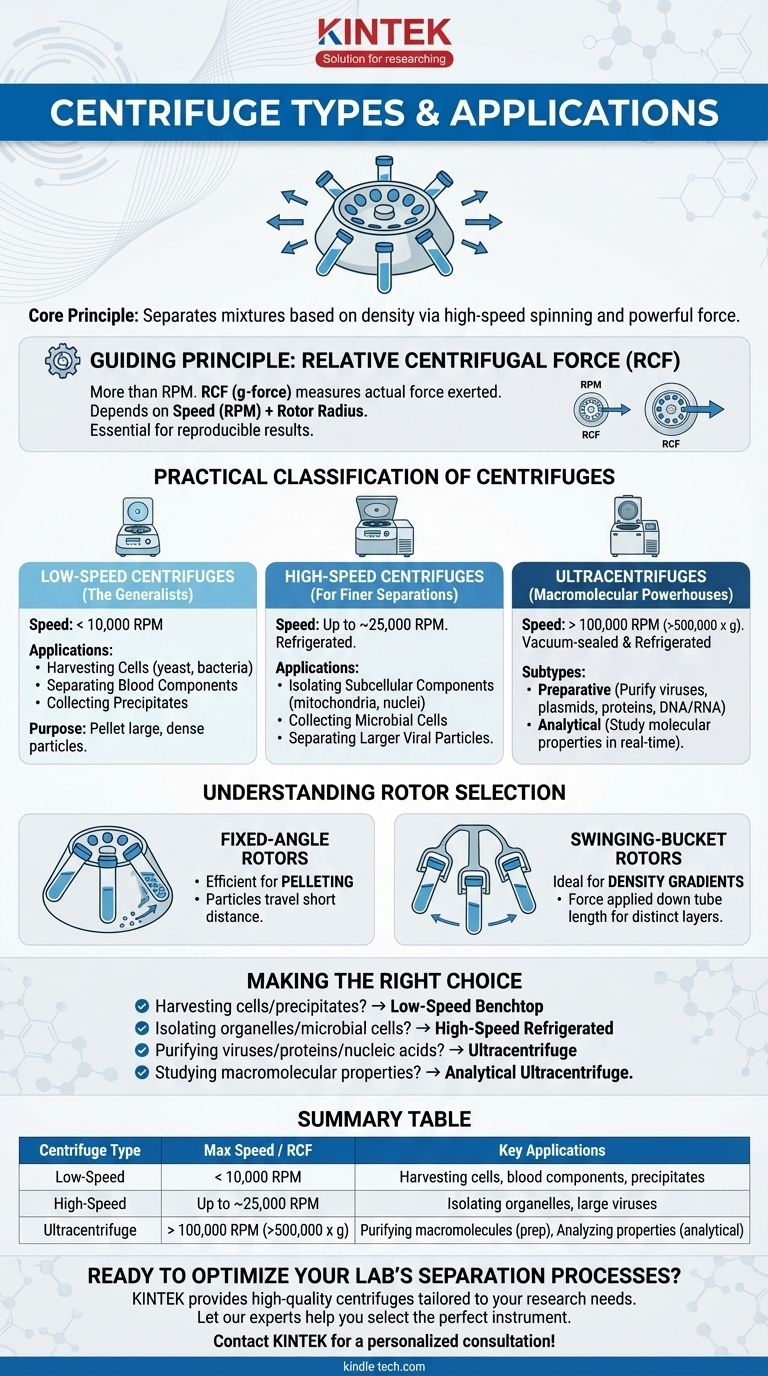
At its core, a centrifuge is a machine that separates mixtures based on density. It achieves this by spinning samples at high speed, generating a powerful force that causes denser components to move outward, away from the center of rotation, while lighter components remain closer to the center. The main types are classified by their maximum speed and volume capacity, which directly dictates their application.
The essential principle to grasp is that choosing a centrifuge is not about the machine itself, but about the size and nature of the particles you need to separate. The smaller the particle, the greater the speed and force required for effective separation.

The Guiding Principle: Relative Centrifugal Force (RCF)
More Than Just RPM
While centrifuges are often described by their revolutions per minute (RPM), the truly important metric is Relative Centrifugal Force (RCF), also known as g-force.
RPM simply measures how fast the rotor is turning. RCF, however, measures the actual force exerted on the contents of the sample.
This force depends not only on the speed (RPM) but also on the radius of the rotor. Two centrifuges spinning at the same RPM but with different-sized rotors will generate very different RCFs. For this reason, scientific protocols always specify RCF, not RPM, to ensure results are reproducible.
A Practical Classification of Centrifuges
Centrifuges are best understood by grouping them based on the RCF they can generate, which aligns directly with their primary applications.
Low-Speed Centrifuges (The Generalists)
These are often benchtop units used for routine separations. They operate at relatively low speeds, typically under 10,000 RPM.
Their purpose is to separate large, dense particles that sediment easily. Think of them as tools for harvesting or clarifying.
Common Applications:
- Pelleting whole cells from a culture, such as yeast or bacteria.
- Separating red blood cells and white blood cells from plasma.
- Collecting bulk chemical precipitates after a reaction.
High-Speed Centrifuges (For Finer Separations)
These more powerful machines can reach speeds up to around 25,000 RPM, generating significantly higher RCF. They are almost always refrigerated.
Refrigeration is critical because the friction from spinning at high speeds generates significant heat, which can damage or denature sensitive biological samples like proteins and enzymes.
Common Applications:
- Isolating subcellular components, such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, or nuclei.
- Collecting microbial cells in large volumes.
- Separating larger viral particles.
Ultracentrifuges (The Macromolecular Powerhouses)
Ultracentrifuges represent the pinnacle of centrifugation, capable of spinning at speeds over 100,000 RPM and generating immense forces (over 500,000 x g).
To achieve these speeds, the rotor chamber is sealed and placed under a high vacuum to eliminate air resistance and friction. They are also heavily refrigerated.
Two Main Subtypes:
- Preparative Ultracentrifuges: Used to isolate and purify very small particles. Their goal is to pellet molecules for further analysis. Applications include purifying viruses, plasmids, DNA, RNA, and individual proteins.
- Analytical Ultracentrifuges: These are specialized research instruments. Their purpose is not to pellet samples but to study them in real-time. They are equipped with optical detection systems that monitor how molecules sediment during the spin, allowing scientists to determine properties like molecular weight, shape, and purity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Rotor Selection
The centrifuge is just the motor; the rotor holds the sample and is the component that truly defines the application. The two most common types have distinct purposes.
Fixed-Angle Rotors
In a fixed-angle rotor, the sample tubes are held at a constant, steep angle (e.g., 25-45 degrees).
This design is highly efficient for pelleting. Particles have a short distance to travel before hitting the side of the tube and sliding down to form a compact pellet. However, this can induce high stress on the sample.
Swinging-Bucket Rotors
In a swinging-bucket (or swinging-head) rotor, the tubes are placed in buckets that are vertical at rest but swing out to a horizontal position as the rotor spins.
This is ideal for separating samples across a density gradient. The force is applied directly down the length of the tube, allowing distinct layers (like blood components) to form without being disturbed, creating a clean separation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct instrument, you must match the required centrifugal force to the size of the component you wish to separate.
- If your primary focus is harvesting whole cells or large precipitates: A simple, low-speed benchtop centrifuge is the appropriate and cost-effective tool.
- If your primary focus is isolating subcellular organelles or microbial cells: You will need a high-speed refrigerated centrifuge to generate sufficient force while protecting your sample from heat.
- If your primary focus is purifying viruses, proteins, or nucleic acids: An ultracentrifuge is the only tool that can generate the extreme force needed to pellet these macromolecules.
- If your primary focus is studying the physical properties of a macromolecule: You need a specialized analytical ultracentrifuge with its integrated optical detection system.
Ultimately, the right centrifuge is the one that provides the necessary force to effectively separate your target component from the rest of the mixture.
Summary Table:
| Centrifuge Type | Max Speed / RCF | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Speed | < 10,000 RPM | Harvesting cells (yeast, bacteria), separating blood components, collecting precipitates |
| High-Speed | Up to ~25,000 RPM | Isolating organelles (mitochondria, nuclei), separating large viruses |
| Ultracentrifuge | > 100,000 RPM (>500,000 x g) | Purifying viruses, plasmids, proteins, and nucleic acids (preparative); analyzing molecular properties (analytical) |
Ready to Optimize Your Lab's Separation Processes?
Choosing the right centrifuge is critical for achieving accurate and reproducible results. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory centrifuges and consumables tailored to your specific research needs—from routine cell harvesting to advanced macromolecular purification.
Let our experts help you select the perfect instrument and rotor configuration to enhance your lab's efficiency and productivity.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tubes
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Variable Speed Peristaltic Pump
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between climbing and falling film evaporator? Choose the Right System for Your Process
- What is the purpose of using permeable steel mesh containers for the synthesis of non-extruded ferroalloy samples?
- What safety features are commonly included in ULT freezers? Protect Your Critical Samples from Catastrophic Loss
- Is biofuel a renewable energy source? Powering a Sustainable Future with Biomass
- Can you harden non-ferrous metals? Yes, with the right methods for aluminum, copper, and titanium
- What are the cons of pyrolysis? The High Costs and Hidden Challenges of Waste-to-Energy
- Is pyrolysis oil same as diesel? Uncover the Critical Differences in Fuel Properties
- What is used as a source of heat in the laboratory? Choose the Right Tool for Safe & Precise Heating



















