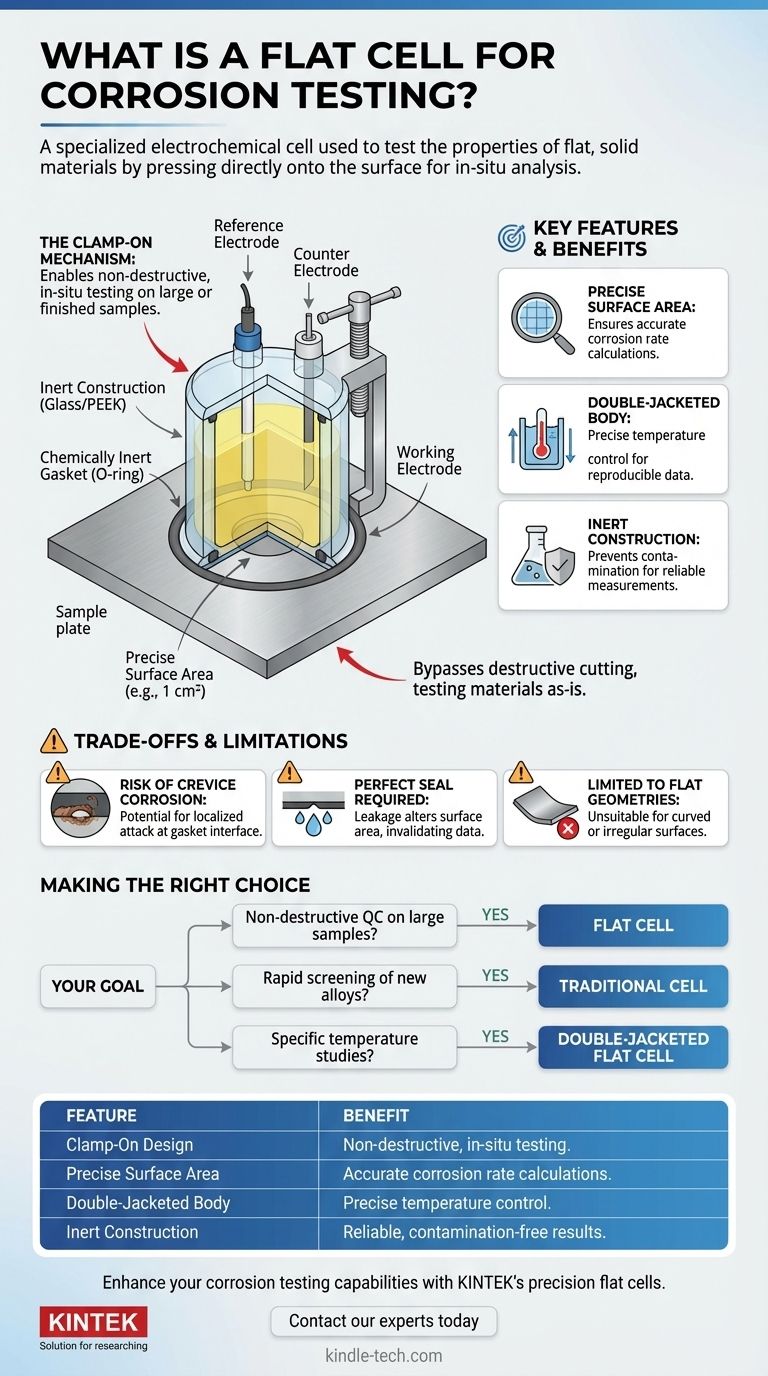
A flat cell is a specialized electrochemical cell used in corrosion science to test the properties of flat, solid materials. Unlike traditional cells that require small, custom-shaped electrodes, a flat cell is designed to press directly onto the surface of a larger sample, such as a metal plate, coated panel, or semiconductor wafer, allowing for in-situ analysis.
The primary advantage of a flat cell is its ability to perform standardized corrosion experiments on large or valuable samples without destroying them. It effectively brings the test to the sample, rather than forcing the sample to conform to the test setup.

How a Flat Cell Solves a Critical Testing Problem
Standard electrochemical testing often involves cutting a small coupon from a larger piece of material to serve as the working electrode. This can be impractical or undesirable.
Overcoming Sample Preparation Hurdles
Traditional methods are destructive. If you need to evaluate a finished, coated panel or a large sheet of a new alloy, cutting a piece out of it may ruin the sample or introduce misleading artifacts like edge effects.
The flat cell bypasses this entirely. It allows you to test the material in its as-is or as-manufactured state, providing a more realistic assessment of its corrosion performance.
The "Clamp-On" Mechanism
A flat cell operates by being pressed firmly against the surface of the material under investigation.
A chemically inert gasket, typically an O-ring, creates a tight seal between the cell body and the sample. This seal isolates a precise, circular area of the material, which is then exposed to the electrolyte inside the cell.
Defining the Working Electrode
The sealed-off area of the sample becomes the working electrode in a standard three-electrode electrochemical setup. The cell body contains ports for inserting the required reference electrode and counter electrode.
This design ensures that all electrochemical measurements, such as corrosion potential or polarization resistance, pertain only to that well-defined surface area of the sample.
Key Features and Their Importance
A well-designed flat cell includes specific features that ensure accurate and repeatable data.
Precise Surface Area
Flat cells are manufactured to expose a known and constant surface area, commonly 1 cm² or 10 cm². This is critical because key corrosion metrics, like corrosion rate (calculated from current density), depend on knowing the exact electrode area.
Double-Jacketed Body for Temperature Control
Many flat cells feature a "double-jacketed" design. An outer chamber surrounds the main electrolyte chamber, allowing a temperature-controlled fluid (like water from a circulating bath) to flow around it.
Since corrosion is a chemical process that is highly sensitive to temperature, this feature is essential for obtaining reliable and reproducible results under specific environmental conditions.
Inert Construction Materials
The cell body is made from materials that will not react with the electrolyte or corrode, such as glass or chemically resistant polymers like PEEK. This prevents contamination that could interfere with the measurement.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the flat cell is not without its challenges. An expert user must be aware of its potential pitfalls.
Risk of Crevice Corrosion
The interface where the O-ring gasket presses against the sample surface creates an artificial crevice. This small, occluded space can sometimes foster crevice corrosion, a localized form of attack that may not be representative of the material's bulk performance.
Requirement for a Perfect Seal
The entire method relies on achieving a leak-proof seal. If the sample surface is too rough, warped, or dirty, the electrolyte can leak out or seep underneath the gasket.
This leakage alters the exposed surface area, invalidating the current density calculations and compromising the entire experiment.
Limited to Flat Geometries
The most obvious limitation is in the name. A flat cell can only be used on planar surfaces. It is unsuitable for testing materials with curved, irregular, or complex geometries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct test setup depends entirely on your experimental objective.
- If your primary focus is non-destructive QC on large panels or coatings: The flat cell is the ideal choice, as it directly tests the finished product without damage.
- If your primary focus is rapid screening of new alloy compositions: A traditional cell using small, easily machined electrode samples may be more efficient for high-throughput testing.
- If your primary focus is studying corrosion under specific temperature profiles: A double-jacketed flat cell is necessary to ensure your data is reliable and directly comparable across experiments.
Ultimately, the flat cell is a crucial tool that bridges the gap between fundamental laboratory science and real-world engineering applications.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Clamp-On Design | Enables non-destructive, in-situ testing on large or finished samples. |
| Precise Surface Area (e.g., 1 cm²) | Ensures accurate corrosion rate calculations from current density. |
| Double-Jacketed Body | Allows for precise temperature control, critical for reproducible data. |
| Inert Construction (Glass, PEEK) | Prevents contamination of the electrolyte and sample for reliable measurements. |
Enhance your corrosion testing capabilities with KINTEK's precision flat cells.
Are you performing quality control on coated panels, evaluating new alloys, or need reliable data under specific temperature conditions? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including flat cells designed for accurate, non-destructive electrochemical analysis. Our cells help you obtain precise, reproducible results without damaging valuable samples.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect flat cell solution for your laboratory's specific corrosion testing needs and discover how we can support your research and quality assurance goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Flat Corrosion Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Sample Support Body for Electrochemical Tests
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- PTFE Electrolytic Cell Electrochemical Cell Corrosion-Resistant Sealed and Non-Sealed
People Also Ask
- What are the complete post-experiment procedures for a flat plate corrosion electrolytic cell? A Step-by-Step Guide to Reliable Results
- What are the primary features of a flat plate corrosion electrolytic cell? Achieve Precise, Repeatable Corrosion Data
- What are the design advantages of using a flat electrochemical cell? Enhance Corrosion Testing Precision
- What is the operating principle of a flat plate corrosion electrolytic cell? A Guide to Controlled Materials Testing
- What are the complete preparation steps to be taken before using a flat plate corrosion electrolytic cell? Ensure Accurate & Repeatable Results



















