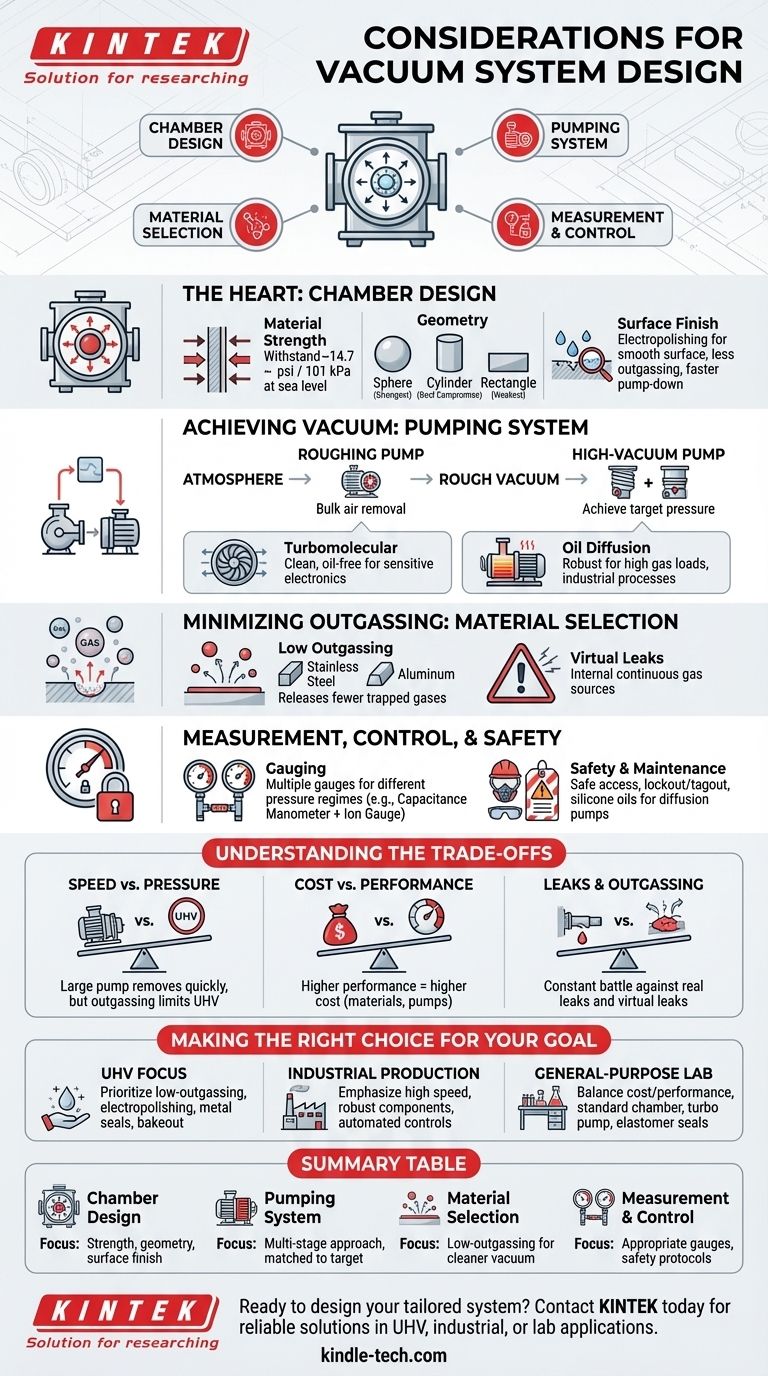
At its core, designing a vacuum system requires a holistic approach that considers four key areas. These are the structural design of the chamber, the selection of materials to minimize outgassing, the choice of an appropriate pumping system to achieve the target pressure, and the integration of components for measurement and control.
A successful vacuum system is not merely a strong container; it is a carefully balanced environment where pumping speed must consistently overcome gas loads from leaks and material outgassing to reach and maintain your desired vacuum level.

The Heart of the System: Chamber Design
The vacuum chamber is the physical foundation of your system. Its design directly impacts the ultimate pressure you can achieve and the system's overall reliability.
Material Selection
Materials must be strong enough to withstand atmospheric pressure, which exerts an enormous force of approximately 14.7 pounds per square inch (101 kPa) at sea level.
Beyond strength, materials must have low outgassing rates. Outgassing is the release of trapped gases from the bulk of a material or its surface, which acts as an internal, continuous gas source that your pumps must overcome. Stainless steel and aluminum are common choices.
Chamber Geometry
The shape of the chamber impacts both its structural integrity and its usability. Spherical chambers are the strongest shape for resisting external pressure but are often impractical.
Cylindrical chambers, whether horizontal or vertical, offer a good compromise between strength and accessibility. Rectangular chambers are the weakest and require significant reinforcement, but they can be necessary to accommodate specific internal equipment.
Surface Finish
The interior surface of the chamber plays a critical role. A rough, unpolished surface has a much larger effective surface area than a smooth one.
This increased area can trap more water vapor and other contaminants, leading to higher outgassing and longer pump-down times. Electropolishing is a common treatment used to create a smooth, clean, and passive interior surface that minimizes this effect.
Achieving the Vacuum: The Pumping System
No single pump can efficiently take a system from atmospheric pressure down to a high vacuum. A well-designed system almost always uses a multi-stage approach.
The Two-Stage Approach
Systems typically pair a roughing pump with a high-vacuum pump. The roughing pump (e.g., a rotary vane or scroll pump) removes the bulk of the air, taking the chamber from atmosphere down to a rough vacuum level.
Once the rough vacuum is achieved, a high-vacuum pump (e.g., a turbomolecular or diffusion pump) takes over. These pumps operate efficiently only at low pressures and are responsible for achieving the final target vacuum.
Matching the Pump to the Process
The type of high-vacuum pump chosen depends on the application. Turbomolecular pumps offer a clean, oil-free vacuum, which is critical for sensitive electronics or research applications.
Oil diffusion pumps are robust and can handle higher gas loads, making them suitable for industrial processes like vacuum furnace brazing. However, they require careful handling to prevent hot pump oil from reacting explosively with air if the system is vented improperly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Designing a vacuum system is an exercise in managing competing priorities. Recognizing these trade-offs is essential for making sound engineering decisions.
Pumping Speed vs. Ultimate Pressure
A large, fast pump will evacuate a chamber quickly, but it may not be able to overcome the persistent gas load from outgassing to reach an ultra-high vacuum (UHV) level. Achieving the lowest possible pressures often depends more on material selection and leak tightness than on raw pumping speed.
Cost vs. Performance
Higher performance almost always comes at a higher cost. Exotic low-outgassing materials, advanced surface treatments like electropolishing, and high-end pumps significantly increase the system's price. You must balance the required vacuum performance for your application against the project budget.
Leaks and Outgassing
A vacuum system is in a constant battle against two gas sources: real leaks from the outside atmosphere and virtual leaks (outgassing) from internal components. A design that is theoretically perfect can be completely undermined by a single leaky fitting or the use of an inappropriate material like plastic inside the chamber.
Measurement, Control, and Safety
A system is incomplete without the means to measure its performance, control its state, and ensure it can be operated and maintained safely.
Gauging: You Can't Control What You Can't Measure
Different vacuum gauges operate in different pressure regimes. A system often requires multiple gauges—for example, a capacitance manometer for the rough vacuum range and an ion gauge for the high-vacuum range—to provide accurate readings across the entire operational spectrum.
Designing for Safe Maintenance
The design must allow for safe access to internal components. This includes implementing electrical lockout/tagout procedures for any high-voltage equipment and adhering to confined space entry protocols if personnel must work inside a large chamber.
Component selection itself is a safety consideration. For example, using silicone-based oils in diffusion pumps can eliminate the explosion hazard associated with traditional hydrocarbon-based oils.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final design should be dictated by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is reaching Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV): Prioritize low-outgassing materials, electropolished surfaces, metal-sealed flanges, and a bakeout system to drive off water vapor.
- If your primary focus is fast-cycling industrial production: Emphasize high pumping speed with oversized pumps, robust and easily serviceable components, and automated valve controls.
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose lab system: Balance cost and performance with a standard stainless-steel chamber, a reliable turbo pump, and elastomer seals for flexibility and ease of use.
Ultimately, a thoughtfully designed vacuum system is one that reliably and safely achieves the specific conditions your process requires.
Summary Table:
| Key Consideration | Primary Focus |
|---|---|
| Chamber Design | Material strength, geometry, and surface finish to minimize outgassing. |
| Pumping System | Multi-stage approach (roughing + high-vacuum pump) matched to the target pressure. |
| Material Selection | Low-outgassing materials (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum) for cleaner vacuum. |
| Measurement & Control | Appropriate gauges and safety protocols for accurate and safe operation. |
Ready to design a vacuum system tailored to your specific application?
Whether your goal is Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV), fast-cycling industrial production, or a versatile general-purpose lab system, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment ensures you get a reliable and efficient solution. Our team can help you select the right components and design a system that balances performance, cost, and safety.
Contact us today to discuss your vacuum system needs and let KINTEK provide the precision and reliability your laboratory requires.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- 304 316 Stainless Steel Vacuum Ball Valve Stop Valve for High Vacuum Systems
- KF/ISO/CF Ultra-High Vacuum Stainless Steel Flange Pipe/Straight Pipe/Tee/Cross
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the attractive feature of liquid phase or reaction sintering? Achieve High Density at Lower Temperatures
- What role do high-precision melting furnaces play in stir casting? Master Precision in Zinc-Based Composites
- What is the function of the vacuum pressure impregnation tank in the PIP process? Achieve High-Density CMCs
- Why is a 1000°C+ furnace needed for LLZO/LLTO? Mastering High-Temperature Sintering for Ceramic Electrolytes
- What is the process of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Material Performance and Purity
- What are the factors influencing shrinkage during sintering? Control Dimensional Changes for Precision Parts
- What is thermal debinding? A Guide to Mastering This Critical Manufacturing Step
- How is vacuum brazing done? Achieve High-Strength, Flux-Free Metal Joining



















