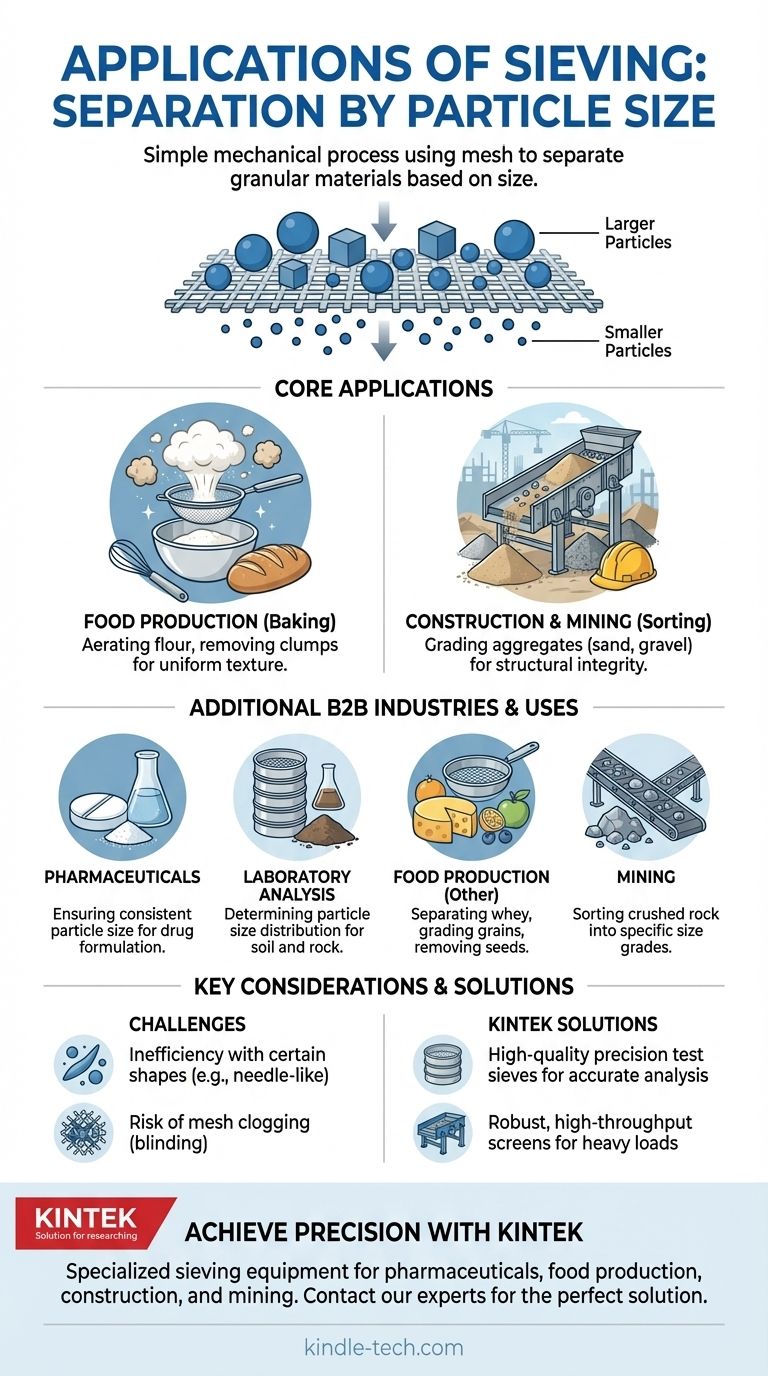
In its simplest terms, two primary applications of sieving are separating fine flour from clumps in baking and sorting sand from larger gravel at a construction site. This process is used across countless industries and everyday tasks to separate materials based on a single, fundamental property: particle size.
Sieving is a straightforward mechanical process for separating granular materials. Its core value lies in its simplicity and effectiveness at ensuring material uniformity and purity by using a mesh to sort particles by size.
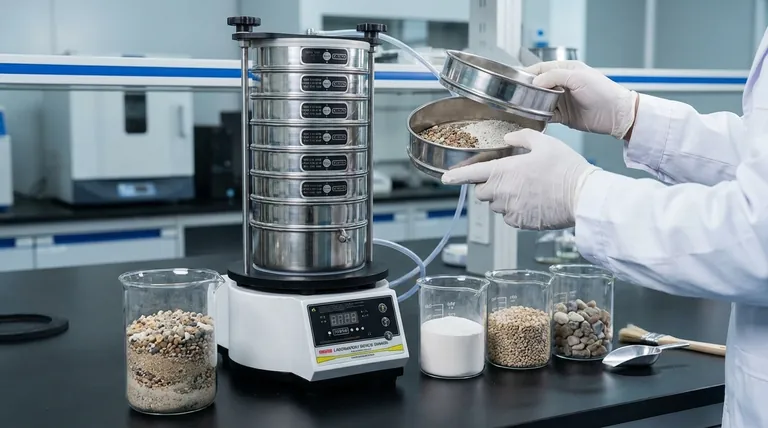

The Fundamental Principle: Separation by Particle Size
Sieving, also known as sifting, is one of the oldest and most intuitive methods of material separation. It operates on a simple mechanical principle that requires no complex chemical or thermal input.
How a Sieve Works
A sieve is a device with a meshed or perforated bottom. When a mixture of particles is placed on it and agitated, particles smaller than the mesh openings fall through, while larger particles are retained on top.
This process effectively sorts a heterogeneous mixture into two or more groups (fractions) based on their physical dimensions.
The Critical Factor: Mesh Size
The effectiveness of sieving depends almost entirely on the aperture size of the sieve's mesh. This is the dimension of the openings.
Industrial and laboratory sieves are manufactured with highly precise and standardized mesh sizes to ensure that separation is consistent and repeatable.
Common Applications in Industry and Daily Life
While the principle is simple, its applications are vast, ranging from home kitchens to large-scale industrial operations. Understanding these use cases reveals why sieving is such a foundational technique.
Food Production and Preparation
In baking, flour is sifted to break up clumps and aerate it, resulting in a lighter final product. Sieving is also used to remove seeds from fruit purées, separate whey from cheese curds, or grade grains and spices.
Construction and Mining
Sieving is essential for sorting aggregates like sand, gravel, and crushed rock into specific size grades. The structural integrity of concrete and asphalt depends on using a precise mixture of different-sized particles, which is achieved through large-scale industrial sieves called screens.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
In pharmacology, ensuring a uniform particle size is critical for drug formulation. Sieving guarantees that powders will mix evenly and that tablets will have a consistent dissolution rate in the body, which directly impacts dosage and effectiveness.
Laboratory Analysis
Geologists and soil scientists use stacks of sieves with progressively smaller mesh sizes to determine the particle size distribution of a sample. This analysis, called a sieve analysis, helps classify soil and rock types.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its utility, sieving is not a perfect solution for every separation task. Understanding its limitations is key to applying it correctly.
Inefficiency with Certain Shapes
Sieving works best with generally spherical or cubical particles. Long, needle-like particles may pass through a mesh end-on, even if their total volume is much larger than the aperture would normally allow, leading to inaccurate separation.
Risk of Mesh Clogging
The sieve mesh can become blocked, a phenomenon known as blinding. This occurs when particles that are very close to the size of the mesh openings become wedged in place, reducing the sieve's efficiency and requiring cleaning.
Limited to Solid-Solid Separation
Sieving is designed to separate dry, granular solids from one another. It is distinct from filtration, which is a process used to separate a solid from a fluid (a liquid or gas) by passing the fluid through a medium.
Applying Sieving to Your Goal
The right sieving method depends entirely on the desired outcome, whether it's precision, volume, or analytical data.
- If your primary focus is high purity in food or pharmaceuticals: Use a series of sieves with progressively finer mesh sizes to isolate a very specific particle size range.
- If your primary focus is large-scale sorting for construction or mining: Employ robust, high-throughput vibrating screens designed to handle heavy loads and large volumes continuously.
- If your primary focus is scientific analysis: Use a standardized stack of laboratory test sieves with calibrated, certified mesh sizes to ensure your results are accurate and reproducible.
Ultimately, sieving is a fundamental tool for imposing order on granular materials, ensuring quality and consistency through the simple act of size-based separation.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Goal | Common Sieve Type |
|---|---|---|
| Food Production (e.g., Baking) | Achieve uniformity, aerate flour, remove clumps | Fine mesh kitchen sieves |
| Construction & Mining | Sort aggregates (sand, gravel) for structural integrity | Heavy-duty industrial vibrating screens |
| Pharmaceutical Manufacturing | Ensure consistent particle size for drug formulation | Precision laboratory test sieves |
| Laboratory Analysis | Determine particle size distribution of soil/rock samples | Stacked, certified test sieves |
Ensure precision and efficiency in your material separation processes with KINTEK.
Whether you're in a lab requiring exact particle size analysis or in an industry needing robust, high-volume sorting, the right sieving equipment is critical. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including precision test sieves and industrial screens, designed to deliver accurate, reproducible results for your specific application—from pharmaceuticals and food production to construction and mining.
Let us help you achieve superior material uniformity and purity. Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision sieving system required to control the particle size of composite powders for thermal spraying?
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- What role does a constant temperature shaker play in evaluating boron removal? Ensure Data Accuracy in Brine Adsorption
- What is the purpose of a sieve shaker? Achieve Accurate & Repeatable Particle Size Analysis
- Why is a constant temperature shaker required during the impregnation of manganese salts onto activated carbon?
- What key role does sieving equipment play for SiC/ZTA ceramic powder? Ensure Uniform Density & Defect-Free Sintering
- What is the primary purpose of using precision sieving equipment for biomass? Ensure Efficient Hydrothermal Liquefaction
- What specific parameters do sieving systems control? Optimize Particle Size for Solid-State Electrolytes



















