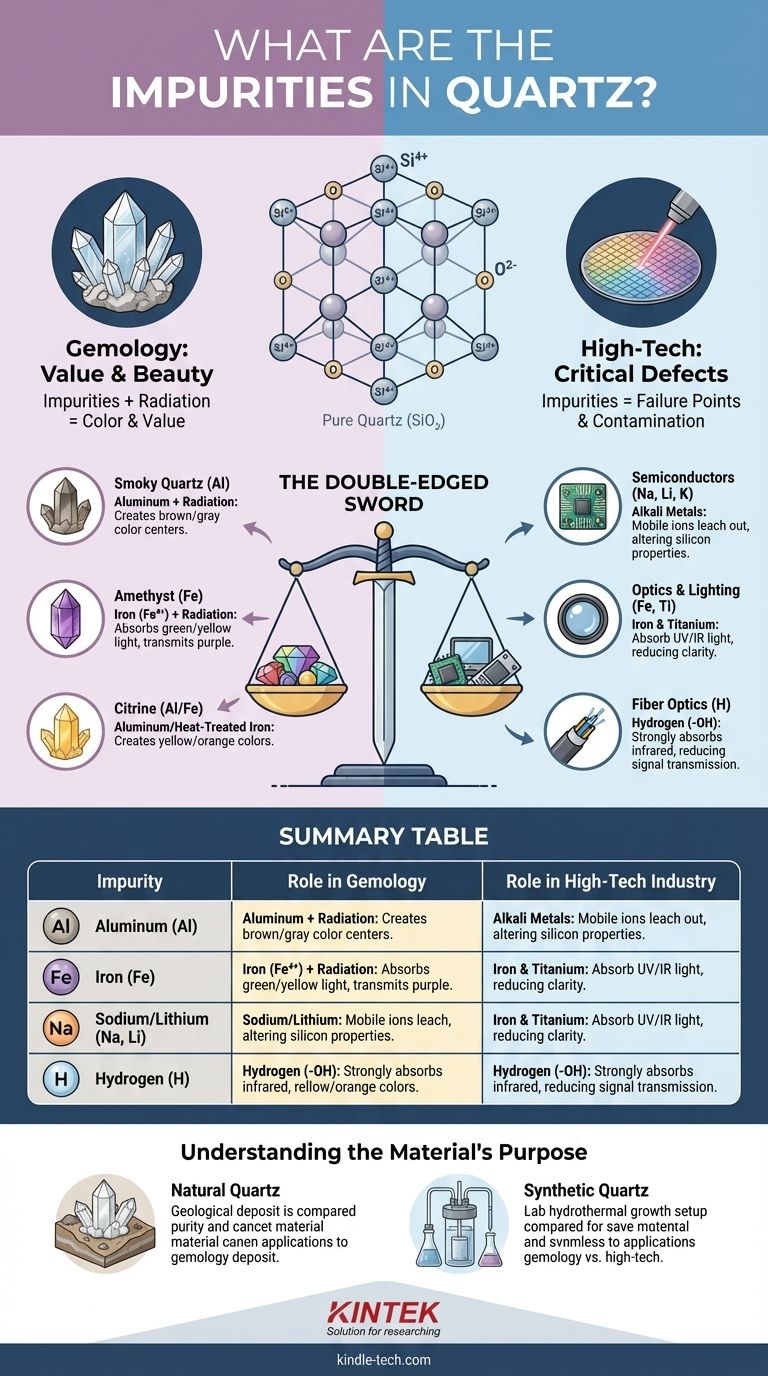
In short, quartz impurities are foreign atoms that disrupt its perfect silicon dioxide (SiO₂) crystal structure. The most common are aluminum, iron, lithium, sodium, titanium, and hydrogen, which can enter the crystal lattice during its formation. These elements are responsible for both the beautiful colors seen in gems like amethyst and the performance-limiting defects in high-tech industrial applications.
The central truth about quartz is that impurities are a double-edged sword. They are either a critical defect to be eliminated at great cost for technology or the very feature that creates value and beauty in the natural world. Understanding which impurities are present, and why, is the key to understanding the material's purpose.

The Role of Impurities: Defect vs. Desired Trait
An ideally pure quartz crystal is a perfectly repeating lattice of silicon and oxygen atoms (SiO₂). It is colorless, transparent to a wide range of light, and an excellent electrical insulator. The introduction of other elements, even in minute quantities, fundamentally changes these properties.
How Impurities Enter the Crystal Lattice
Most impurities enter the quartz structure through a process called substitution. Because an aluminum atom (Al³⁺) is similar in size to a silicon atom (Si⁴⁺), it can take silicon's place in the crystal lattice.
This substitution, however, creates a charge imbalance. The lattice is now missing the +1 charge from the absent Si⁴⁺ that was replaced by Al³⁺. To maintain electrical neutrality, other small, positively charged ions, known as charge compensators, are drawn into nearby empty spaces (interstitial sites) in the lattice. Common compensators include lithium (Li⁺), sodium (Na⁺), or a hydrogen proton (H⁺).
The Origin of Color: Impurities and Color Centers
The combination of a substitutional impurity (like aluminum or iron) and natural radiation from the surrounding rock is what creates color in most quartz varieties.
This radiation can knock an electron away from a part of the lattice near the impurity, creating a "hole." This new configuration, called a color center, absorbs specific wavelengths of visible light, and the light that is not absorbed is what we perceive as the crystal's color.
- Smoky Quartz (Brown/Gray): Caused by an aluminum impurity. Natural radiation creates a color center around the aluminum that absorbs parts of the visible spectrum, producing a smoky color.
- Amethyst (Purple): Caused by an iron (Fe³⁺) impurity substituting for silicon. When irradiated, it becomes Fe⁴⁺, creating a color center that strongly absorbs green and yellow light, allowing purple light to pass through.
- Citrine (Yellow/Orange): Most natural citrine involves aluminum-based color centers, similar to smoky quartz but formed under different temperature and radiation conditions. Many commercial citrines are simply heat-treated amethysts, which alters the iron's state.
- Rose Quartz (Pink): The cause is more complex and less certain. It is often attributed to microscopic fibrous inclusions of a mineral related to dumortierite, though some theories suggest titanium or aluminum/phosphorus impurities may also play a role.
When Purity is Paramount: High-Purity Quartz (HPQ)
While impurities create beautiful gems, they are a critical failure point in technological applications. Industries like semiconductors and optics rely on High-Purity Quartz (HPQ), where impurity levels are measured in parts per billion (ppb).
The Semiconductor Industry's Demand
The semiconductor industry is the largest consumer of HPQ. It is used to make quartz crucibles for growing large single-crystal silicon ingots, as well as quartz glass tubing, windows, and fixtures used inside chip manufacturing equipment.
Impurities like alkali metals (Na, Li, K) are especially damaging. At the high temperatures of silicon processing, these mobile ions can leach out of the quartz and contaminate the silicon wafer, altering its electrical properties and ruining the microscopic circuits. Impurities like boron (B) and phosphorus (P) are also strictly controlled as they are primary dopants used to create transistors in silicon.
Optics and Lighting Applications
For applications like high-performance lenses, fiber optic cables, and deep-UV lamps, chemical purity is directly related to optical transparency.
Metallic impurities like iron (Fe) and titanium (Ti) create absorption bands that block UV and infrared light, reducing the efficiency and performance of the optical system. Even trace amounts of hydrogen (present as hydroxyl groups, -OH) can strongly absorb infrared light, making the material unsuitable for fiber optics.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Natural vs. Synthetic
The source of the quartz dictates its purity and, therefore, its use.
Natural Quartz: A Spectrum of Purity
All natural quartz contains impurities. The specific geology of the deposit determines the type and concentration. While beautiful for gems, only a few rare geologic deposits in the world (like the Spruce Pine district in North Carolina, USA) produce quartz with low enough impurity levels to be considered feedstock for the HPQ industry.
Synthetic Quartz: Engineered for Perfection
To meet the extreme demands of modern technology, most HPQ is now created synthetically. In a process called hydrothermal synthesis, small, high-quality natural quartz crystals are dissolved in a solution and re-precipitated onto a seed crystal under high temperature and pressure.
This process gives manufacturers precise control over the growth environment, allowing them to create ultra-pure quartz with impurity levels far lower than anything found in nature. This material is more expensive but absolutely essential for cutting-edge technology.
How to Interpret Impurities for Your Goal
Your perspective on impurities depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is gemology or mineralogy: View impurities (especially iron and aluminum) as the essential ingredients that, with radiation, create the beautiful and diverse colors that give quartz varieties their value.
- If your primary focus is industrial manufacturing: View impurities (especially alkalis like sodium and lithium) as critical defects that must be rigorously eliminated to ensure the thermal stability, electrical insulation, and chemical inertness of the final product.
- If your primary focus is material science: See impurities as dopants that can be intentionally used to tune the optical, electrical, and physical properties of SiO₂ for specific, engineered outcomes.
Ultimately, understanding the role of these trace elements unlocks the true nature and potential of quartz in all its forms.
Summary Table:
| Impurity | Role in Gemology | Role in High-Tech Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum (Al) | Creates smoky quartz color centers | Can cause electrical instability in semiconductors |
| Iron (Fe) | Creates amethyst (purple) and citrine (yellow) | Absorbs light, reducing optical clarity in lenses and fiber optics |
| Sodium/Lithium (Na, Li) | Minor role in color compensation | Major contaminant; can ruin silicon wafers in semiconductor manufacturing |
| Hydrogen (H) | Present as hydroxyl groups | Strongly absorbs infrared light, making material unsuitable for fiber optics |
Need High-Purity Quartz for Your Laboratory or Manufacturing Process?
The right quartz material is critical for your application's success. Whether you require high-purity quartz crucibles for semiconductor production or specialized quartz glass for optical systems, KINTEK has the expertise and products to meet your stringent requirements. Our lab equipment and consumables are designed to deliver the performance and purity your work demands.
Let us help you select the perfect material for your specific needs. Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover the KINTEK difference.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- Does quartz have a high melting point? Discover Its Superior High-Temperature Performance
- What temperature does quartz glass melt at? Understanding Its Softening Point and Practical Limits
- What is the high temperature of quartz? Key Thresholds for Crystalline vs. Fused Silica
- What is the working temperature of quartz glass? Master Its High-Temp Limits & Applications
- How does quartz differ from glass? A Guide to Material Selection for Performance


















