil of glass tubing through which a coolant (like cold water or a glycol mixture) is circulated.
As the hot solvent vapor passes over these cold coils, it condenses back into a liquid. This is the core of the solvent recovery process.
The Receiving Flask (The Collection Point)
Positioned at the bottom of the condenser, this flask simply collects the re-condensed solvent. This allows for the easy recovery and potential reuse or proper disposal of the solvent.
The Vacuum System (The Pressure Controller)
An external vacuum pump is connected to the system. This is arguably the most important component for gentle evaporation.
By removing air and reducing the pressure inside the apparatus, the vacuum lowers the boiling point of the solvent. This allows you to evaporate solvents at a much lower temperature than you could at normal atmospheric pressure, protecting sensitive samples from thermal degradation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While highly effective, a rotovap is a precision instrument where improper technique can lead to poor results or safety hazards.
The Risk of Bumping
Bumping is the sudden, violent boiling of a liquid. In a rotovap, this can cause your sample to splash out of the rotating flask and contaminate the entire system.
This is often caused by applying the vacuum too quickly or setting the bath temperature too high before rotation begins. Always start the rotation before lowering the pressure.
Solvent Compatibility Issues
High-boiling-point solvents like water or DMSO can be very slow to remove, even under a deep vacuum. This requires higher bath temperatures and more patience.
Additionally, highly corrosive solvents like concentrated acids can damage the seals and joints of the apparatus over time if not used with appropriately rated equipment.
Not for Complete Drying
A rotovap is a tool for bulk solvent removal. It is excellent for reducing a sample from hundreds of milliliters down to a few, but it is not designed to produce a perfectly dry, solvent-free powder.
Achieving a completely dry sample typically requires a secondary step, such as placing the sample in a vacuum oven or on a high-vacuum line.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational settings should always be dictated by the nature of your sample and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is speed for a robust compound: You can use a higher bath temperature (about 20°C below the solvent's atmospheric boiling point) and a faster rotation speed.
- If your primary focus is protecting a heat-sensitive sample: Use the lowest possible bath temperature and find the optimal vacuum level that allows for a steady, controlled rate of evaporation.
By understanding how each component contributes to the whole, you can move from simply using a rotovap to mastering it for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Rotating Flask | Increases surface area for evaporation by spinning the sample |
| Motor & Drive Unit | Provides controlled rotation of the flask |
| Heating Bath | Supplies thermal energy to vaporize the solvent |
| Vapor Duct & Seal | Creates a vacuum-tight pathway for vapor to travel |
| Condenser | Cools vapor back into liquid for recovery |
| Vacuum Pump | Lowers pressure to reduce solvent boiling point |
| Receiving Flask | Collects the distilled solvent |
Ready to optimize your solvent removal process? The right rotary evaporator is key to efficiency and sample integrity. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including reliable rotovap systems and consumables designed for precise, safe evaporation. Let our experts help you select the perfect system for your laboratory's specific needs.
Contact KINTALK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- How does a Rotary Vane Pump operate? Discover Efficient Vacuum Technology for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of rotary vane pumps? Unlock Cost-Effective, High-Performance Vacuum
- Why is a gas ballast valve necessary on a rotary vane vacuum pump? Protect Your Oil and Extend Pump Life
- What are the limitations of rotary vane pumps? Understanding Oil Dependence and Gas Compatibility
- What are the common configurations and typical performance specifications of Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps? Expert Guide



















