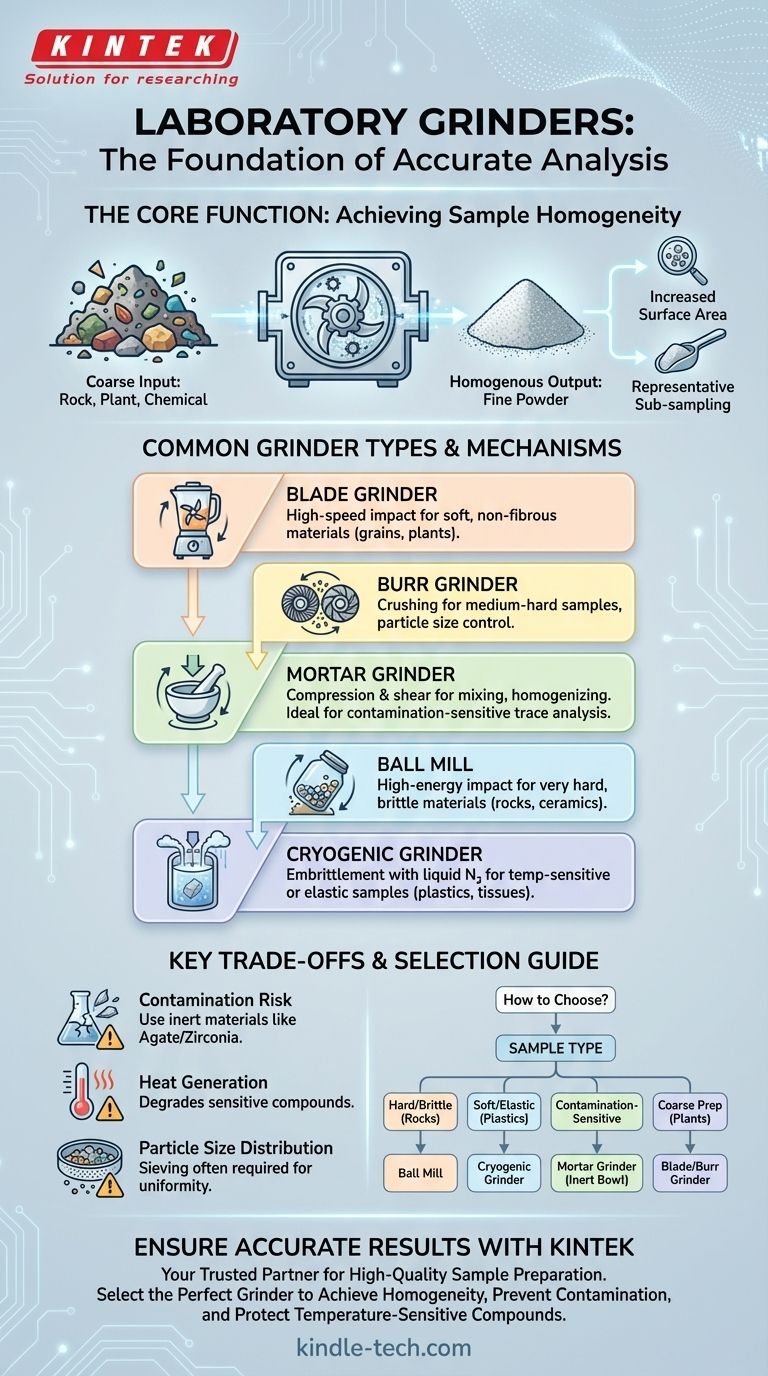
In essence, a laboratory grinder is a specialized device engineered to reduce the particle size of solid samples. Its fundamental purpose is to take a coarse, heterogeneous material—like rock, plant tissue, or a chemical compound—and pulverize it into a fine, uniform powder. This process, known as comminution, is a critical preparatory step for a vast range of scientific analyses.
The core function of a lab grinder is not merely to break things down. It is to create a homogenous sample with a massively increased surface area, ensuring that any small portion taken for analysis is truly representative of the whole. This principle underpins the accuracy and reproducibility of countless scientific experiments.

The Purpose: Why Grinding is a Non-Negotiable Step
Before any meaningful analysis can occur, the sample must be properly prepared. Grinding is often the first and most crucial step in that preparation workflow.
Achieving Sample Homogeneity
A raw sample, whether it's a piece of soil or a plant leaf, is rarely uniform. Grinding and mixing pulverize these different components into a consistent powder, eliminating variations and ensuring that every subsample is identical.
Increasing Reactive Surface Area
Chemical reactions, dissolution, and extraction processes all happen at the surface of a particle. By breaking a large solid into millions of tiny particles, you dramatically increase the total surface area, allowing for faster, more efficient, and more complete chemical processing.
Ensuring Representative Sub-sampling
Imagine needing to analyze a one-kilogram rock for its gold content. Analyzing the whole rock is impractical. Grinding it into a fine powder and then taking a one-gram sample gives you a much higher statistical probability that your small sample accurately reflects the composition of the original kilogram.
Preparing for Instrumental Analysis
Many advanced analytical techniques require samples in powder form. Techniques like X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), and various forms of spectroscopy depend on a homogenous, fine powder to produce reliable and accurate data.
Common Types of Laboratory Grinders
The right grinder depends entirely on the sample's properties—its hardness, toughness, and thermal sensitivity. Each type uses a different physical mechanism to achieve size reduction.
Blade Grinders
These function like a kitchen blender, using high-speed rotating blades to chop and shatter material through impact. They are best suited for soft, non-fibrous materials like grains or some plant tissues.
Burr Grinders
A burr grinder uses two revolving abrasive surfaces (burrs) to crush and grind material caught between them. This method offers more control over the final particle size than a blade grinder and is often used for medium-hard samples.
Mortar Grinders
This is the automated version of the classic mortar and pestle. It uses a combination of compression and shear forces as the pestle rotates within the mortar bowl. They are excellent for mixing and homogenizing powders and can be made from various materials (agate, zirconia, tungsten carbide) to prevent contamination.
Ball Mills
A ball mill uses a rotating jar partially filled with grinding media (balls). As the jar rotates, the balls cascade from the top, crushing and grinding the sample through high-energy impact and friction. This method is highly effective for pulverizing very hard, brittle materials into extremely fine powders.
Cryogenic Grinders
Some samples, like plastics, rubber, or biological tissue, are too soft or elastic to grind at room temperature. A cryogenic grinder immerses the sample in liquid nitrogen, making it brittle enough to be shattered by impact, while also preserving temperature-sensitive compounds.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Selecting a grinder involves balancing efficiency with the integrity of your sample. Ignoring these factors can invalidate your results before you even begin your analysis.
The Risk of Sample Contamination
The material of the grinding components (blades, bowls, balls) can wear down and introduce trace elements into your sample. If you are performing trace metal analysis, using a steel grinder could ruin your experiment. This is why grinding sets made of inert materials like agate or zirconia are essential for sensitive applications.
The Problem of Heat Generation
All grinding methods generate heat through friction. This can cause thermal degradation of sensitive organic compounds, proteins, or pharmaceuticals. For heat-sensitive samples, you must either use a cryogenic grinder or grind in short bursts with cooling periods.
Particle Size Distribution
No grinder produces particles of a single, perfect size. You will always get a distribution of sizes. The type of grinder and the duration of grinding will influence this distribution. Often, grinding must be followed by sieving to isolate the desired particle size range.
Wet vs. Dry Grinding
Grinding can be performed dry or with a liquid (wet grinding). Wet grinding can help keep the sample cool, prevent fine powders from becoming airborne, and sometimes lead to a finer final product. However, the liquid must be chemically compatible with your sample and easily removed afterward.
How to Select the Right Grinder for Your Application
The choice is dictated by your sample type and your analytical goal.
- If your primary focus is hard, brittle materials (rocks, ceramics, glass): A ball mill is the superior choice for reducing these samples to the fine powder required for X-ray analysis.
- If your primary focus is temperature-sensitive biological tissue or elastic polymers: A cryogenic grinder is the only reliable option to ensure the sample becomes brittle enough for pulverization without degrading.
- If your primary focus is contamination-sensitive chemical analysis: An automated mortar grinder with a bowl and pestle made of agate or zirconia is critical to prevent introducing metallic impurities.
- If your primary focus is coarse preparation of soft plant or food materials: A simple and cost-effective blade or burr grinder is often sufficient for the task.
Ultimately, choosing the correct grinding method is the foundational step toward ensuring the integrity and reliability of your final analytical results.
Summary Table:
| Grinder Type | Best For | Key Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Blade Grinder | Soft, non-fibrous materials (grains, some plants) | High-speed impact and chopping |
| Burr Grinder | Medium-hard materials | Crushing between two abrasive surfaces |
| Mortar Grinder | Mixing, homogenizing, contamination-sensitive samples | Compression and shear forces |
| Ball Mill | Very hard, brittle materials (rocks, ceramics) | High-energy impact from grinding media |
| Cryogenic Grinder | Temperature-sensitive samples (plastics, tissues) | Embrittlement with liquid nitrogen before impact |
Ensure Accurate Results with the Right Grinding Equipment
Choosing the correct laboratory grinder is the first critical step to achieving reliable, reproducible analytical data. The wrong choice can lead to sample contamination, thermal degradation, or an unrepresentative sample, compromising your entire experiment.
KINTEK is your trusted partner in sample preparation. We specialize in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, offering a comprehensive range of grinders—from ball mills for hard materials to cryogenic mills for sensitive samples—to meet your specific application needs.
Let our experts help you select the perfect grinder to:
- Achieve perfect sample homogeneity.
- Prevent contamination with inert grinding sets (agate, zirconia).
- Protect temperature-sensitive compounds.
Don't let sample preparation be the weak link in your analysis. Contact our technical team today for a personalized consultation and ensure your lab's success from the very first step.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Jar Mill with Agate Grinding Jar and Balls
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of laboratory mills? Choose the Right Grinder for Your Sample Material
- Why is an alumina mortar used for grinding dried Yttrium Oxide precursor materials? Ensure Maximum Purity and Quality
- What is the function of a mortar and pestle in ZnS nanoparticle prep? Optimize Your Sample Refinement
- What is a mortar and pestle used for in a lab? A Guide to Precision Grinding and Mixing
- What is the laboratory apparatus used for grinding? Find the Perfect Mill for Your Sample



















